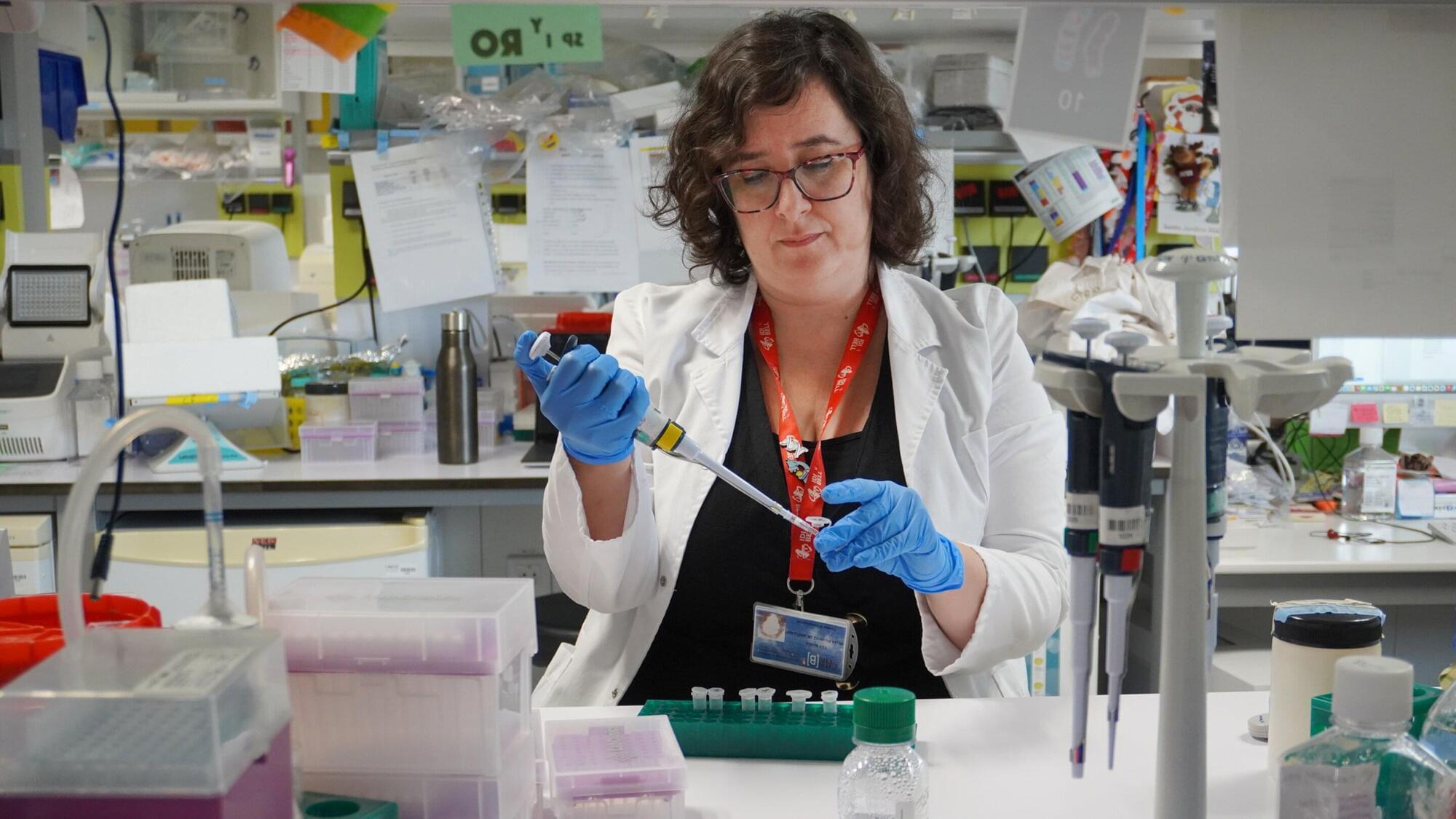
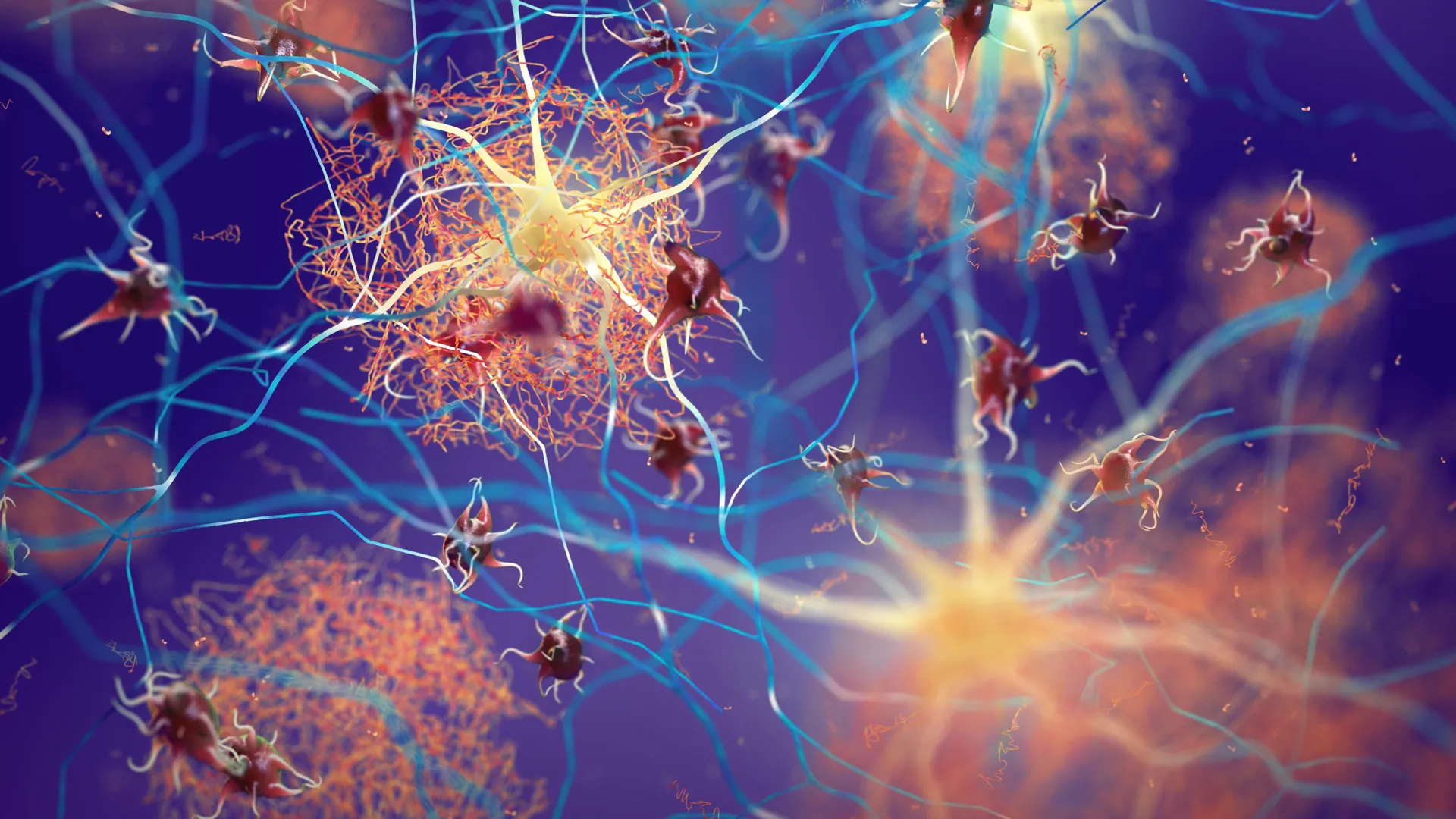
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have identified a natural process in the brain that can remove existing amyloid plaques in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease while also helping preserve memory and thinking ability. This process relies on astrocytes, star shaped support cells, which can be guided to clear out the toxic plaque buildup commonly seen in Alzheimer’s. When the team increased the amount of Sox9, a protein that influences many astrocyte functions during aging, the cells became more effective at removing amyloid deposits. The findings, reported in Nature Neuroscience, suggest that strengthening astrocyte activity could one day help slow cognitive decline linked to neurodegenerative disorders.
“Astrocytes perform diverse tasks that are essential for normal brain function, including facilitating brain communications and memory storage. As the brain ages, astrocytes show profound functional alterations; however, the role these alterations play in aging and neurodegeneration is not yet understood,” said first author Dr. Dong-Joo Choi, who conducted this work while at the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy and the Department of Neurosurgery at Baylor. Choi is now an assistant professor at the Center for Neuroimmunology and Glial Biology, Institute of Molecular Medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston.