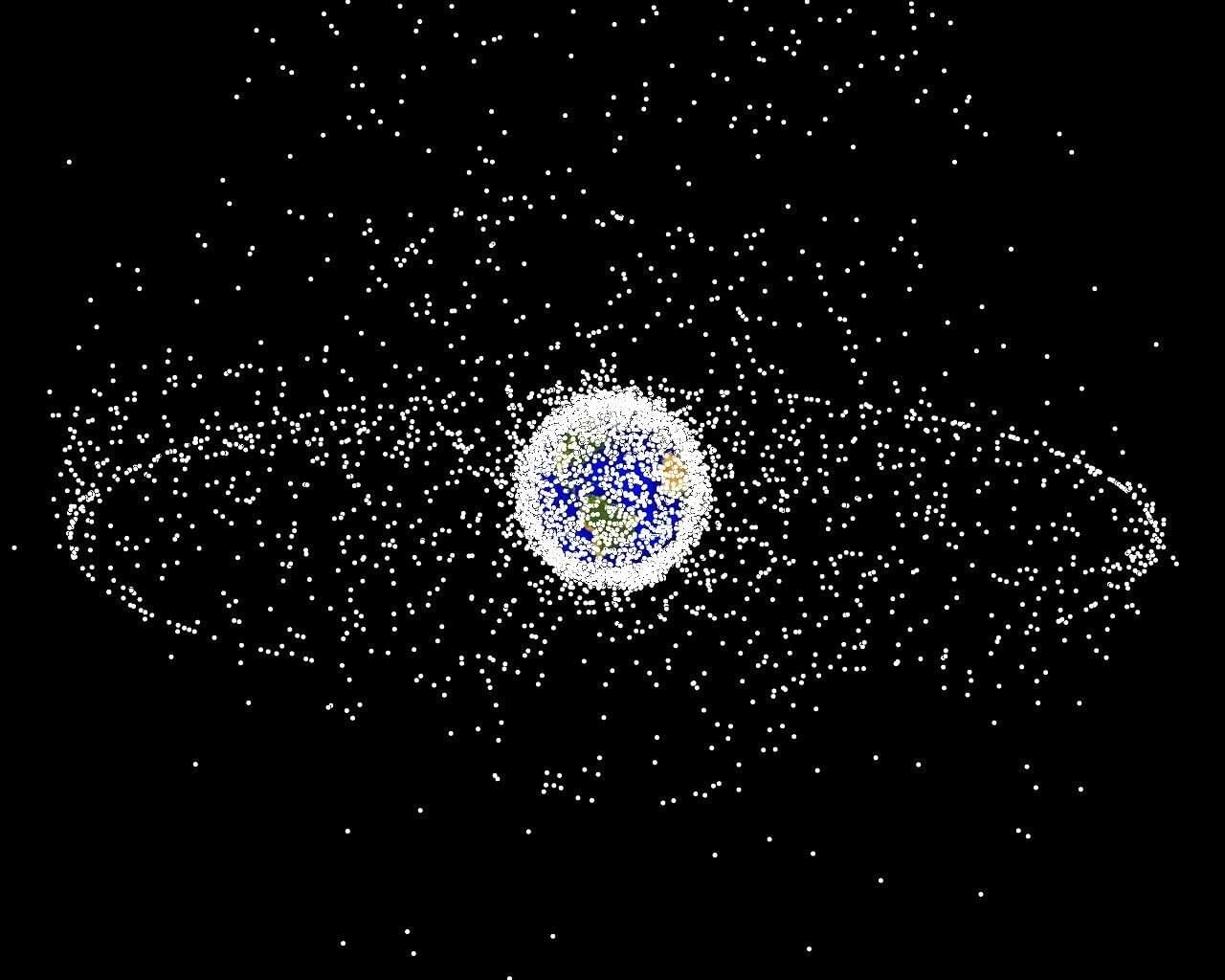
High up in Earth’s orbit, millions of human-made objects large and small are flying at speeds of over 15,000 miles per hour. The objects, which range from inactive satellites to fragments of equipment resulting from explosions or collisions of previously launched rockets, are space debris, colloquially referred to as space junk. Sometimes the objects collide with each other, breaking into even smaller pieces.
No matter the size, all of this debris poses a problem. Flying at high speeds caused by prior launches or explosions, they create danger for operational satellites and spacecraft, which are vital for the efficacy of modern technologies like GPS, digital communication and weather forecasting. At orbital speeds, even tiny fragments can cause significant damage to operational equipment, endangering future space missions and the people who would participate in them.
“Even if a tiny, five-millimeter object hits a solar panel or a solar array of a satellite, it could break it,” says Assistant Professor Hao Chen, whose research involves space systems design. “And we have over 100 million objects smaller than one centimeter in orbit. So if you want to avoid a collision, you have to maneuver your spacecraft, which takes up fuel and is costly. Additionally, we have humans on the International Space Station who sometimes must go outside the spacecraft where the space debris can hit them too. It’s really dangerous.”