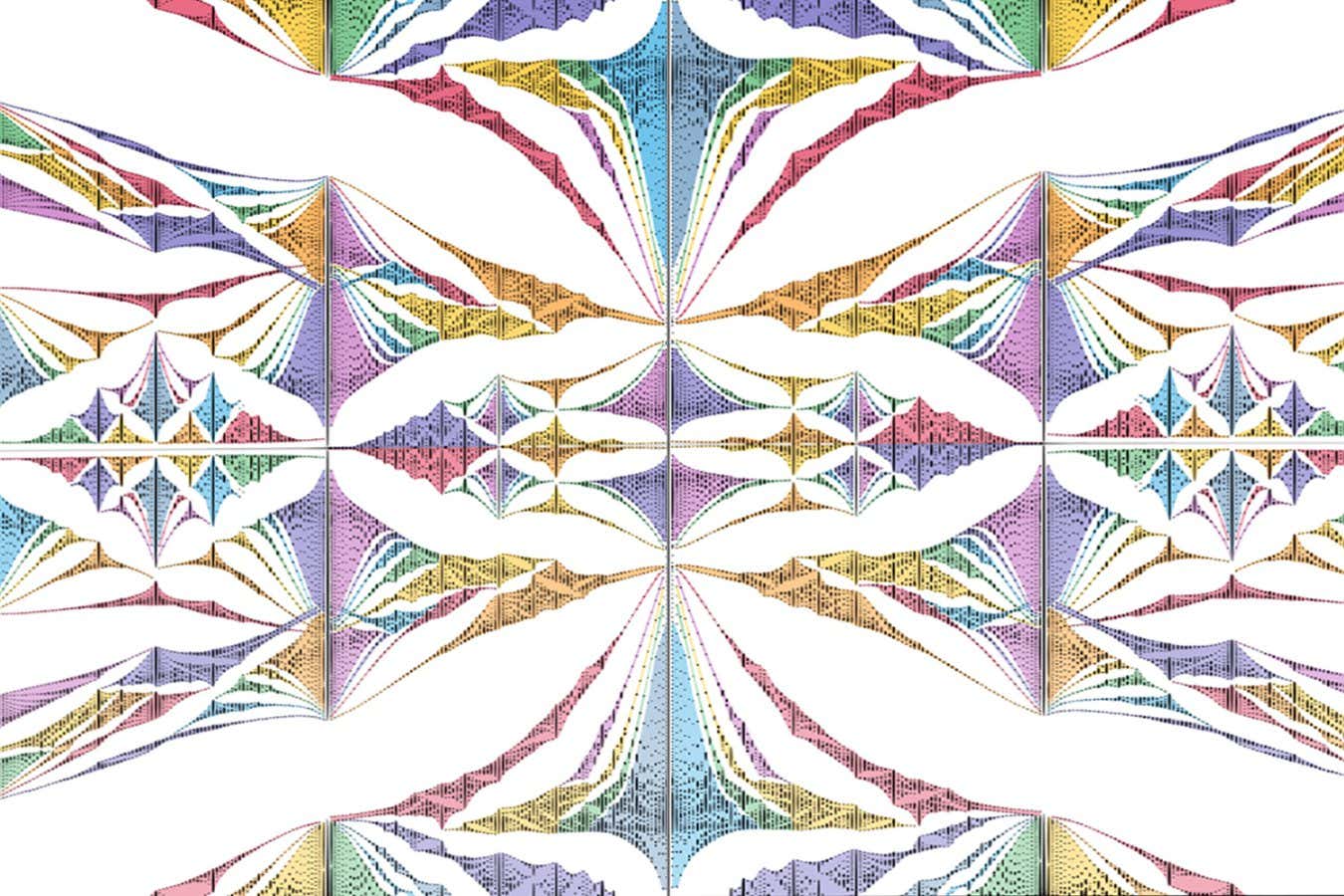
A fractal butterfly pattern produced by an unusual configuration of magnetic fields, first predicted almost 50 years ago, has been seen in detail for the first time in a twisted piece of graphene.
While a physics student in 1976, the computer scientist Douglas Hofstadter predicted that when certain two-dimensional crystals were placed in magnetic fields, their electrons’ energy levels should produce a strange pattern that looks the same no matter how far you zoom in, known as a fractal. At the time, however, Hofstadter calculated that the atoms of the crystal would have to be impossibly close together to produce such a pattern.
Image: Yazdani Lab, Princeton University
The electrons in a twisted piece of graphene show a strange repeating pattern first predicted in 1976, but never directly measured until now.
By Alex Wilkins