Quantum computing offers mind-boggling problem-solving potential. Here are four ways to buy quantum computing stocks.



Capcom is experimenting with generative AI to create the “hundreds of thousands” of ideas needed for in-game environments.
As video game development costs rise, publishers are increasingly looking to controversial AI tools to speed up work and cut costs. Call of Duty reportedly sold an “AI-generated cosmetic” for Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 3 in late 2023, and fans accused Activision of using generative AI again for a loading screen last year. EA said in September that AI was “the very core” of its business.
In a new interview with Google Cloud Japan, Kazuki Abe, a technical director at Capcom who has worked on huge titles like Monster Hunter: World and Exoprimal, explained how the company is experimenting with implementing AI in its game development processes.
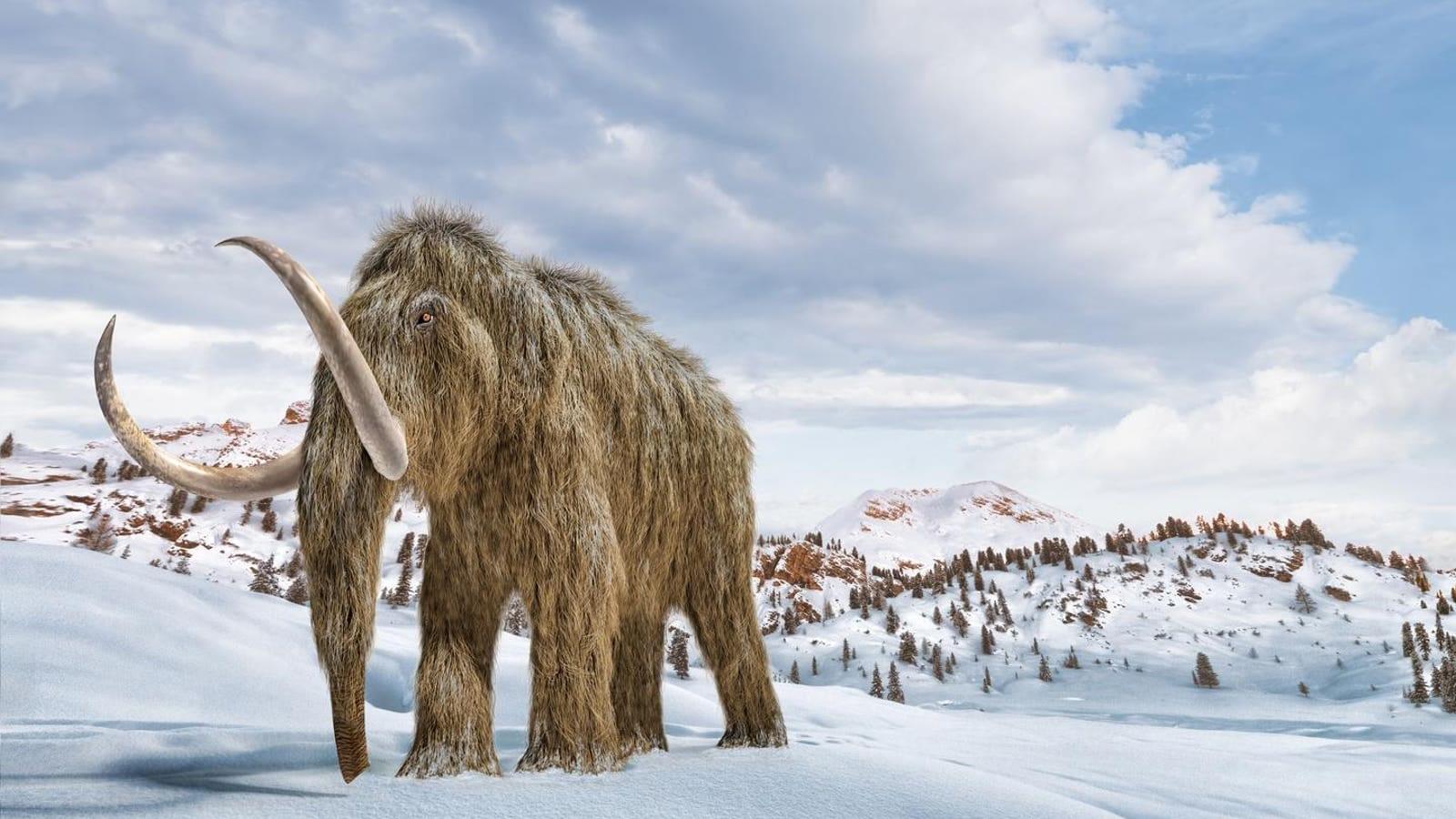

It’s a mission that is less a nostalgic yearning for a prehistoric past than it is a solution to combat climate change, the company’s founders have said. By reintroducing mammoths to Arctic environments, they hope to rejuvenate grasslands and reduce permafrost thaw—a major source of methane emissions.
The potential ripple effects of such an ecological intervention have raised profound ethical and scientific questions but have nonetheless captivated researchers, investors and the public alike.
Colossal Bioscience’s approach to de-extinction is rooted in cutting-edge advances in genetic engineering and synthetic biology.
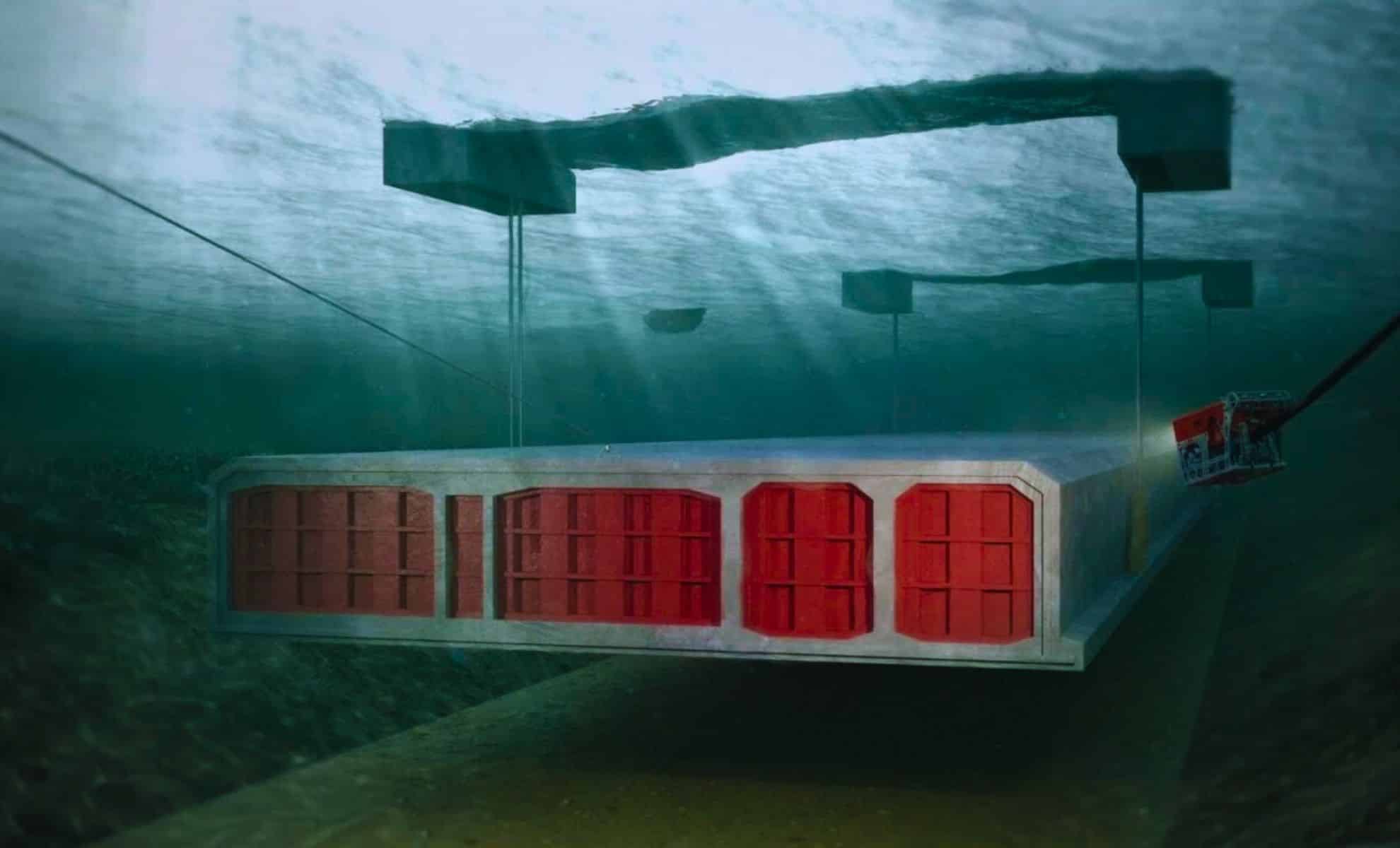

What if the future of tunnels wasn’t about digging? The Fehmarnbelt Tunnel, the world’s largest immersed tunnel, is being built without a single tunnel boring machine. Instead, engineers are using a bold, unconventional method that’s faster, more precise, and environmentally conscious. Stretching 18 kilometers beneath the Baltic Sea, this $7 billion project is set to transform travel and trade in Europe.
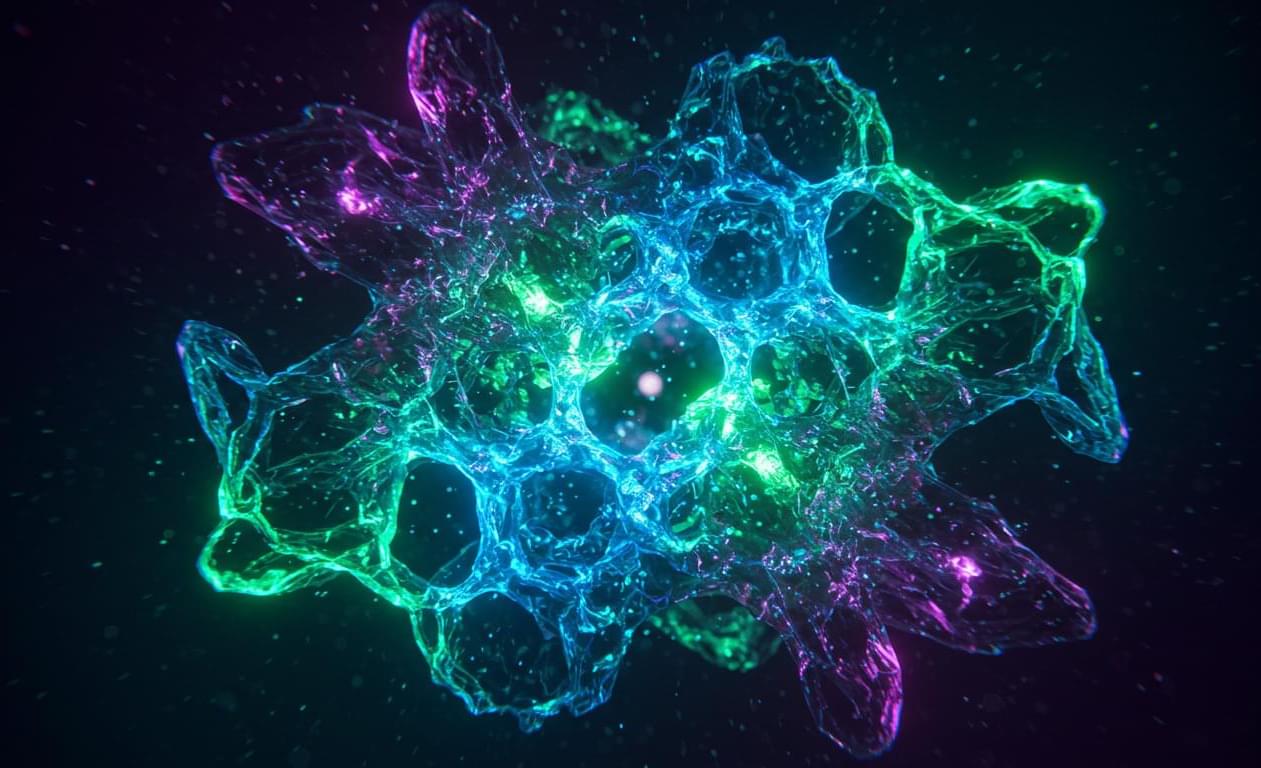

In a landmark achievement, an international team of researchers has successfully engineered the world’s first ideal Weyl semimetal, a quantum crystal that exhibits exotic electromagnetic properties. This innovative material, synthesized from a topological semiconductor, hosts a single pair of Weyl fermions without any irrelevant electronic states, paving the way for potential applications in terahertz devices, high-performance sensors, and low-power electronics.
The discovery, published in Nature, marks a major milestone in the decade-long pursuit of quantum materials, where researchers have been hindered by the presence of undesired electrons that obscure the unique properties of Weyl fermions. By revisiting a theoretically proposed strategy from 2011, the team has created a semimetal with a vanishing energy gap, enabling it to absorb low-frequency light and unlocking new possibilities for optoelectronics and quantum technology.
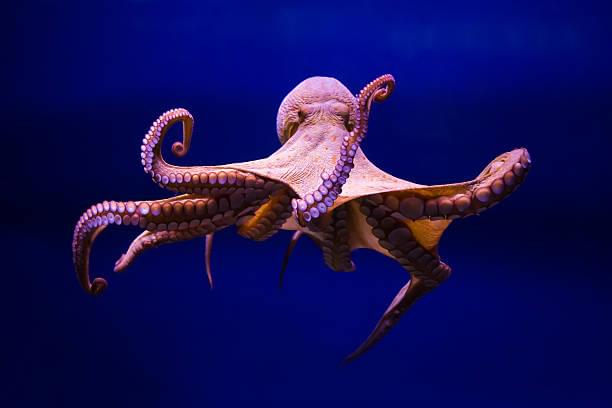

New research from the Academy of Military Medical Sciences in Beijing has uncovered a rather intriguing finding: natural melanin nanozymes (NMNs) derived from octopus ink may potentially slow ageing, protect against neurodegenerative diseases, and extend lifespan. Published in ACS Omega, the study reveals how these nanozymes work at the cellular level to mitigate oxidative stress, improve gut health, and enhance brain function, offering a new frontier in anti-ageing and neurological research.
What are Melanin Nanozymes?
Melanin, best known as the pigment responsible for skin and hair colour, has also been recognized for its potent antioxidant properties. Nanozymes created from natural melanin, like those extracted from octopus ink, mimic the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD). These nanozymes neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and improve cellular health—processes that are critical in mitigating ageing and the onset of neurodegenerative diseases.
Daniel Dennett might be closer to truth on consciousness.
Full Episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMxTS7eKkNM
Title: “Michael Levin: What Is The Field Of Diverse Intelligence (DI)? All Possible Intelligent Agents”
CONNECT:
- Website: https://tevinnaidu.com.
- Podcast: https://podcasters.spotify.com/pod/show/drtevinnaidu.
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/drtevinnaidu.
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/drtevinnaidu.
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/drtevinnaidu.
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/drtevinnaidu.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this channel is for educational purposes only. The content is shared in the spirit of open discourse and does not constitute, nor does it substitute, professional or medical advice. We do not accept any liability for any loss or damage incurred from you acting or not acting as a result of listening/watching any of our contents. You acknowledge that you use the information provided at your own risk. Listeners/viewers are advised to conduct their own research and consult with their own experts in the respective fields.
#MichaelLevin #Consciousness #MindBodyProblem #Panpsychism
Many of the strongest limitations on our technology and civilization at this time are from problems moving energy around with us, in a way which is light, energy dense, and cheap. Today we’ll look at some ways we might increase that vastly, and challenges to do that and the impact such dense portable power would have.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
/ @isaacarthursfia.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: / portable-power.
Cover Art by Jakub Grygier: https://www.artstation.com/artist/jak…
Writers.
Isaac Arthur.
Mark Warburton.
Stuart Graham.
Script Editors.
Darius Said.
Edward Nardella.
Keith Blockus.
N Kern.
Graphics Team:
Edward Nardella.
Jarred Eagley.
Justin Dixon.
Katie Byrne.
Kris Holland of Mafic Stufios: www.maficstudios.com.
Misho Yordanov.
Pierre Demet.
Sergio Botero: https://www.artstation.com/sboterod?f…
Stefan Blandin.
Music Supervisor.
Luca De Rosa — [email protected].
Synthetic Biology is on the cusp of revolutionizing biomedicine.
at NextMed Health 2023 (http://NextMedHealth.com)
Andrew Hessel is chairman of Project-write, and Author of The Genesis Machine, Our Quest to Rewrite Life in the Age of Synthetic Biology.
More about Andrew Hessel: https://www.nextmed.health/bio-andrewhessel.
NextMed Health is a unique platform and community focused on the conversations. Join us at http://NextMed.Health/join