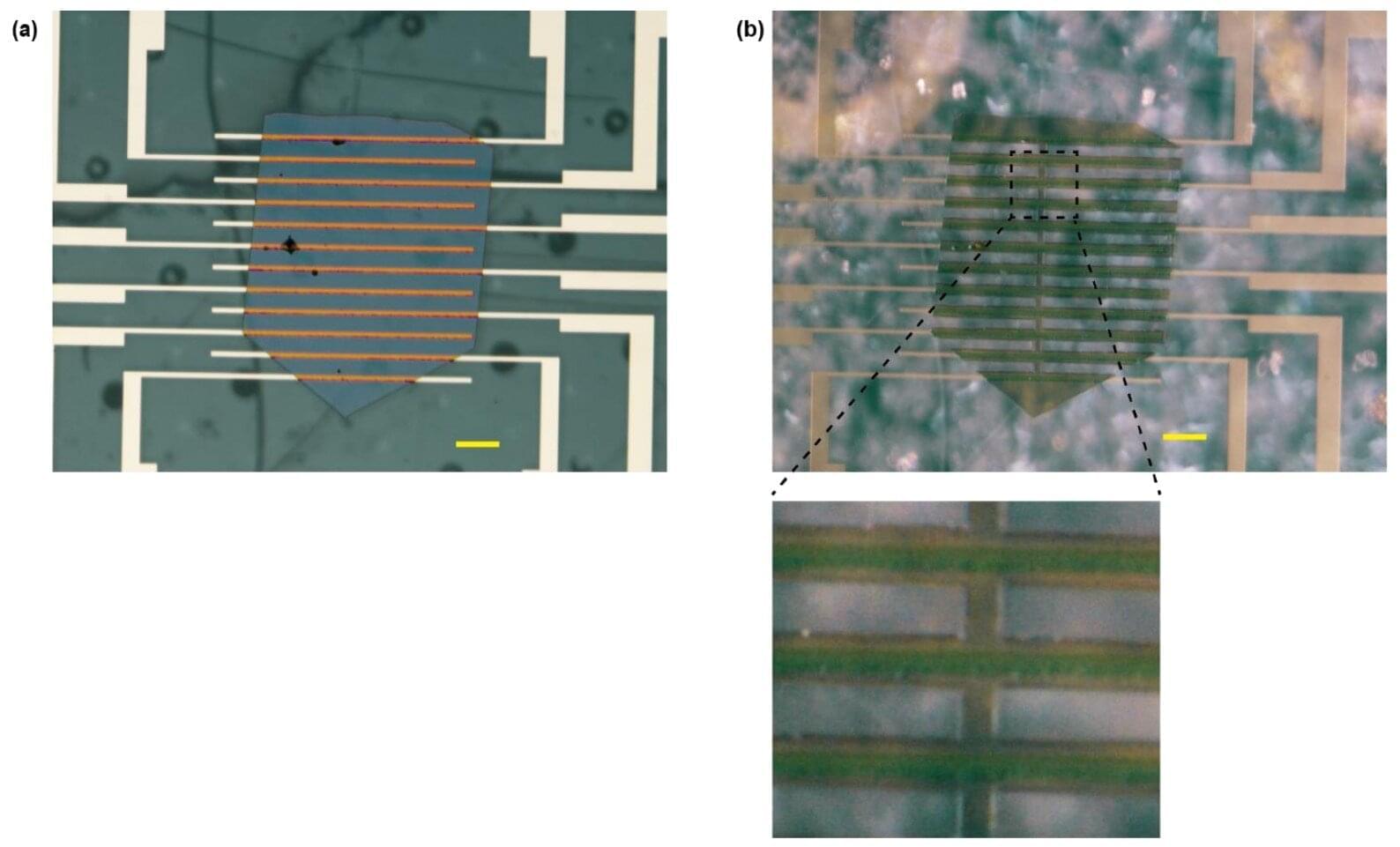
Recent studies have revealed that electrons passing through chiral molecules exhibit significant spin polarization—a phenomenon known as chirality-induced spin selectivity. This effect stems from a nontrivial coupling between electron motion and spin within chiral structures, yet quantifying it remains challenging.
To address this, researchers at the Institute for Molecular Science (IMS) /SOKENDAI investigated an organic superconductor with chiral symmetry. They focused on nonreciprocity related to spin-orbit coupling and observed an exceptionally large nonreciprocal transport in the superconducting state, far exceeding theoretical predictions. Remarkably, this was found in an organic material with inherently weak spin-orbit coupling, suggesting that chirality significantly enhances charge current-spin coupling with inducing mixed spin-triplet Cooper pairs.
The work is published in the journal Physical Review Research.