A novel CRISPR-based screening method offers high throughput potential for studying extracellular vesicles.

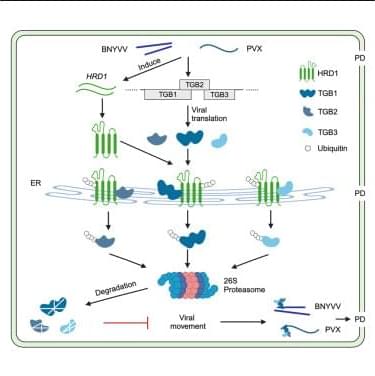
(K) A proposed model illustrating how the E3 ligase NbHRD1 negatively regulates viral infection in plants. Plant viruses with a TGB, BNYVV and PVX, as models, infect N. benthamiana plants, inducing the expression of NbHRD1 interacts with TGB movement proteins of BNYVV and PVX in the ER membrane. NbHRD1 triggers the ubiquitination and 26S proteasome-mediated degradation of TGB proteins, thereby suppressing viral movement to inhibit virus infection.
In (D), (G), and (J), EF1α served as an internal reference. The GFP gene was used as the indicator of viral RNA accumulation. Values are means ± SDs of three independent repeats. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant (Student’s t test).

All episodes of Common Side Effects available on Max.
Watch Adult Swim on Max: http://bit.ly/3Gy0aXA
SUBSCRIBE: https://youtube.com/adultswim1?sub_confirmation=1
About Adult Swim:
Watch Adult Swim on Max, www.adultswim.com or by downloading the Adult Swim app. Binge marathons or watch selected episodes of many of your favorite shows including Rick and Morty, SMILING FRIENDS, The Boondocks, Aqua Teen Hunger Force, and many more.
Connect with Adult Swim Online:
Download the APPS: http://www.adultswim.com/apps/
Visit Adult Swim WEBSITE: http://www.adultswim.com.
Like Adult Swim on FACEBOOK: https://facebook.com/adultswim.
Follow Adult Swim on TWITTER: https://twitter.com/adultswim.
Follow Adult Swim on INSTAGRAM: http://instagram.com/adultswim.
Watch Adult Swim in your country:
United Kingdom: https://bit.ly/AS_GB
Republic of Ireland: https://bit.ly/AS_GB
USA: https://bit.ly/AS_US
France: https://bit.ly/AS_FRA
Germany: https://bit.ly/AS_GER
Italy: https://bit.ly/AS_IT
Central and Eastern Europe: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Denmark: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Finland: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Hungary: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Netherlands: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Norway: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Poland: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX


In our day-to-day lives, we’re constantly making a slew of decisions, from immediate matters to prospects on the far horizon. But the evolutionary nuts-and-bolts of how our brains weigh these numerous daily decisions and what role is played by the neurotransmitter serotonin has been shrouded in mystery.
Now, a new study led by an interdisciplinary University of Faculty of Medicine team delivers fascinating findings that potentially unravel a hidden aspect of what our nervous system’s extraordinarily complex serotonin system is really doing inside our skulls.
Published in the journal Nature, this study from a highly impactful international collaboration offers “broad implications across neuroscience, psychology, and psychiatry, enhancing our understanding of serotonin’s role in mood regulation, learning, and motivated behavior.”

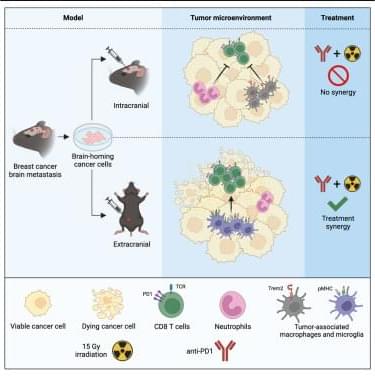
Wischnewski et al. demonstrate suppressed CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity in breast cancer brain metastases, contrasting with genetically identical extracranial tumors. Neutrophils and Trem2+ macrophages drive this suppression, limiting the efficacy of combined irradiation and anti-PD1 therapy, highlighting potential therapeutic targets for brain metastases.