Aug 30, 2023
Waves of Entanglement Seen Rippling Through a Quantum Magnet For The First Time
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: quantum physics, space
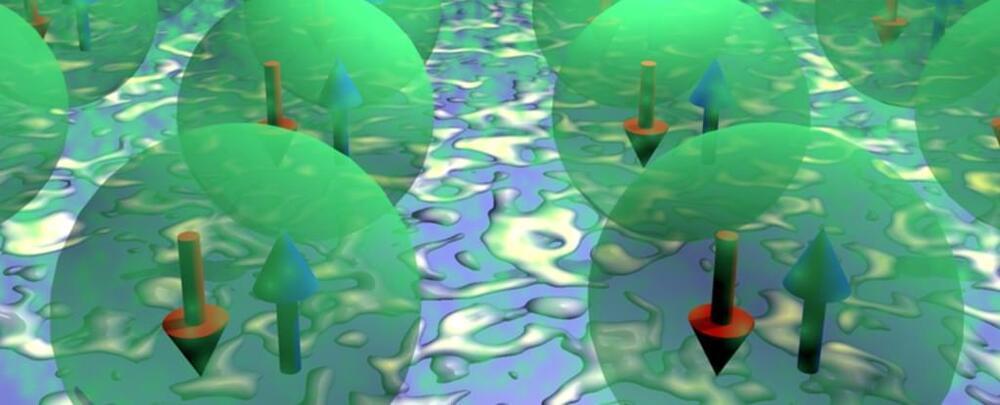
Crafting organic molecules into a bizarre kind of magnet, physicists from Aalto University and the University of Jyväskylä in Finland have created the perfect space for observing the elusive activity of an electronic state called a triplon.
Where a garden variety magnet is typically best described as having two poles surrounded by a nest of field lines, the curious construct known as a quantum magnet defies such a simple description.
As is the case any time the word ‘quantum’ appears, you can imagine a landscape where nothing is certain. Like spinning roulette wheels in a dimly lit casino, all states are a maybe until the croupier says “no more bets”.