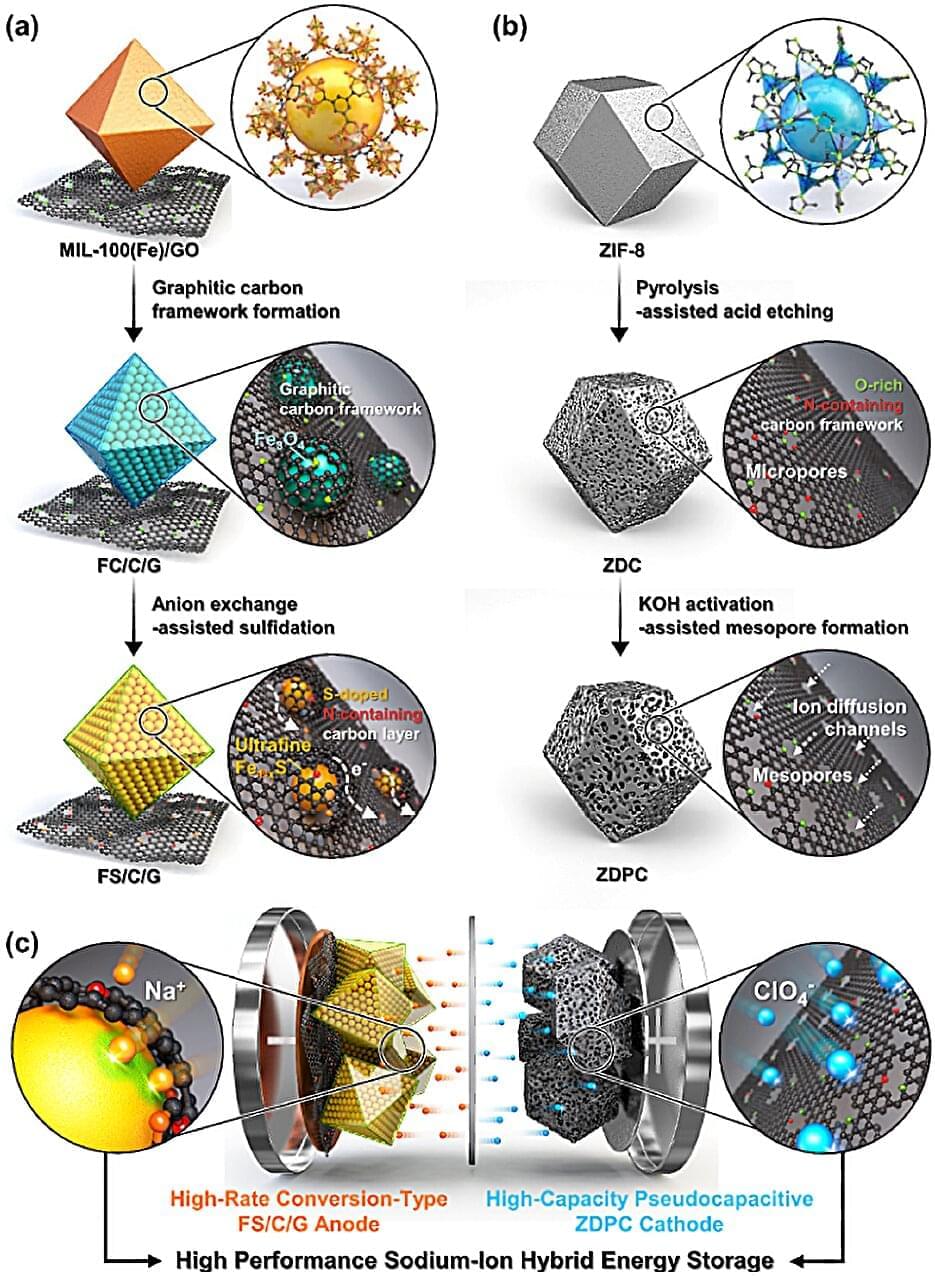
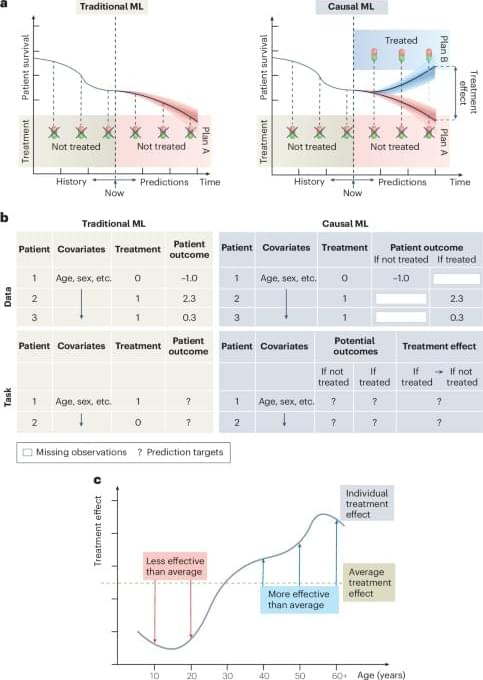
A new technique can be used to predict the actions of human or AI agents who behave suboptimally while working toward unknown goals.
MIT and other researchers developed a framework that models irrational or suboptimal behavior of a human or AI agent, based on their computational constraints. Their technique can help predict an agent’s future actions, for instance, in chess matches.
To build AI systems that can collaborate effectively with humans, it helps to have a good model of human behavior to start with. But humans tend to behave suboptimally when making decisions.