Quantum promises huge breakthroughs in drug discovery and last-mile delivery, but there are still unknowns about what a world in quantum’s hands will mean.




A major breakthrough in quantum computing has just been achieved by American researchers at MIT. This innovation, dubbed the “quantum superhighway”, revolutionizes communication between quantum processors and opens up promising new prospects for the development of more powerful and efficient supercomputers.
Quantum computers today represent the cutting edge of computing technology, capable of solving problems far beyond the capabilities of conventional supercomputers. However, their efficiency depends on fast, precise communication between their various processors. This is precisely the challenge that American engineers have just met.
The innovation developed by the MIT team consists of an interconnection device enabling instant communication between quantum processors. Unlike traditional “point-to-point” link systems, which are prone to increasing errors during data transfer, this “quantum superhighway” promotes far more efficient “all-to-all” communication.

Combining space topology and time topology, topological states that are localized simultaneously in space and time are theoretically and experimentally demonstrated, potentially enabling the space-time topological shaping of light waves with applications in spatiotemporal wave control for imaging, communications and topological lasers.
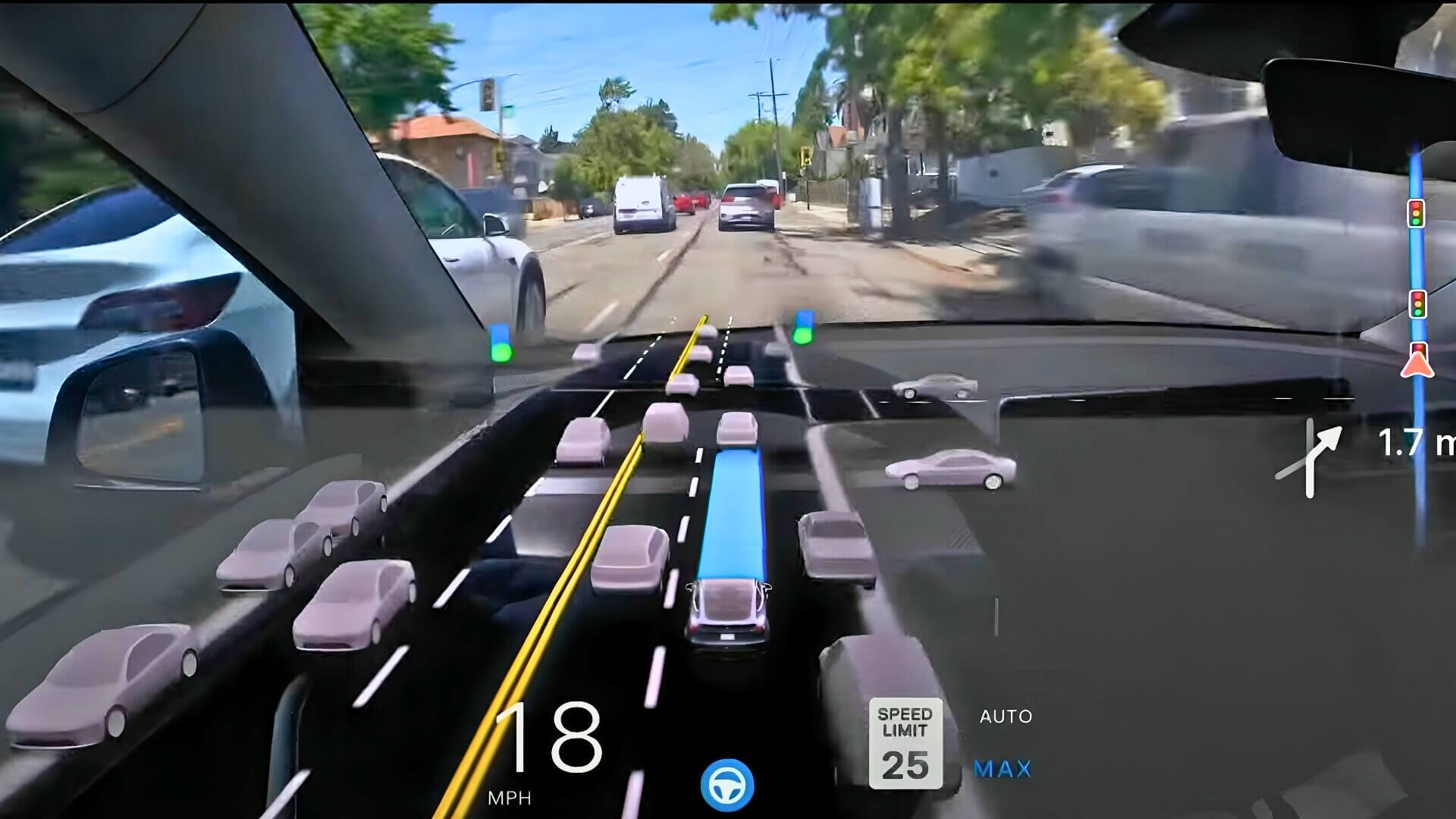
Tesla is now shipping the Full Self-Driving (FSD) (Supervised) Early Access Program to the USA. This is a big step forward in Tesla’s work to improve and project its autonomous driving technology. Tesla expects that the capability will eventually extend to all FSD owners in North America, letting them try out pre-release versions of the automaker’s most sophisticated automotive-driving-assistance software.
Enrolling in this program will allow Tesla owners to test out high-end upgrades before the rest of the public gains access. Most importantly, participants will offer useful info and vehicle data that will aid in refining and fine-tuning future versions.

“I give you God’s view,” said Toby Cubitt, a physicist turned computer scientist at University College London and part of the vanguard of the current charge into the unknowable, and “you still can’t predict what it’s going to do.”
Eva Miranda, a mathematician at the Polytechnic University of Catalonia (UPC) in Spain, calls undecidability a “next-level chaotic thing.”
Undecidability means that certain questions simply cannot be answered. It’s an unfamiliar message for physicists, but it’s one that mathematicians and computer scientists know well. More than a century ago, they rigorously established that there are mathematical questions that can never be answered, true statements that can never be proved. Now physicists are connecting those unknowable mathematical systems with an increasing number of physical ones and thereby beginning to map out the hard boundary of knowability in their field as well.


Yesterday, Richard Dinan, CEO of Pulsar Fusion, sent me a ton of new information about their new Sunbird Fusion Drive! Specific capabilities, travel times to multiple destinations throughout the Solar System…they’ve got it all!
And now, Angry is bringing it to you!
#space #fusion #nasa.
Please support my channel!
DISCORD MEMBERSHIP, EXCLUSIVE CONTENT AND EARLY RELEASES!
https://www.patreon.com/AngryAstronaut.
https://cash.app/$Angry70
https://www.paypal.com/paypalme/AngryAstro.
Follow me on twitter:
Tweets by Astro_Angry
