Black holes are fundamental to the structure of galaxies and critical in our understanding of gravity, space, and time. A stellar mass black hole is a type of black hole that forms from the gravitational collapse of a massive star at the end of its life cycle. These black holes typically have masses ranging from about 3 to 20 times the mass of our sun.
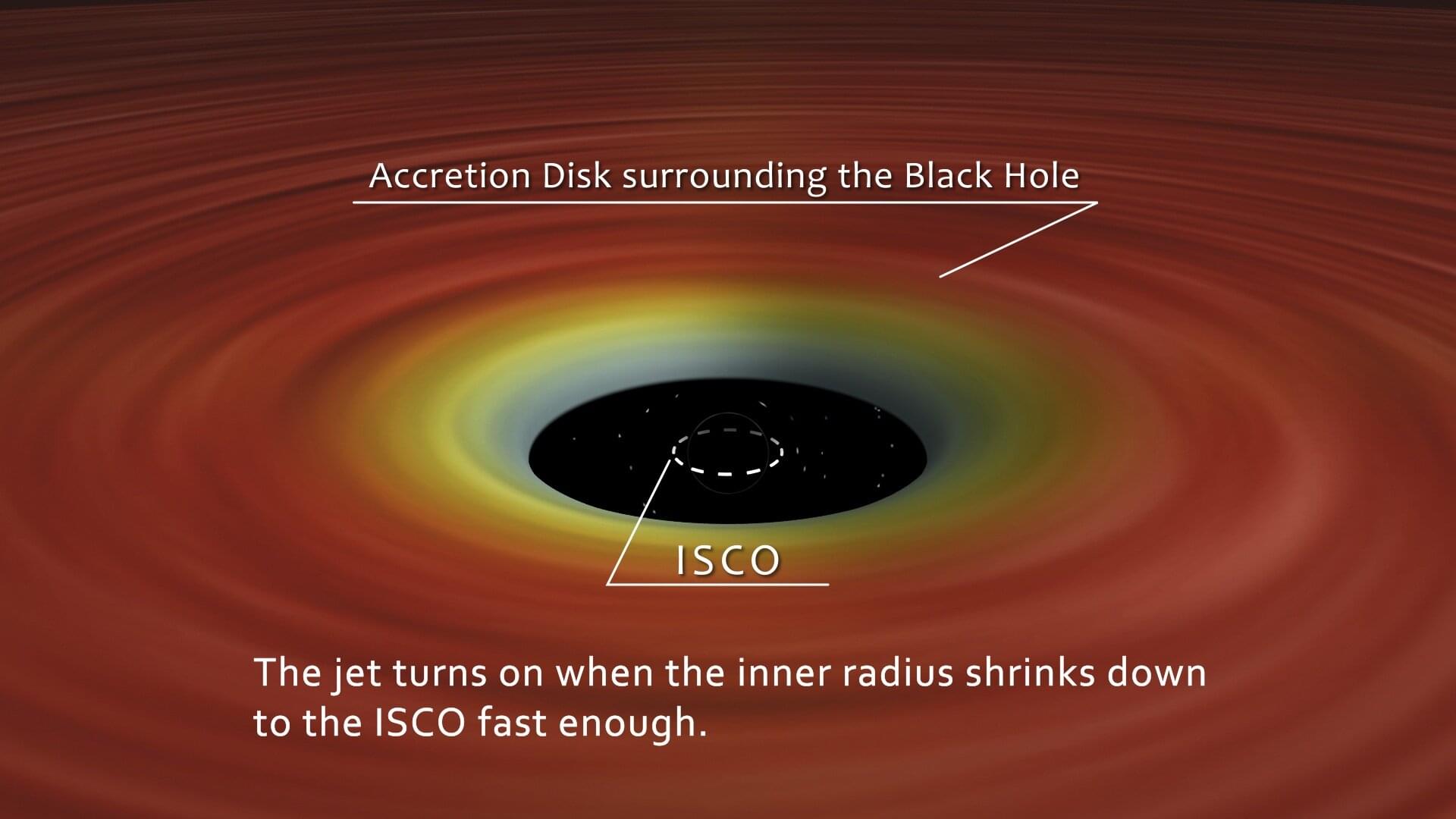
Sometimes black holes generate beams of ionized gas (plasma) that shoot outward at nearly light speed. Although discovered more than a century ago, how and why jets occur has remained a mystery, described as one of the “wonders of physics.”
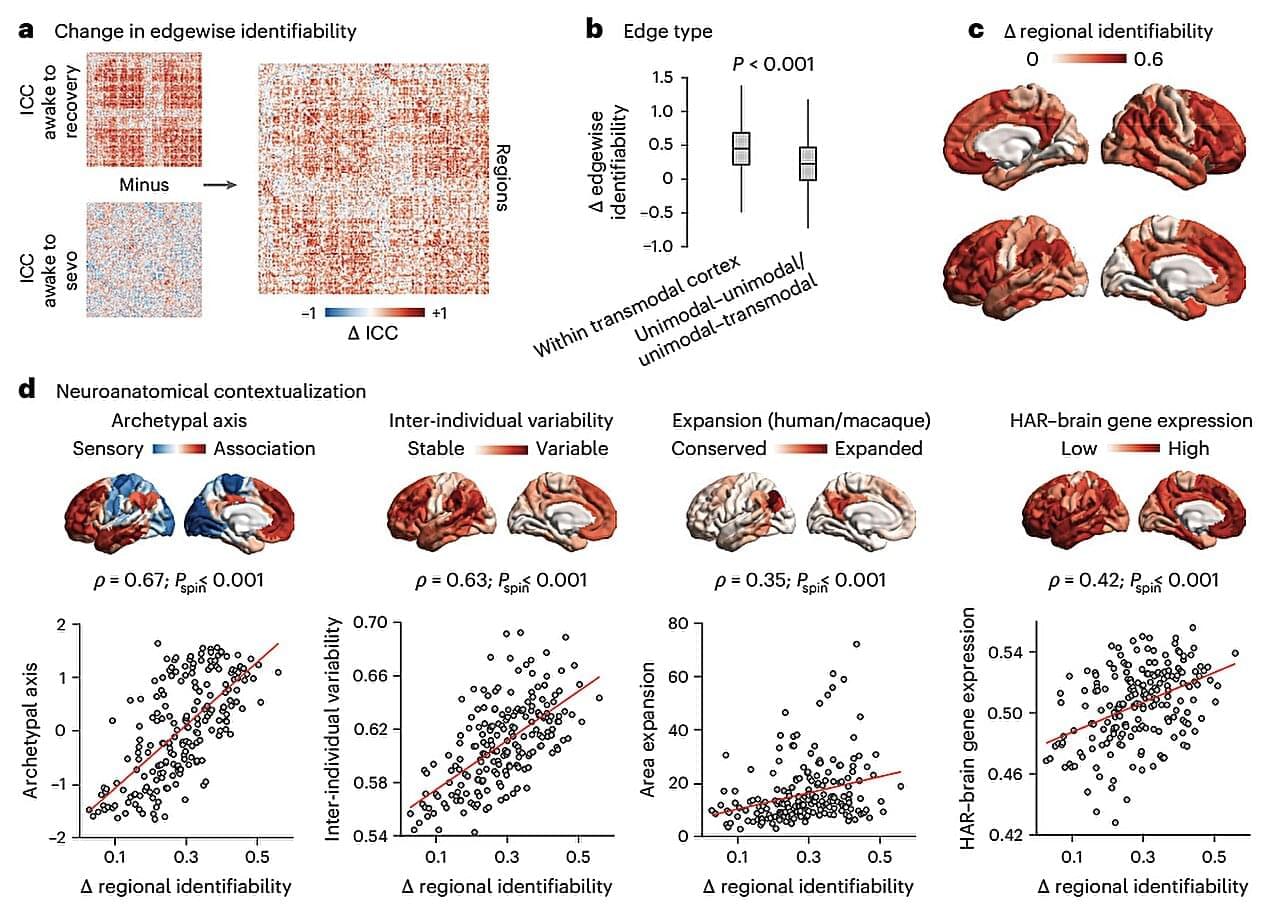
Prof. Kazutaka Yamaoka from Nagoya University in Japan, along with his colleagues from the University of Toyama and other international institutes, have discovered key conditions needed for a stellar black hole to create plasma jets. Their findings, published in Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, show that when superheated gas material experiences a rapid shrinkage toward the black hole, jet formation occurs.