A new drug targets Alzheimer’s at its earliest, most silent stage — before memory loss ever begins.



Large doses of vitamin C may provide our lungs with a degree of protection from the harmful effects of fine particles in the air. Referred to as PM2.5, in reference to their micrometer-wide particle size, these pollutants have been linked to issues such as asthma and lung cancer.
Researchers led by a team from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) conducted a series of experiments on male mice and lab-grown human tissues to test the effects of vitamin C on tissues exposed to fine particulate matter, finding that the vitamin protected against some of the core damage to cells that air pollution typically does to the lungs.
In particular, vitamin C reduced the loss of the cells’ mitochondrial ‘power stations’, reduced harmful inflammation, and prevented cells from being damaged by the effects of oxidative stress – attacks caused by unstable, reactive molecules that then lead to numerous malfunctions.
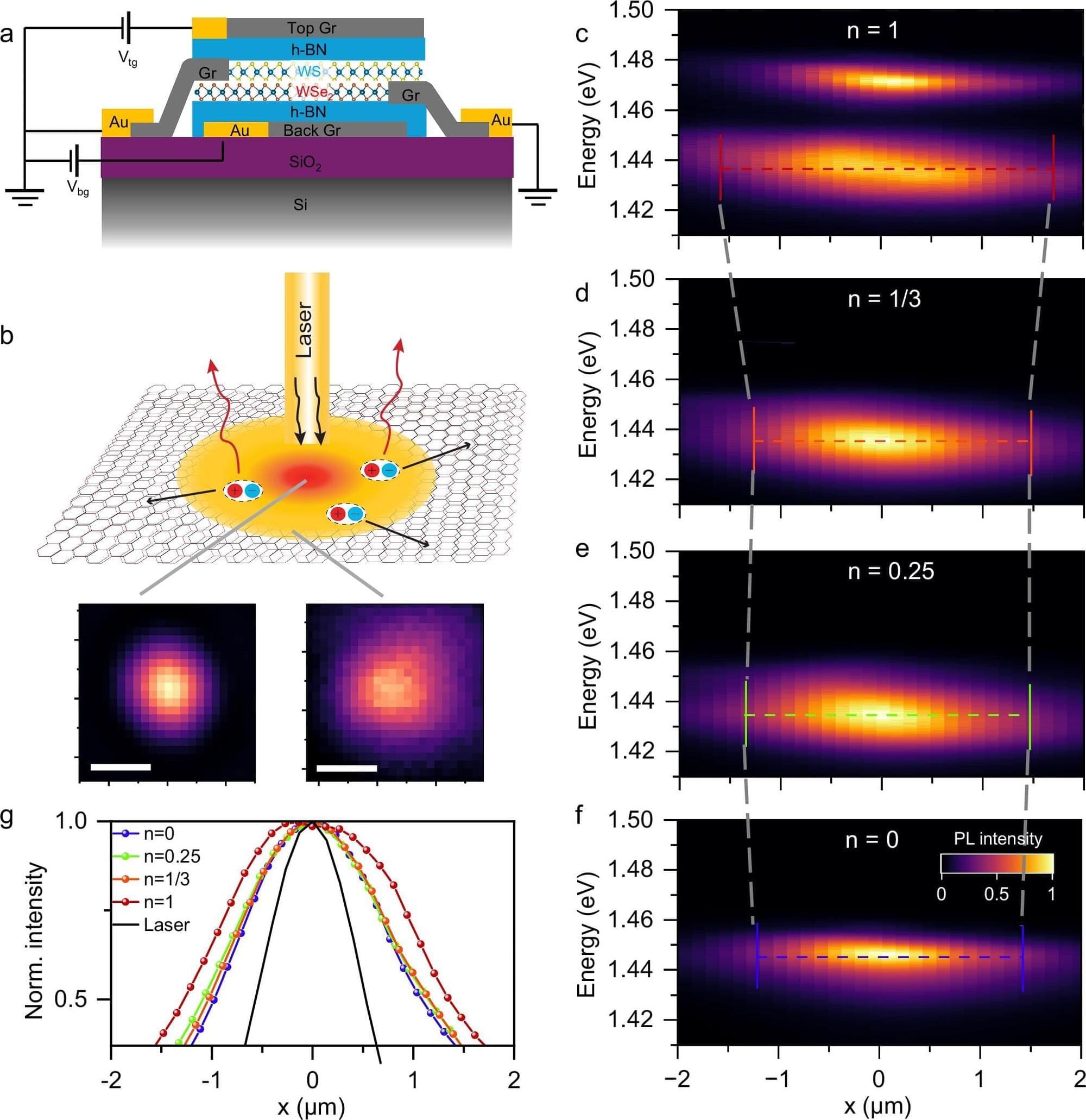
Excitons are pairs of bound negatively charged electrons and positively charged holes that form in semiconductors, enabling the transport of energy in electronic devices. These pairs of charge carriers also emerge in transition metal dichalcogenides, thin semiconducting materials comprised of a transition metal and two chalcogen atoms.
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, UC Riverside, and other institutes have introduced a new strategy to control the flow of energy in structures comprised of two transition metal dichalcogenide layers stacked with a small rotational mismatch, also known as moiré superlattices.
Their proposed approach, introduced in a paper published in Nature Communications, entails the active tuning of electronic states in moiré superlattices in ways that alter the transport of excitons.
At the same time, estimates from the US indicate that power consumption from IT applications has doubled over the past eight years, with the rise of AI. Researchers from California’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory suggest that more than half of the electricity used by data centers will be used solely for AI by 2028.
This puts the rapid advance of the digital revolution at risk as energy demand can no longer be met. Traditional silicon chips, which draw power even when idle, are becoming a critical limitation. As a result, researchers worldwide are exploring alternative microelectronic technologies that are far more energy-efficient.
To address the challenge, the team will begin developing superconducting circuits on January 1. These circuits, which were first envisioned by Hungarian-American mathematician and physicist John von Neumann in the 1950s, exploit quantum effects to transmit data using extremely short voltage pulses.
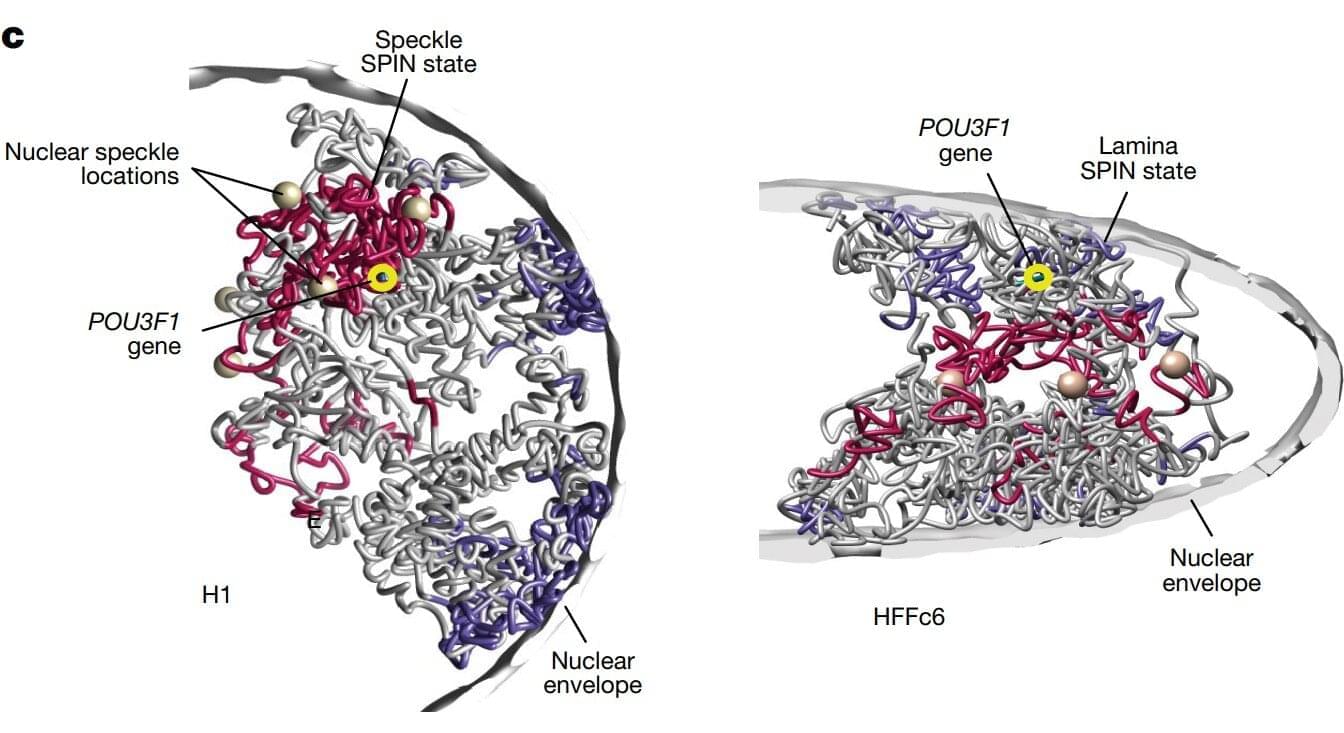
One of the most detailed 3D maps of how the human chromosomes are organized and folded within a cell’s nucleus is published in Nature.
Chromosomes are thread-like structures that carry a cell’s genetic information inside the nucleus. Rather than existing as loose strands or only as the familiar X-shapes seen in textbooks, chromosomes fold into specific three-dimensional forms. How they fold, the structures they form, and their placement play crucial roles in maintaining proper cellular functions, gene expression, and DNA replication.
The team involved in the 4D Nucleome Project, whose goal was to understand the 3D organization of human chromosomes in the nucleus and how it changes over time, identified over 140,000 DNA looping interactions in human embryonic stem cells and fibroblasts. They also presented computational methods that can predict genome folding solely from its DNA sequence, making it easier to determine how genetic variations—including those linked to disease—affect genome structure and function.

The emergence of resistant subpopulations often underlies the development of resistance to cancer therapy. Here, using a DNA barcoding approach, the authors demonstrate EGFR TKI treatment in non-small cell lung cancer enriches for resistant subpopulation which can be prevented by treatment with the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib via inhibition of MKNK, STAT3 and MCL1.
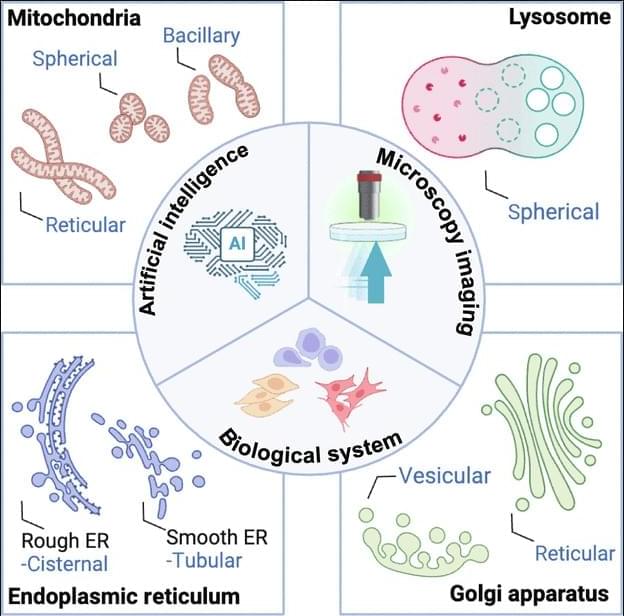
JUST PUBLISHED: artificial intelligence for organelle segmentation in live-cell imaging
Click here to read the latest free, Open Access article from Research, a Science Partner Journal.
Investigations into organelles illuminate the intricate interplay of cellular systems, uncovering how specialized structures orchestrate homeostasis, regulate metabolic pathways, and modulate signal transduction. The structural and functional integrity of organelles, including mitochondria, ER, GA, and lysosomes, is critical for cellular health. Deviations in organelle shape and behavior are frequently associated with disease development [51]. Consequently, precise characterization of organelles is crucial for advancing our understanding of cell biology and mechanisms.
Organelle image segmentation is important for extracting precise spatial and structural information, forming the foundation for subsequent quantitative analyses. Unlike whole-cell or nuclear, organelle segmentation is inherently more challenging due to the smaller size, irregular shapes, and intricate distributions of these structures. Additionally, many organelles exhibit dynamic behaviors such as fusion, fission, and trafficking, requiring accurate segmentation across both temporal and spatial dimensions. Advances in segmentation technologies have notably improved the ability to identify and characterize organelles with high-precision accuracy, opening new avenues for understanding cellular functions in health and disease.
Ever wondered how the different cells in our body communicate with each other to fulfill their different roles-be it cells repairing a tissue injury or immune cells moving towards an invading pathogen (microorganisms that causes disease) to engulf it? To move forward or migrate, cells must exert forces or interact with their surrounding environment. Interestingly, however, a fault in these interactions can also be the reason for spread of deadly cancer cells, such as in glioblastoma or brain tumor. While the importance of these interactions is well-understood, the machinery involved in these interactions at the molecular level remains a mystery.
Now, a team of researchers led by Professor Naoyuki Inagaki from Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Japan, along with Dr. Yonehiro Kanemura from NHO Osaka National Hospital, Japan; Dr. Tatsuo Kinashi from Kansai Medical University, Japan; and Dr. Daisuke Kawauchi from Nagoya City University, Japan, has identified the underlying mechanism involving a protein called shootin1b that promotes cell migration or movement in glioblastoma. The study was published online in Advanced Science on August 13, 2025.
“We discovered that an abnormal activity of shootin1b promotes the movement of cancer cells and spread of glioblastoma, the most common and difficult to treat brain tumor in adults,” explains Professor Inagaki.

Yang et al. demonstrate that the goblet cell-expressed microprotein FXYD3 interacts with SERCA2 to regulate ER calcium homeostasis, promoting mucus granule secretion and sialylation. FXYD3 deficiency impairs mucin sialylation and mucus barrier function, increasing susceptibility to intestinal inflammation.
A team, including researchers in MIT ChemE, designed new nanoparticles that can deliver an immune-stimulating molecule called IL-12 directly to ovarian tumors. When given along with immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors, IL-12 helps the immune system launch an attack on cancer cells.
“What’s really exciting is that we’re able to deliver IL-12 directly in the tumor space. And because of the way that this nanomaterial is designed to allow IL-12 to be borne on the surfaces of the cancer cells, we have essentially tricked the cancer into stimulating immune cells to arm themselves against that cancer,” says MIT ChemE Professor Paula Hammond, a senior author of the study.
📸: Courtesy of the researchers.
MIT researchers designed nanoparticles that can deliver an immune-stimulating molecule called IL-12 directly to ovarian tumors. When given to mice along with checkpoint inhibitors, the treatment eliminated metastatic tumors more than 80 percent of the time.