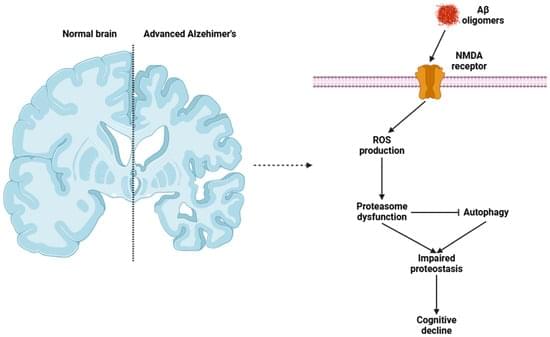
Aging is a complex, progressive, and irreversible biological process that entails numerous structural and functional changes in the organism. These changes affect all bodily systems, reducing their ability to respond and adapt to the environment. Chronic inflammation is one of the key factors driving the development of age-related diseases, ultimately causing a substantial decline in the functional abilities of older individuals. This persistent inflammatory state (commonly known as “inflammaging”) is characterized by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, an increase in oxidative stress, and a perturbation of immune homeostasis. Several factors, including cellular senescence, contribute to this inflammatory milieu, thereby amplifying conditions such as cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, and metabolic disorders.