This engaging new post-apocalyptic show hails from Argentine director Bruno Stagnaro.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
The Kardashev Scale: Type 1 to Type 7 Civilizations
Make sure to watch this next video about Type 1 to Type 4 Civilizations: https://youtu.be/5fTNGvuPTMU.
💡 Future Business Tech explores AI, emerging technologies, and future technologies.
SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO
This video explores the Kardashev scale and the type 1 to type 7 civilizations. Related terms: ai, future business tech, future technology, future tech, future business technologies, future technologies, artificial intelligence, kardashev scale, type 7 civilization, type 6 civilization, type 5 civilization, type 4 civilization, type 3 civilization, type 2 civilization, type 1 civilization, etc.
ℹ️ Some links are affiliate links. They cost you nothing extra but help support the channel so I can create more videos like this.
#technology #ai


Massive data breach exposes 184 million passwords for Google, Microsoft, Facebook, and more
The problem? The file was unencrypted. No password protection. No security. Just a plain text file with millions of sensitive pieces of data.
Based on his analysis, Fowler determined the data was captured by some kind of infostealer malware. A popular tool used by cybercriminals, an infostealer is designed to grab usernames, passwords, and other sensitive data from breached sites and servers. Once the criminals get their hands on the data, they can use it to launch their own attacks or peddle the information on the dark web.
After finding the database, Fowler contacted the hosting provider, which removed it from public access. Since the provider would not disclose the name of the file’s owner, Fowler said he didn’t know if the database was created legitimately and then accidentally exposed or intentionally used for malicious reasons.

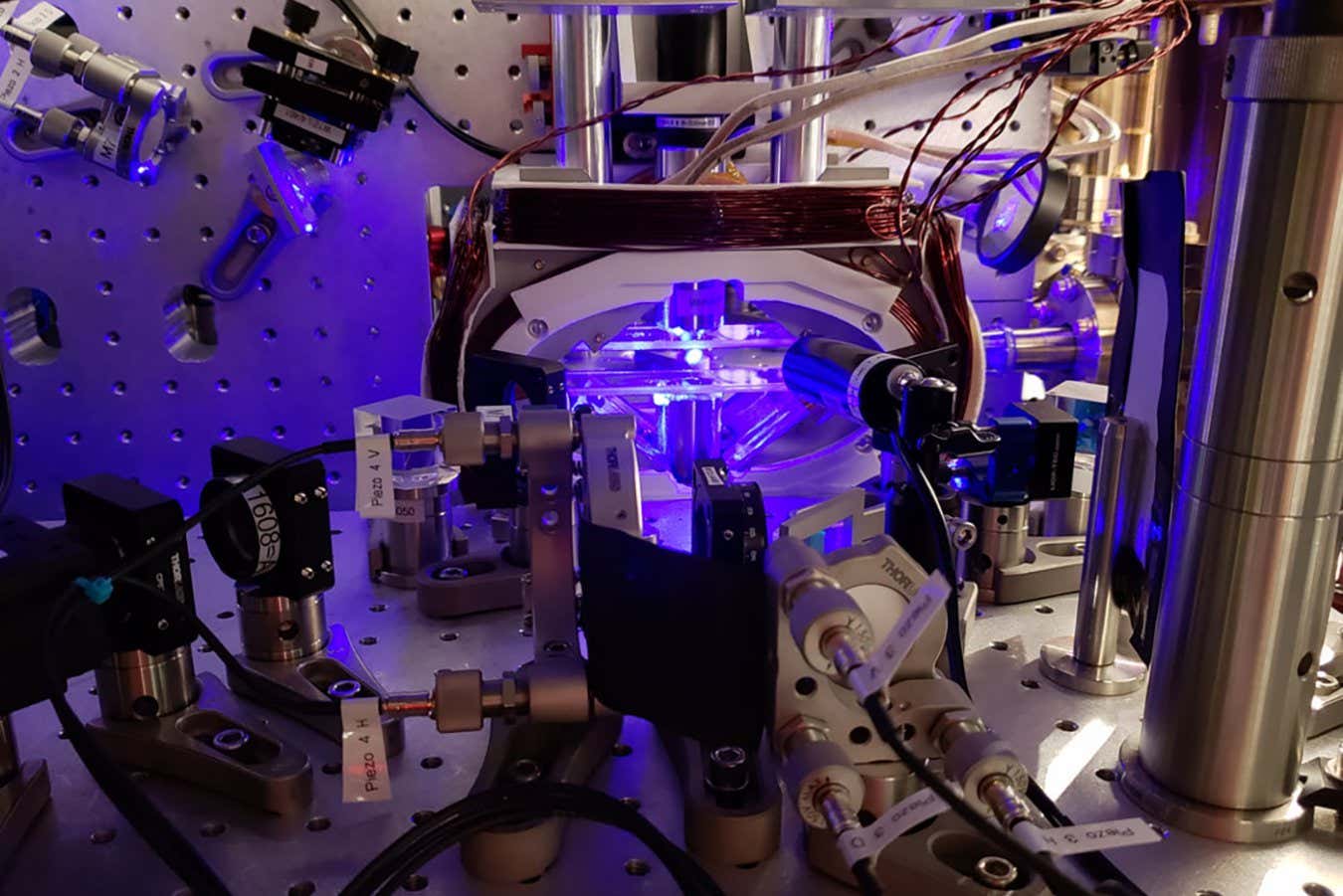


Machine learning method generates circuit synthesis for quantum computing
Researchers from the University of Innsbruck have unveiled a novel method to prepare quantum operations on a given quantum computer, using a machine learning generative model to find the appropriate sequence of quantum gates to execute a quantum operation.
The study, recently published in Nature Machine Intelligence, marks a significant step forward in realizing the full extent of quantum computing.
Generative models like diffusion models are one of the most important recent developments in machine learning (ML), with models such as Stable Diffusion and DALL·E revolutionizing the field of image generation. These models are able to produce high quality images based on text description.
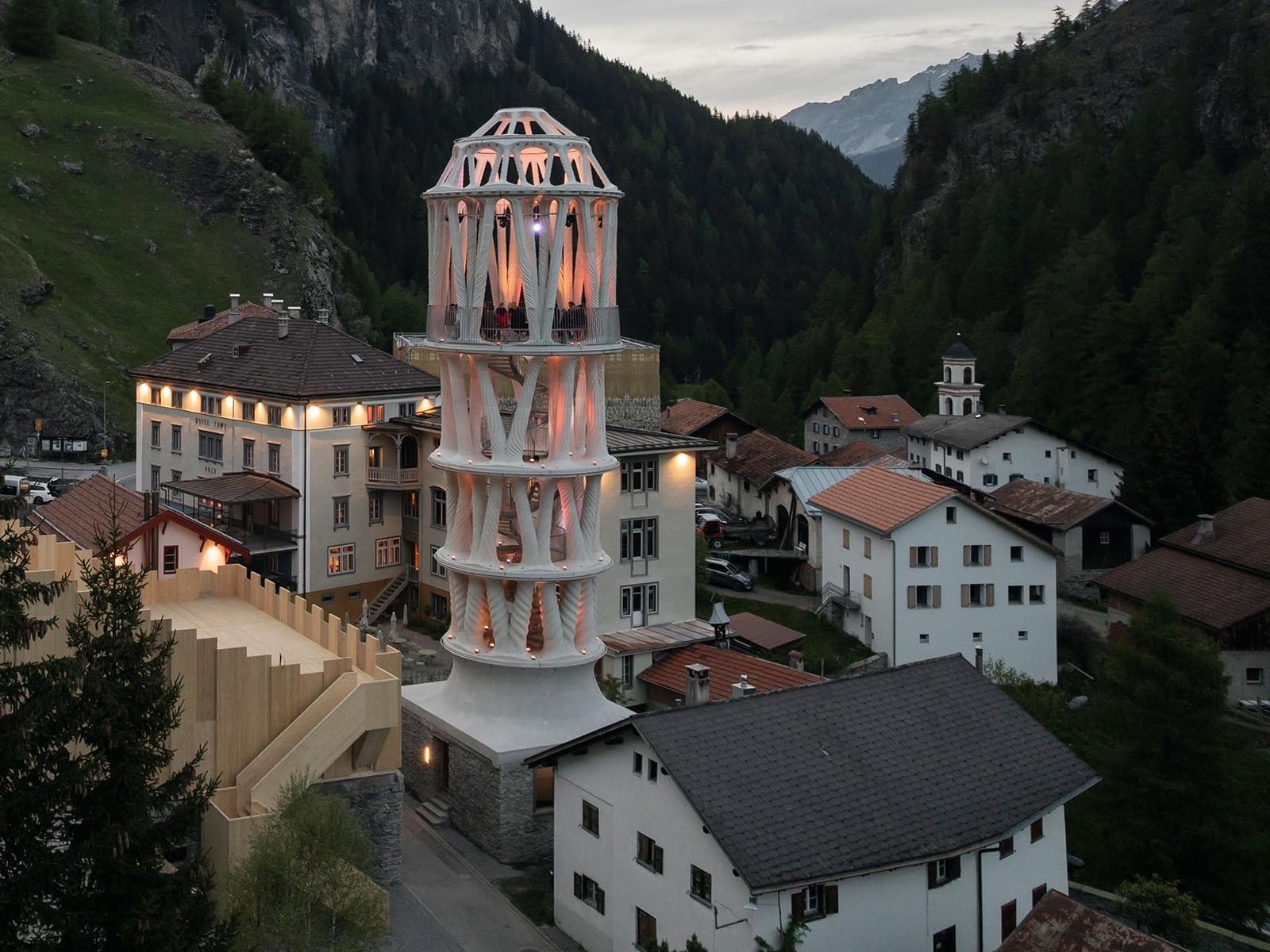

World’s tallest 3D-printed building reaches a height of 100 feet
Likened by its creators to an “ornate layered cake,” the Tor Alva has been completed in Switzerland. Hailed as the world’s tallest 3D-printed building, this remarkable structure rises to an impressive height of 30 m (98.5 ft).
Tor Alva (aka White Tower) is located in the small alpine village of Mulegns that’s currently home to just 11 people. It was created by researchers at ETH Zurich, in collaboration with cultural foundation Fundaziun Origen, to show off the capabilities of cutting-edge 3D-printing techniques.
Architect Michael Hansmeyer and ETH Professor of Digital Building Technologies Benjamin Dillenburger designed its actual form, which consists of an intricate structure of 32 white concrete columns that rise over four floors and taper before fanning out to top out with a dome. The interior, meanwhile, has a capacity for 32 visitors and includes stairs on each floor, with a performance space at the top.