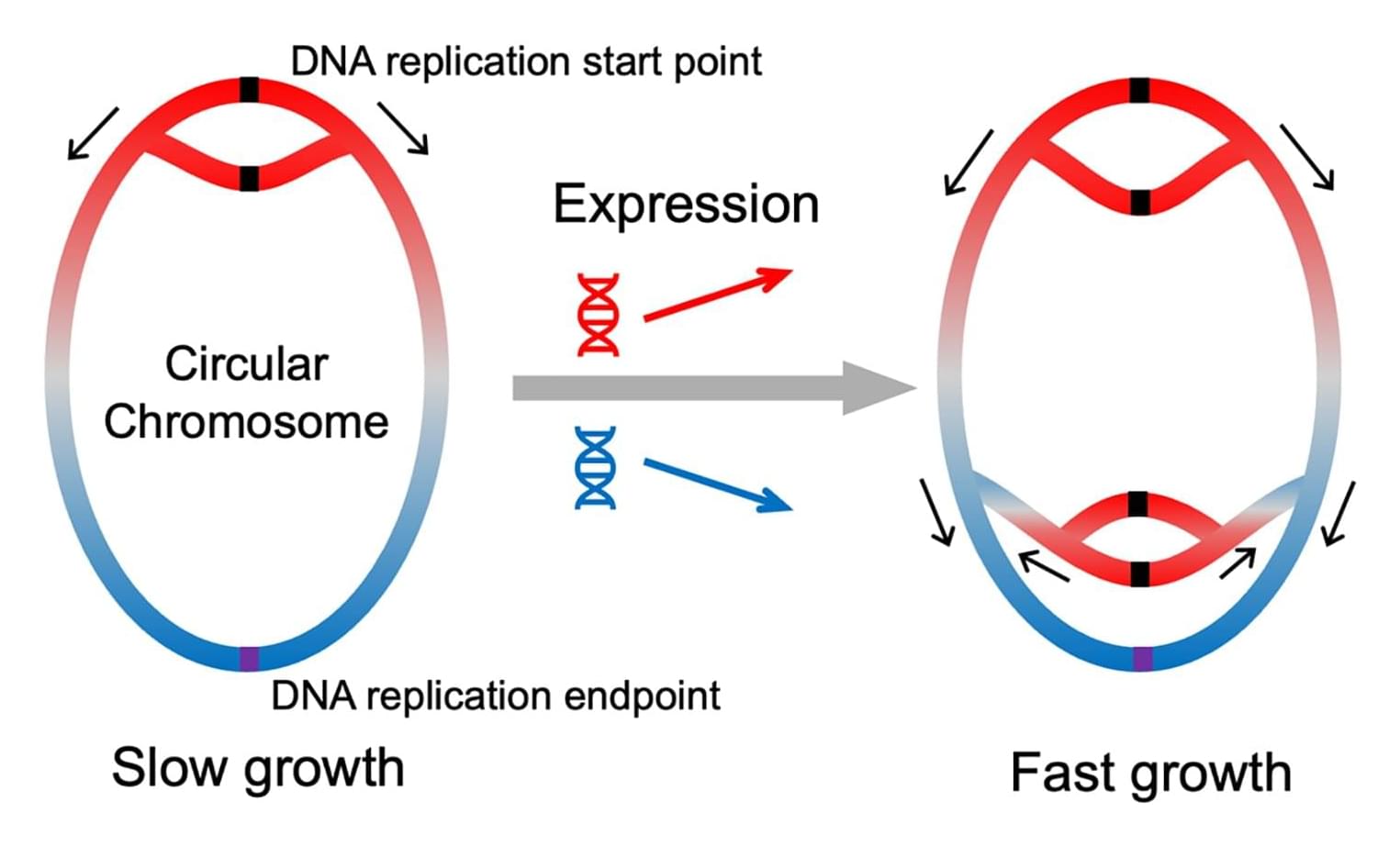
Bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the university in Linköping (Sweden) have established that the genes in bacterial genomes are arranged in a meaningful order. In the journal Science, they explain that the genes are arranged by function: If they become increasingly important for faster growth, they are located near the origin of DNA replication. Accordingly, their position influences how their activity changes with the growth rate.
Are genes distributed randomly along the bacterial chromosome, as if scattered from a salt shaker? This opinion, which is held by a majority of researchers, has now been disputed by a team of bioinformaticians led by Professor Dr. Martin Lercher, head of the research group for Computational Cell Biology at HHU.
When bacteria replicate their genetic material in preparation for cell division, the process starts at a specific point on the bacterial chromosome and continues along the chromosome in both directions.