One harrowing study reveals that the ‘dead internet theory’ which would leave the internet dominated by bots could come true in less than three years



The collision and merger of two neutron stars—the incredibly dense remnants of collapsed stars—are some of the most energetic events in the universe, producing a variety of signals that can be observed on Earth.
New simulations of neutron star mergers by a team from Penn State and the University of Tennessee Knoxville reveal that the mixing and changing of tiny particles called neutrinos that can travel astronomical distances undisturbed impacts how the merger unfolds, as well as the resulting emissions. The findings have implications for longstanding questions about the origins of metals and rare earth elements as well as understanding physics in extreme environments, the researchers said.
The paper, published in the journal Physical Review Letters, is the first to simulate the transformation of neutrino “flavors” in neutron star mergers. Neutrinos are fundamental particles that interact weakly with other matter, and come in three flavors, named for the other particles they associate with: electron, muon and tau. Under specific conditions, including the inside of a neutron star, neutrinos can theoretically change flavors, which can change the types of particles with which they interact.
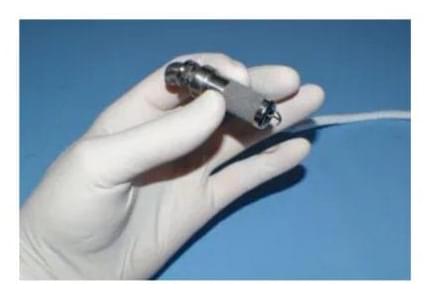
A new type of surgically implanted pump that can support a child’s failing heart has passed the first stage of human testing in a Stanford Medicine-led trial.



Oligonucleotide therapies — engineered strands of DNA or RNA — are transforming modern medicine. These cutting-edge treatments bring a new level of precision in combating disease by targeting specific genes to be silenced, activated or edited. “Nucleotide therapeutics allow us to design predictable outcomes by modifying sequences to address almost any condition,” says Peter Guterstam, product manager at biotechnology company Cytiva.
Due to an influx of research in recent years, many nucleotide-based drug candidates, including genetic therapies and vaccines for cancer and viral infections, are now in advanced clinical trial stages. “The development timeline is much quicker than we are used to,” notes Guterstam.
Significant challenges arise during development of RNA and DNA based therapies. From mRNA vaccines to gene editing, scientists are refining delivery methods, optimizing synthesis, and tackling scaling hurdles.
Buy poster metal plate other products


A person will have Alzheimer’s years before ever knowing it. The disorienting erasure of memories, language, thoughts—in essence, all that makes up one’s unique sense of self—is the final act of this enigmatic disease that spends decades disrupting vital processes and dismantling the brain’s delicate structure.
Once symptoms surface and doctors make a diagnosis, though, it can often be too late. Damage is widespread, impossible to reverse. No cure exists.
Attempts to develop drugs that clear away toxic accumulations of amyloid-beta and tau proteins—hallmarks of the disease that cause neurons to die—have ended in hundreds of failed clinical trials. Today, some scientists are skeptical over whether removing amyloid plaques is even enough. Others have a hunch that the best line of attack won’t target just one aspect of the disease, but many of them, all at once.