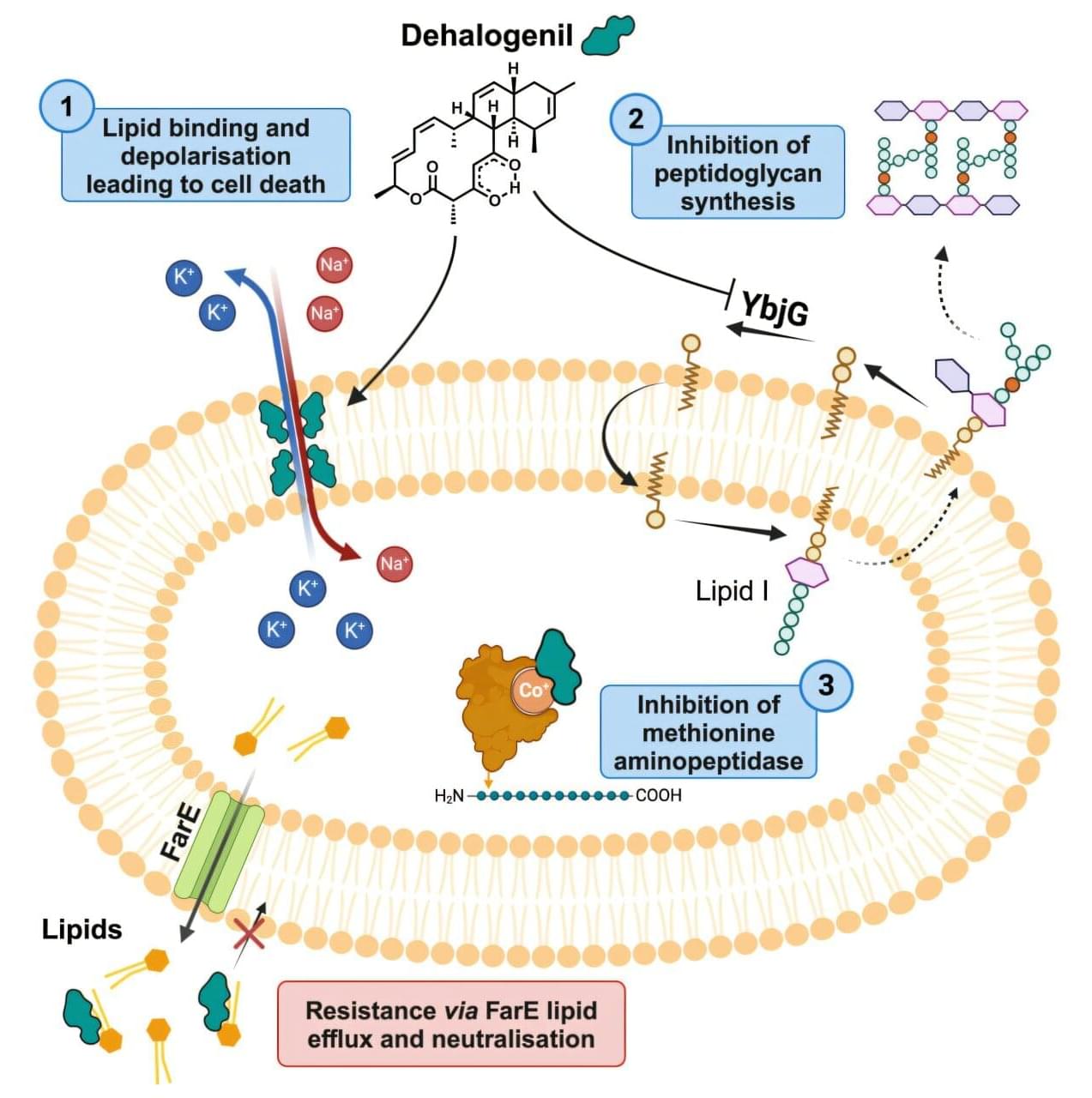
The development and spread of antibiotic resistance represents one of the greatest threats to global health. To overcome these resistances, drugs with novel modes of action are urgently needed.
Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland (HIPS) have now uncovered the mode of action of a promising class of natural products—the chlorotonils. These molecules simultaneously target the bacterial cell membrane and the bacteria’s ability to produce proteins, enabling them to break through resistance. The team published its findings in Cell Chemical Biology.
The more frequently antibiotics are used, the faster pathogens evolve mechanisms to evade their effects. This leads to resistant pathogens against which common antibiotics are no longer effective. To ensure that effective treatments for bacterial infections remain available in the future, antibiotics that target different bacterial structures than currently approved drugs are essential.