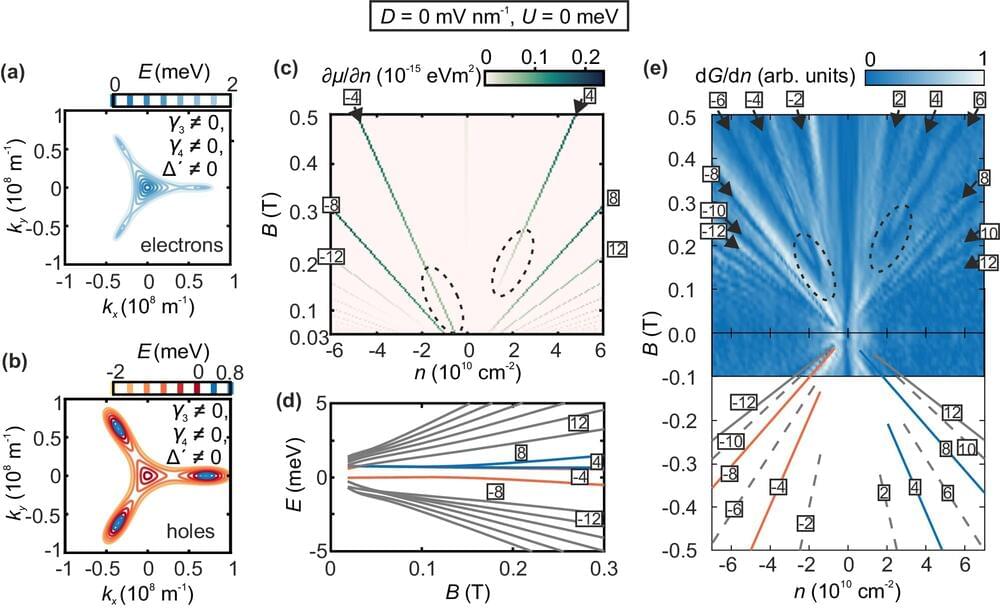
An international research team led by the University of Göttingen has demonstrated experimentally that electrons in naturally occurring double-layer graphene move like particles without any mass, in the same way that light travels. Furthermore, they have shown that the current can be “switched” on and off, which has potential for developing tiny, energy-efficient transistors—like the light switch in your house but at a nanoscale.
Tim Cook said Apple will “look at” manufacturing in Indonesia following a meeting with its president in Jakarta.
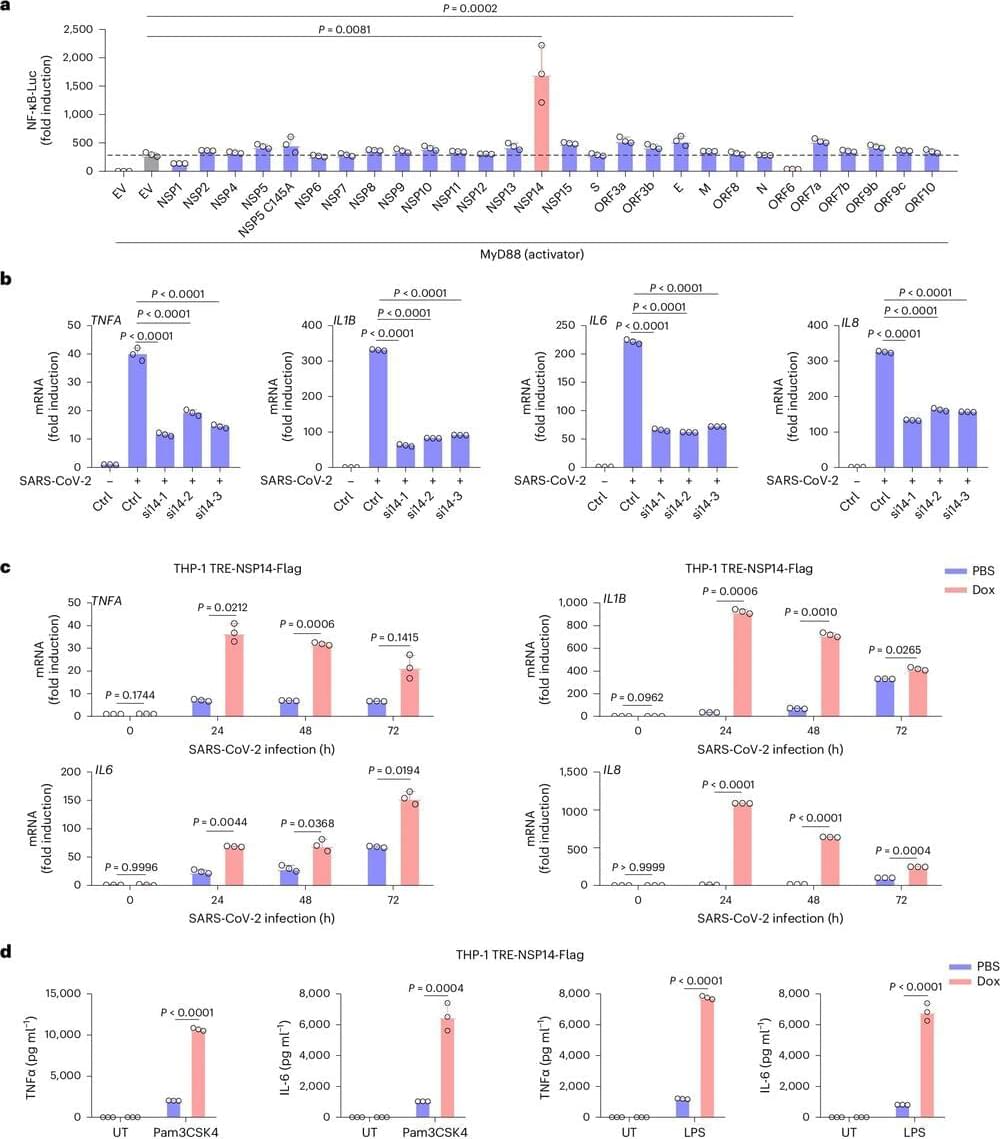
A recent USC study provides new information about why SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind the COVID-19 pandemic, may elicit mild symptoms at first but then, for a subset of patients, turn potentially fatal a week or so after infection. The researchers showed that distinct stages of illness correspond with the coronavirus acting differently in two different populations of cells.
The study, published in Nature Cell Biology, may provide a roadmap for addressing cytokine storms and other excessive immune reactions that drive serious COVID-19.
The team found that when SARS-CoV-2 infects its first-phase targets, cells in the lining of the lung, two viral proteins circulate within those cells—one that works to activate the immune system and a second that, paradoxically, blocks that signal, resulting in little or no inflammation.
Stars like the sun are remarkably constant. They vary in brightness by only 0.1% over years and decades, thanks to the fusion of hydrogen into helium that powers them. This process will keep the sun shining steadily for about 5 billion more years, but when stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, their deaths can lead to pyrotechnics.
The sun will eventually die by growing large and then condensing into a type of star called a white dwarf. But stars more than eight times more massive than the sun die violently in an explosion called a supernova.
Supernovae happen across the Milky Way only a few times a century, and these violent explosions are usually remote enough that people here on Earth don’t notice. For a dying star to have any effect on life on our planet, it would have to go supernova within 100 light years from Earth.
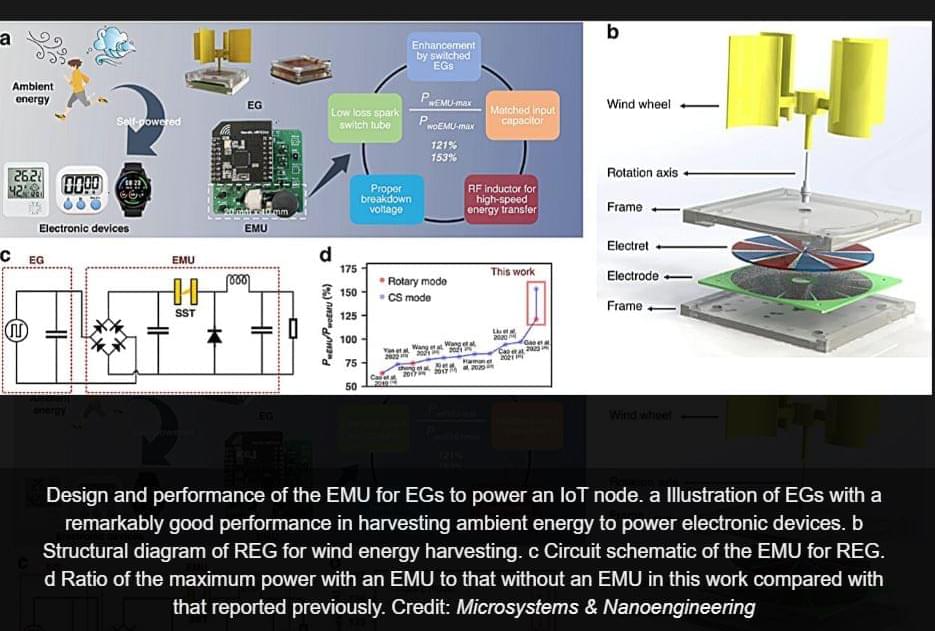
Researchers have developed a high-performance energy management unit (EMU) that significantly boosts the efficiency of electrostatic generators for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. This breakthrough addresses the challenge of high impedance mismatch between electrostatic generators and electronic devices, unlocking new possibilities for ambient energy harvesting.
Electrostatic generators have emerged as a promising solution for powering low-power devices in Internet of Things (IoT) networks, utilizing energy from environmental sources such as wind and human motion. Despite their potential, the effectiveness of these generators has been hampered by an impedance mismatch when connected to electronic devices, leading to low energy utilization efficiency.
A study published in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering introduces an efficient energy management unit (EMU) designed to significantly boost the power efficiency of electrostatic generators for IoT devices. This innovation addresses the longstanding challenge of impedance mismatch and propels forward the potential for using environmental energy harvesting within the IoT domain.
Is time an illusion? If not, what is time? Why does time flow forward? You are watching this video. Your brain cells are firing in anticipation. A story is unfolding. Time is moving forward. Or is it? What if I told you that nothing is happening. There is no story unfolding. The story has already been told. The video has already been uploaded and seen by others. You are just watching it one second at a time, so there is a story unfolding for you only. What if your entire life was like this video upload, like a DVD. The story of your life is already on that DVD. The only difference is that you don’t have a forward and reverse button. You are forced to experience your DVD one moment at a time. There is some strong scientific evidence that this may be the true nature of reality. If so, that could mean that everything you think you know is utterly an illusion. Einstein’s theory of relativity supports something called the block universe, which is really a four dimensional space time structure. This means that every event has its own coordinates not only in space but in time. So for example, wherever you are right now corresponds to a location in 3 dimensions, like London, England — and a location in time, 2PM on Feb 2, 2019. But just like the space 10 feet ahead of you is as real as the space 10 feet behind you, so too is the moment 10 minutes into the future and 10 minutes into the past. In other words, the past and future exist just as much as the present. MIT physicist Max Tegmark says we can view the universe as a three dimensional space where stuff happens, or four dimensional block universe where nothing happens. If it is the latter, he says, then change is really an illusion, because nothing is changing. It’s all there – past, present and future – like a DVD. A drama maybe unfolding in the movie recorded on the dvd, but nothing about the DVD is changing in any way. We may have the illusion, at any given moment, that the past already happened and the future doesn’t yet exist, and that things are changing. But the only reason we may have a past is that our brain contains memories of the past. If we did not have any memories, would we have any sense of the past, or of a sense of time at all? Is it possible that time doesn’t actually exist except through our perception of it? Physics doesn’t help us when it comes to the arrow of time – it is time-agnostic. If time was running backwards, all the equations would still be valid. So mathematically, physics does not say that time goes forward or backward. It just says that time Time can not be zero, but it can run either forward or backward without violating any laws. Time is symmetric. But this is counterintuitive. Reality seems to be telling us that time does exist, and that its arrow points in only one direction — forward. Why doesn’t the arrow of time flow backward, if physics says it is equally likely. It would have been possible if it were not for one aspect of physics, and that is the law of entropy. Entropy is a measure of the disorderliness of the universe. Things always get more disorderly. You can scramble and egg, but you can’t unscramble it. This is entropy increasing. Entropy appears to be the only reason the arrow of time is what it is. But why is Entropy always becoming higher? Why doesn’t it become lower? There doesn’t appear to be any fundamental reason for that. Alan Guth, professor at MIT, who pioneered the idea of cosmic inflation, may have solved this riddle. He argues that information and entropy are almost the same thing. In order to know your past, you have to form memories. Adding memories means adding information. Adding information increases entropy. Therefore a conscious system can only be conscious in one direction – when entropy increases, which allows information to increase. This implies that we are conscious because we live in a universe of increasing entropy. Consciousness cannot exist in a universe where entropy decreases. So if entropy has been increasing since the beginning of time, it means that the universe must have started at the lowest possible state of entropy at the beginning…at the big bang. Why then did the universe start off this way, resulting in forward time? Alan Guth says that if the universe is infinitely large, then the total potential entropy of the universe is infinite. If that is the case, then any entropy you start with is low entropy. The entropy will increase from any given starting point he says. This means that it doesn’t matter what the entropy of the big bang was, it would always be the lowest entropy, because there will always be a larger entropy number that the universe can flow to. And seemingly, we exist because time has flowed in a favorable direction for causality to occur, namely, it has flowed forward in our universe. But what about the block universe, are we living inside a DVD?…watch the video for the answer.
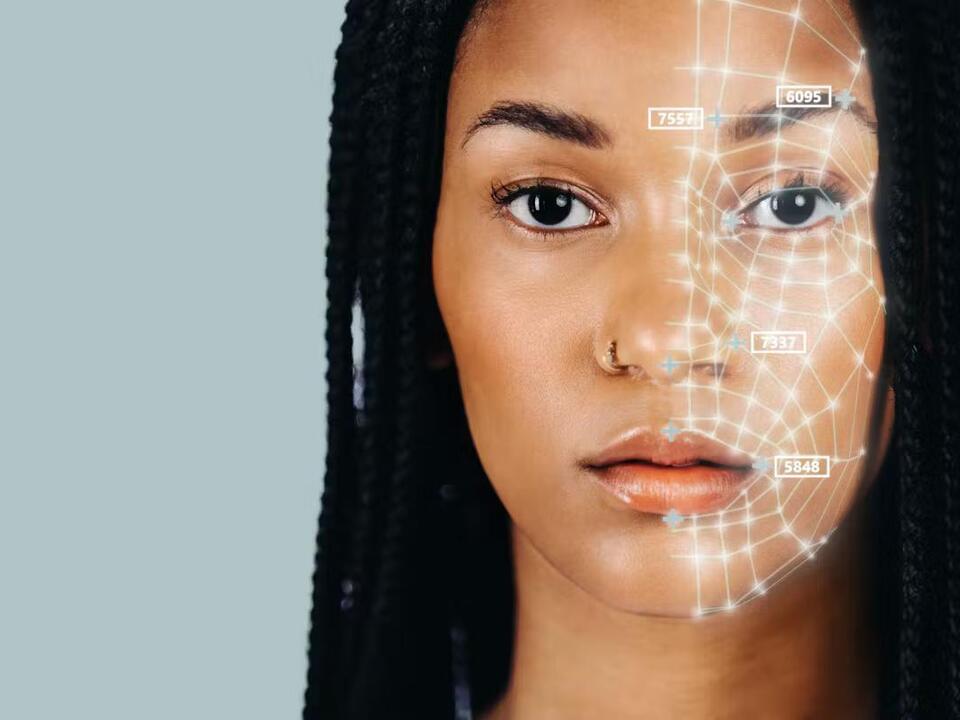
I found this on NewsBreak: Deepfake detection improves when using algorithms that are more aware of demographic diversity.
New research found a way to both improve the accuracy of deepfake detection algorithms while also enhancing fairness.
I found this on NewsBreak: SETI Institute Claims They’ve Successfully Communicated With a Whale.
I found this on NewsBreak.
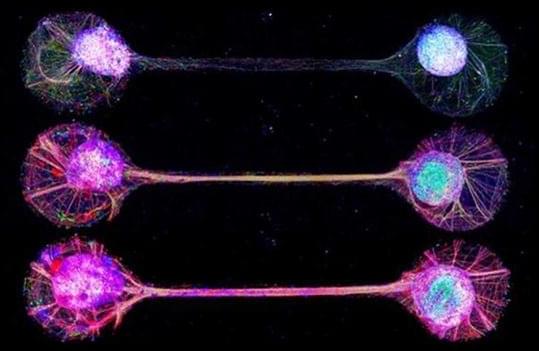
According to reports, Japanese scientists have devised a technique for connecting lab-grown brain-mimicking tissue„ like how circuits in our brain work.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo released a study in Nature Communications journal that looked into making a seemingly impossible idea a reality.
The scientists discovered a new approach to establishing physiological connections between lab-grown neuronal organoids. These organoids are experimental model tissues created by growing human stem cells into 3D-developed brain-like structures.
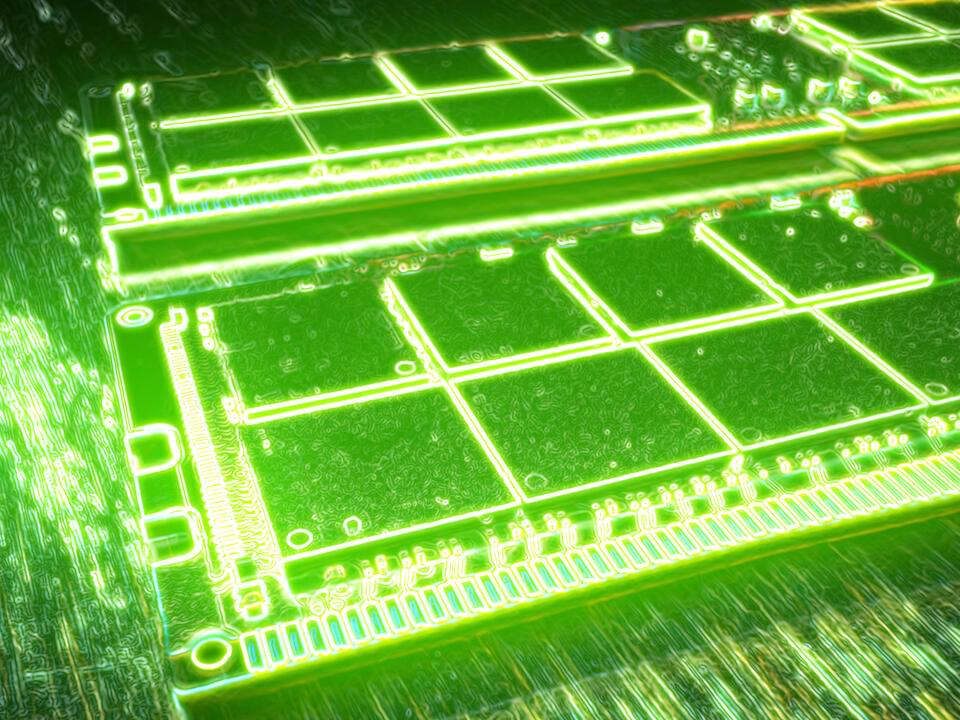
I found this on NewsBreak: Ultrafast laser-powered ‘magnetic RAM’ is on the horizon after new discovery.
Researchers have found an elemental physical interaction between light and magnetism that might lead to the next generation of computing memory.