Extract from “Evolution, Basal Cognition and Regenerative Medicine”, kindly contributed by Michael Levin in SEMF’s 2023 Interdisciplinary Summer School (http…
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
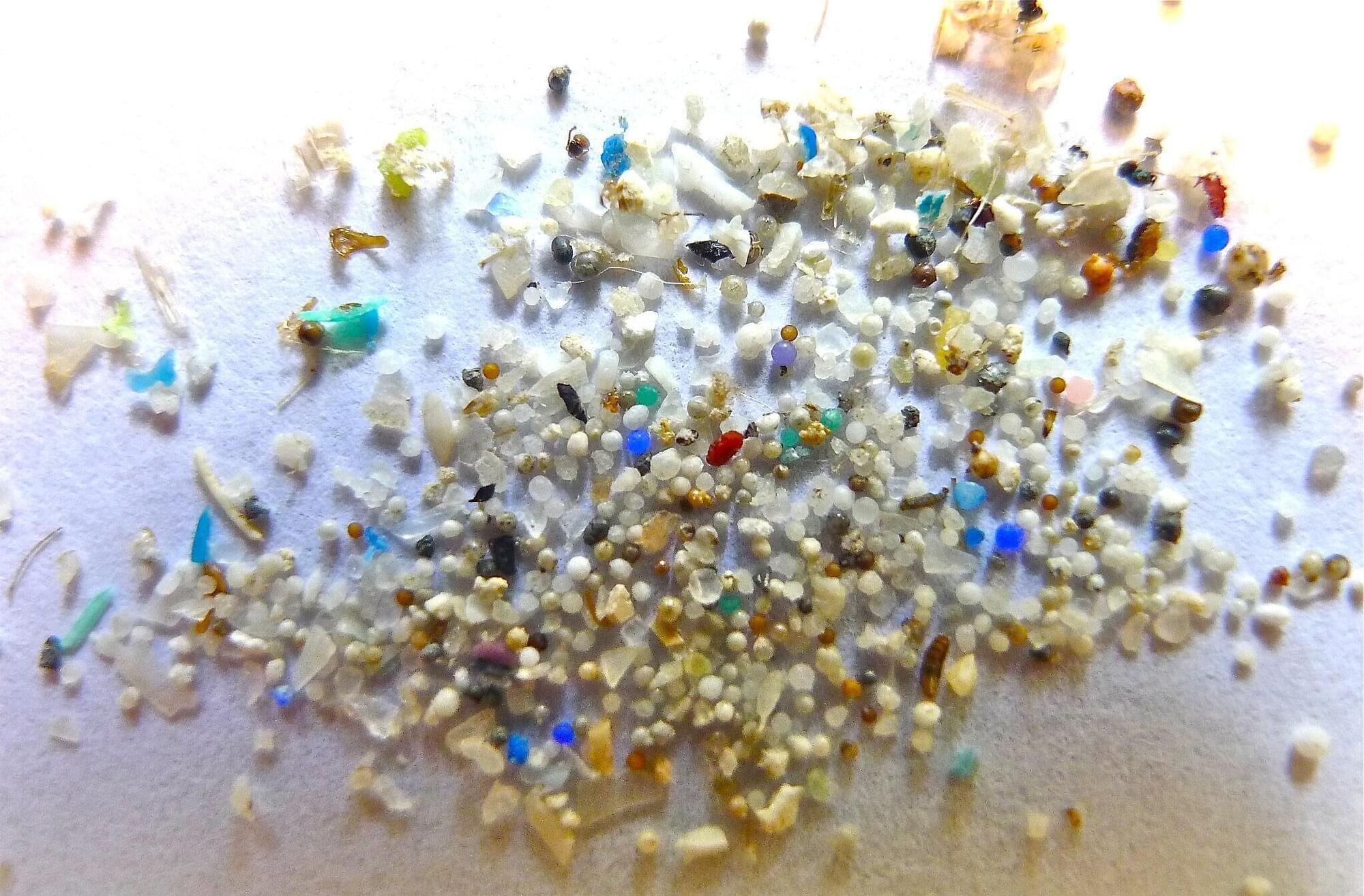

Nanoplastics generated from real-world plastic waste readily adsorb heavy metal ions, study reveals
Some 460 million metric tons of plastic are produced globally each year, out of which a staggering 91% of plastic waste is never recycled—with 12% incinerated and 79% left to end up in landfills and oceans and linger in our environment.
Exposure to various elements causes the plastics to break down into microplastics (5 mm) and nanoplastics (1,000 nm). There is a growing public health concern as these nanoplastics (NPs) make their way into the human body through air, water, food and contact with skin.
A recent study published in ACS ES&T Water has revealed that the already detrimental effects of NPs are further amplified by their ability to interact with various toxic environmental contaminants, such as heavy metal ions.

China to launch new modules to Tiangong space station
HELSINKI — China is preparing to launch new modules to its Tiangong space station to meet growing demands for science and potentially boost international cooperation.
The Long March 5B, currently China’s most powerful rocket, is slated to launch new Tiangong modules, according to an official with China’s state-owned main space contractor.
“According to the plan, the Long March 5B rocket will also carry out the future launches of additional modules for the crewed space station,” Wang Jue from China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) told China Central Television (CCTV) April 30.


Why the humanoid workforce is running late
Roboticists, from what I’ve seen, are normally a patient bunch. The first Roomba launched more than a decade after its conception, and it took more than 50 years to go from the first robotic arm ever to the millionth in production. Venture capitalists, on the other hand, are not known for such patience.
Perhaps that’s why Bank of America’s new prediction of widespread humanoid adoption was met with enthusiasm by investors but enormous skepticism by roboticists. Aaron Prather, a director at the robotics standards organization ASTM, said on Thursday that the projections were “wildly off-base.”
As we’ve covered before, humanoid hype is a cycle: One slick video raises the expectations of investors, which then incentivizes competitors to make even slicker videos. This makes it quite hard for anyone—a tech journalist, say—to peel back the curtain and find out how much impact humanoids are poised to have on the workforce. But I’ll do my darndest.
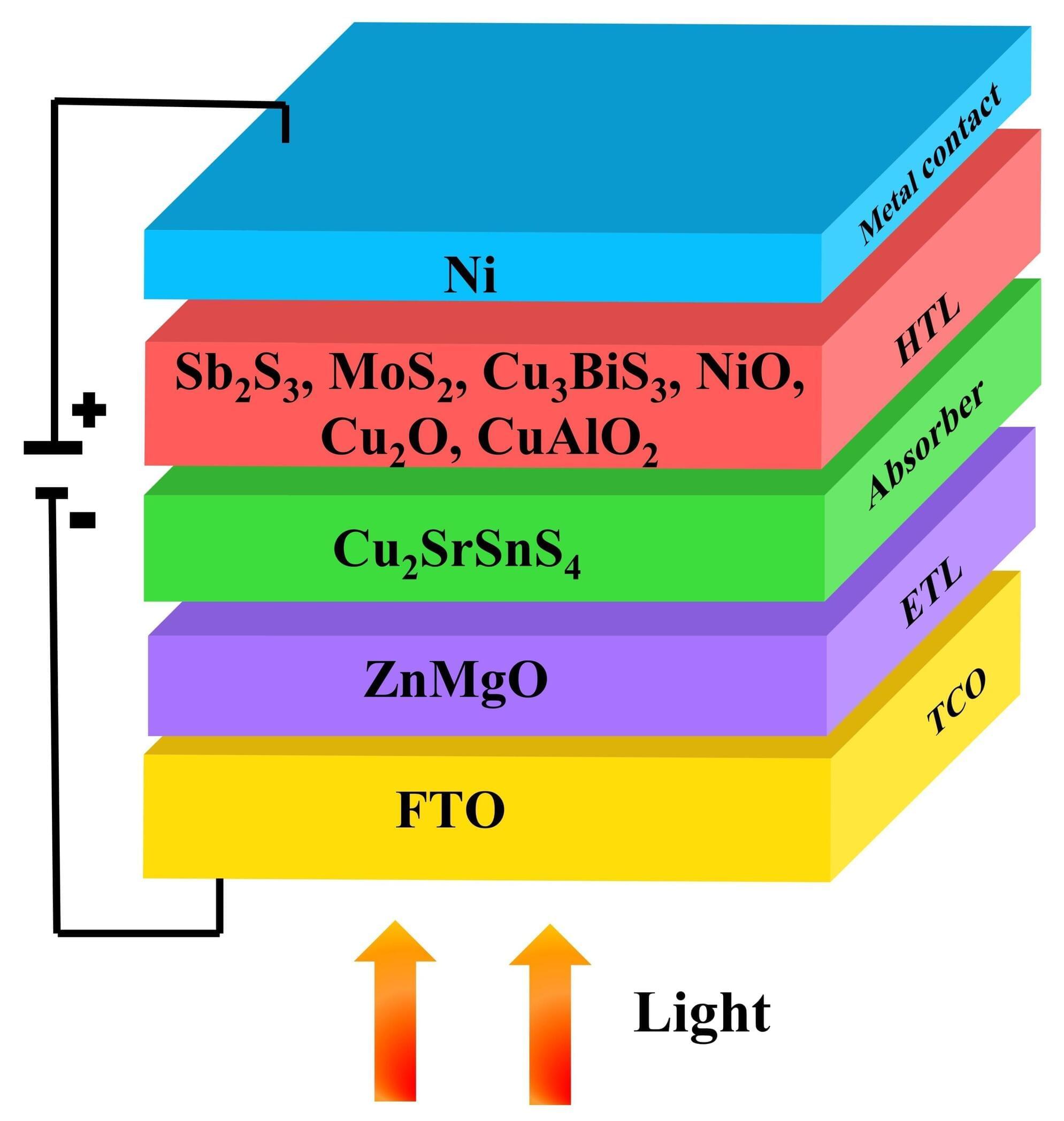
Improving the performance of Cu₂SrSnS₄ solar cells with inorganic hole transport layers
Thin film solar cells such as CdTe and CIGSe have gained significant attention due to their low production cost and excellent power conversion efficiencies (PCE). Nevertheless, toxicity and scarcity of constituent elements restrict their widespread usage.
Recently, Cu2SrSnS4 semiconductor has emerged as a potential substitute due to its remarkable absorber characteristics, including non-toxicity, Earth abundance, tunable bandgap, etc. But still, it’s in the emerging stage with a low PCE of 0.6%, revealing that it requires remarkable enhancement to compete with traditional solar cells.
The large open circuit voltage (VOC) loss constricts its performance, which primarily originates from improper band alignment with the transport layers. Discovering the ideal device configuration is the best solution to enhance its PCE.
Mass spectrometry method identifies pathogens within minutes instead of days
Traditionally, bacterial diseases are diagnosed by the tedious isolation of pathogens and the creation of bacterial cultures. Waiting times of several days are the rule here. Only then can targeted treatment of the disease begin.
Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Imperial College London have developed a new method to identify bacteria with unprecedented speed. This means that the waiting time can be reduced from several days to just a few minutes.
The work is published in the journal Nature Communications.
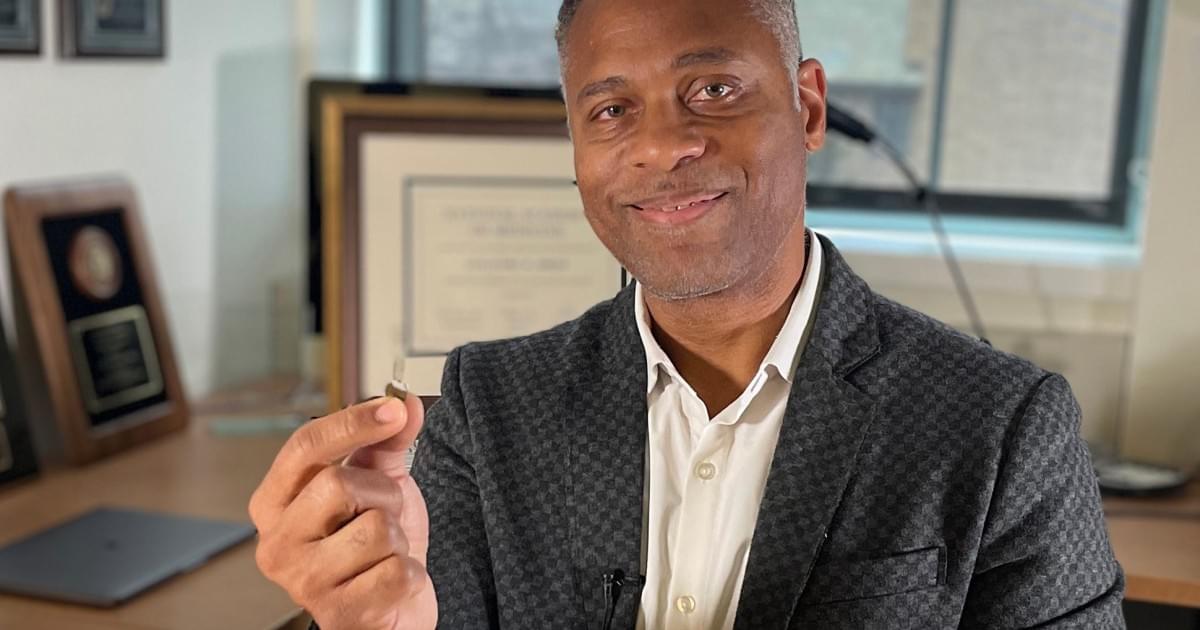

Northwestern launches pioneering medical research institute with $10 million gift from Trustee Kimberly Querrey, bringing her total University giving to $391 million
Northwestern University Trustee Kimberly K. Querrey (’22, ’23 P) has made a $10 million gift to create and enhance the Querrey Simpson Institute for Regenerative Engineering at Northwestern University (QSI RENU), bringing her total giving to the institute to $35 million. The new institute will advance the development of medical tools that empower the human body to heal, focusing on the regeneration or reconstruction of various tissues and organs, such as the eyes, cartilage, spinal cord, heart, muscle, bone and skin.
The Querrey Simpson Institute for Regenerative Engineering at Northwestern University will advance research to regenerate and reconstruct tissues and organs.
Guillermo Ameer, director of the new Querrey Simpson Institute for Regenerative Engineering at Northwestern University, showcases his bioresorbable bandage, which delivers electrotherapy to wounds, accelerating diabetic ulcer healing and dissolving safely after use. QSI RENU combines engineering, biology, medicine and data science to develop technologies for tissue and organ function.