QUT researchers have identified a new material which could be used as a flexible semiconductor in wearable devices by using a technique that focuses on the manipulation of spaces between atoms in crystals.
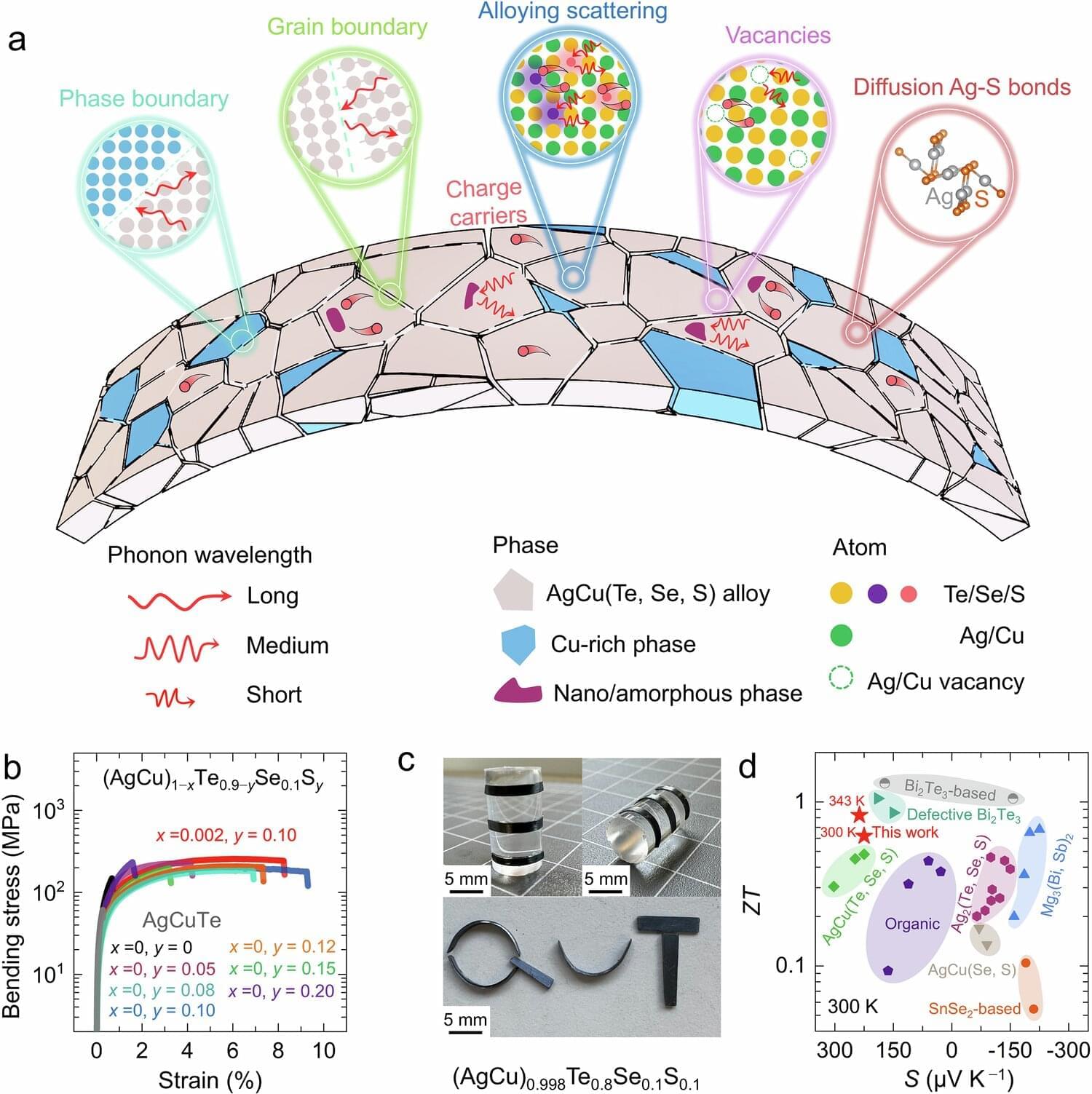
In a study published in Nature Communication, the researchers used “vacancy engineering” to enhance the ability of an AgCu(Te, Se, S) semiconductor, which is an alloy made up of silver, copper, tellurium, selenium and sulfur, to convert body heat into electricity.
Vacancy engineering is the study and manipulation of empty spaces, or “vacancies,” in a crystal where atoms are missing, to influence the material’s properties, such as improving its mechanical properties or optimizing its electrical conductivity, or thermal properties.