Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Health Talks Episode 1: The Longevity Benefits of Acarbose and Rapamycin
Dr. Elana Miller talks about The Longevity Benefits of Acarbose and Rapamycin.
Join our community: https://community.gethealthspan.com/faq.
follow us on twitter: @healthspanmed.
follow us on instagram: @healthspanmed
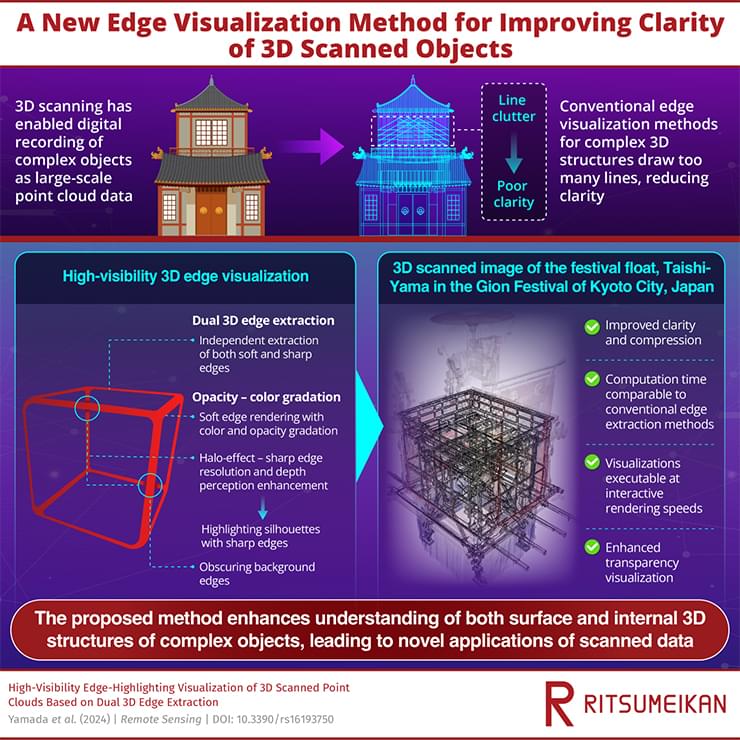
Breakthrough in 3D Object Scanning: Boosting Clarity and Depth Perception for Complex Structures
Researchers develop a novel edge-highlighting visualization technique for more comprehensible 3D-scanned objects. Improvements in three-dimensional (3D) scanning have enabled quick and accurate scanning of 3D objects, including cultural heritage objects, as 3D point cloud data. However, conventional edge-highlighting visualization techniques, used for understanding complex 3D structures, result in excessive line clutter, reducing clarity. Addressing these issues, a multinational team of researchers have developed a novel technique, involving independent rendering of soft and sharp edges in 3D structures, resulting in improved clarity and depth perception.
Recent advances in three-dimensional (3D) scanning, particularly in photogrammetry and laser scanning, have made it possible to quickly and accurately scan complex 3D objects in the real world. These techniques generate detailed models by collecting large-scale point cloud data, representing the object’s surface geometry through millions of individual points. This technology has applications in different fields, such as the 3D scanning of cultural heritage objects. By preserving these objects in digital formats, researchers can analyze their structures in greater depth. However, the complexity of data is often significant, especially when the scanned object has internal 3D structures, like rough edges.
Edge-highlighting visualization is a technique used to improve the clarity of complex 3D structures by emphasizing the object’s edges, making its shape and structure more distinguishable. However, existing methods struggle when applied to highly complex objects. These methods draw too many lines, which decreases clarity by impairing resolution and depth perception.
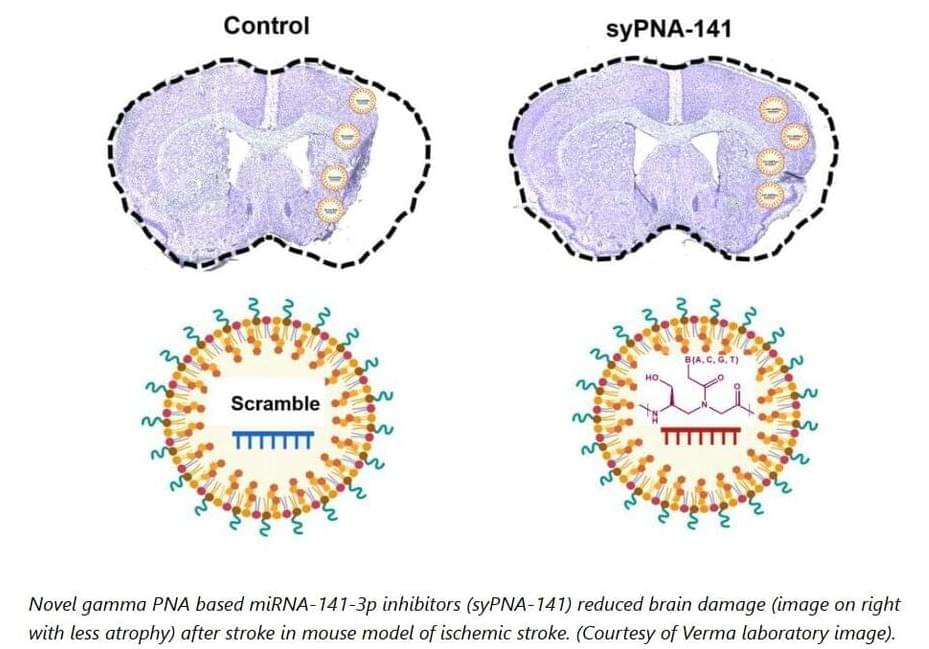
New miRNA Inhibitor could Extinguish the ‘Inflammatory Fire’ that Stroke causes in the Brain
It’s been more than three decades, but still there are only two treatments for a stroke: either rapid use of a clot-busting medication called tPA or surgical removal of a clot from the brain with mechanical thrombectomy. However, only 5% to 13% percent of stroke cases are actually eligible for these interventions.
“We need to be persistent with our research to find a new therapy for stroke,” says Rajkumar Verma, M.Pharm., Ph.D., assistant professor, Department of Neuroscience at UConn School of Medicine working in cross-campus collaboration with Professor Raman Bahal Ph.D. of the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences in the UConn School of Pharmacy. “Stroke research is hard and challenging to do. But without trying we won’t make progress. We need to keep trying. UConn is determined to keep trying.”
In addition to being life-threatening, stroke is the major cause of long-term disability worldwide.

Physicists think they may know the key to unlocking time travel
Imagine a thread so thin it’s invisible to the naked eye but packed with the mass of thousands of stars. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the theoretical description of cosmic strings, structures that may hold answers to the Universe’s greatest mysteries. If confirmed, researchers believe these theoretical strings could unlock the key to time travel.
Cosmic strings, if they exist, are thought to be incredibly slender. Some say they’d be long tubes, either stretching infinitely or looping back on themselves. Despite their thinness, a cosmic string’s mass could rival tens of thousands of stars, and it would gradually shrink over time, radiating gravitational waves as it “wiggles.”
Physicists have proposed two types of cosmic strings thus far. The first, “cosmic superstrings,” stems from string theory, a framework suggesting the Universe’s fundamental particles are vibrating strings. Superstrings could be stretched across the cosmos, providing clues about the fabric of reality and possibly holding the key to time travel, too.

Covid might cure cancer. No, you didn’t read that wrong
Illinois researchers have found an unbelievable link between infection with Covid and cancer regression where tumors decrease in size or extent.
Using animals and tissue from humans, scientists observed that the RNA molecules of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is responsible for the disease, triggered the development of a special cell in the immune system that has anti-cancer properties.
Known as “inducible nonclassical monocytes” or “I-NCMs,” these special cells attack cancer cells and could be used to treat cancers that are resistant to current therapies, according to Northwestern Medicine Canning Thoracic Institute scientists.

Human evolution in an AI world: Predicting changes in brain size, attention and social behaviors
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more common and sophisticated, its effects on human lives and societies raises new questions. A new paper published in The Quarterly Review of Biology posits how these new technologies might affect human evolution.
In “How Might Artificial Intelligence Influence Human Evolution?” author Rob Brooks considers the inevitable but incremental evolutionary consequences of AI’s everyday use and human-AI interactions—without “dramatic but perhaps unlikely events, including possibilities of human annihilation, assimilation, or enslavement.”
In the paper, Brooks considers (“often with considerable speculation”) some possible forms of human-AI interaction and the evolutionary implications of such interactions via natural selection, including forms of selection that resemble the inadvertent and deliberate selection that occurred when humans domesticated crops, livestock, and companion animals.


Time may be an illusion, new study finds
Researchers propose that time is a result of quantum entanglement, the mysterious connection between particles separated by vast distances. Their findings, published in the journal Physical Review A, could offer a clue to solving the problem of time.
“There exists a way to introduce time which is consistent with both classical laws and quantum laws, and is a manifestation of entanglement,” explained Alessandro Coppo, a physicist at the National Research Council of Italy and the study’s lead author. “The correlation between the clock and the system creates the emergence of time, a fundamental ingredient in our lives.”
In quantum mechanics, time is a fixed phenomenon, an unchanging flow from past to present. It remains external to the ever-changing quantum systems it measures and can only be observed through changes in external entities, like the hands of a clock.