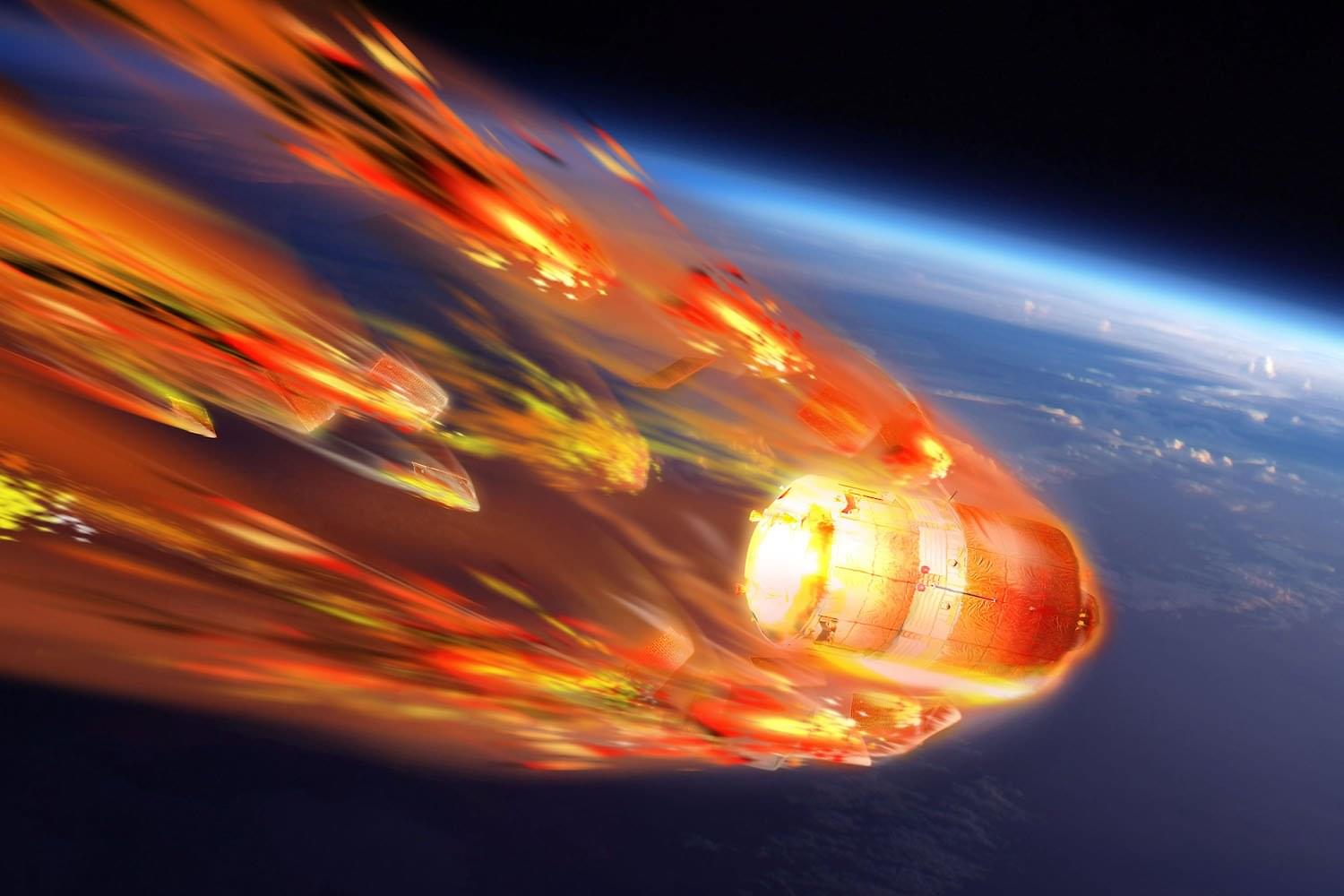
The spacecraft suffered an engine anomaly that left it stuck in Earth’s orbit for decades, and now it’s slated for an uncontrolled reentry.


Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3W5FWUN5w2Q
Thank you for listening ❤ Check out our sponsors: https://lexfridman.com/sponsors/cv8729-sb.
See below for guest bio, links, and to give feedback, submit questions, contact Lex, etc.
*GUEST BIO:*
Jeffrey Wasserstrom is a historian of modern China.
*CONTACT LEX:*
*Feedback* — give feedback to Lex: https://lexfridman.com/survey.
*AMA* — submit questions, videos or call-in: https://lexfridman.com/ama.
*Hiring* — join our team: https://lexfridman.com/hiring.
*Other* — other ways to get in touch: https://lexfridman.com/contact.
*EPISODE LINKS:*
Jeffrey Wasserstrom’s Books:
China in the 21st Century: https://amzn.to/3GnayXT
Vigil: Hong Kong on the Brink: https://amzn.to/4jmxWmT
Oxford History of Modern China: https://amzn.to/3RAJ9nI
The Milk Tea Alliance: https://amzn.to/42DLapH
*SPONSORS:*
To support this podcast, check out our sponsors & get discounts:
*Oracle:* Cloud infrastructure.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/oracle-cv8729-sb.
*Tax Network USA:* Full-service tax firm.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/tax_network_usa-cv8729-sb.
*Shopify:* Sell stuff online.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/shopify-cv8729-sb.
*LMNT:* Zero-sugar electrolyte drink mix.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/lmnt-cv8729-sb.
*AG1:* All-in-one daily nutrition drink.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/ag1-cv8729-sb.
*PODCAST LINKS:*
Future drops, freebies & digital gifts – Don’t miss out! Join here:
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSdeuqNNvEjhpL_PQrF4…usp=dialog.
Ray Kurzweil, one of the world’s leading futurists, has made hundreds of predictions about technology’s future. From portable devices and wireless internet to brain-computer interfaces and nanobots in our bloodstream, Kurzweil has envisioned a future that sometimes feels like science fiction—but much of it is becoming reality.
In this video, we explore 7 of Ray Kurzweil’s boldest predictions:
00:00 — 01:44 Intro.
01:44 — 02:42 Prediction 1: Portable Devices and Wireless Internet.
02:42 — 03:34 Prediction 2: Self-Driving Cars by Early 2020s.

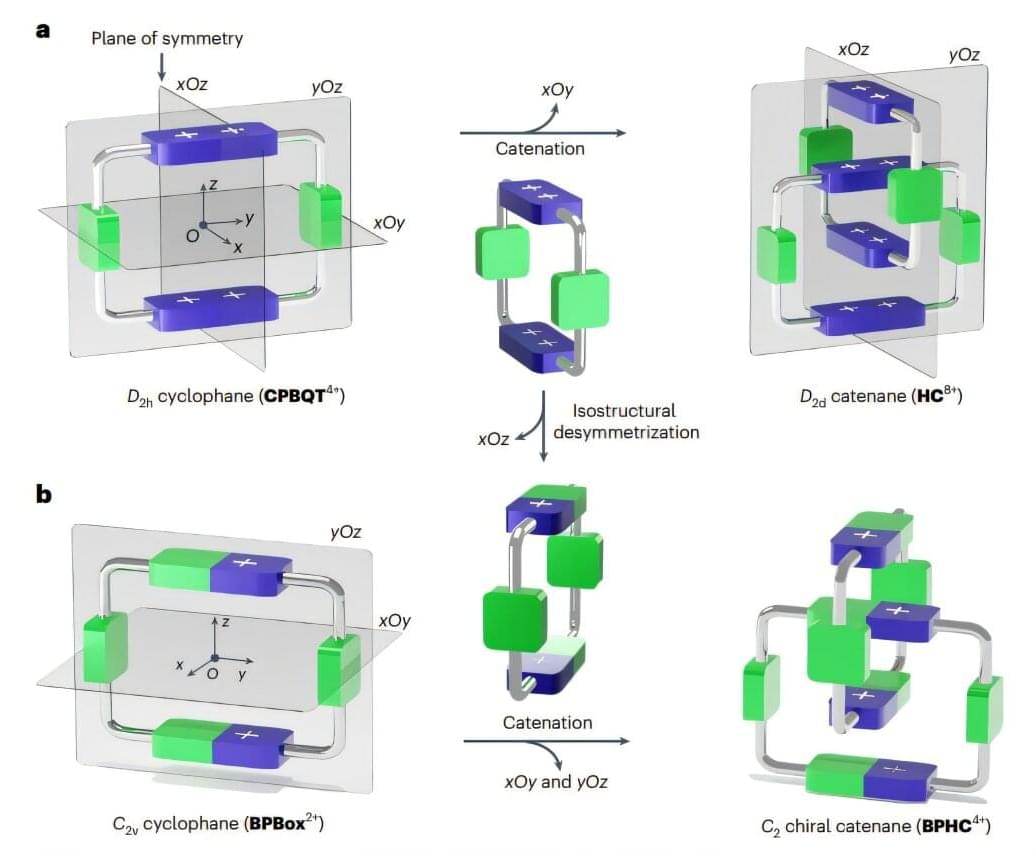
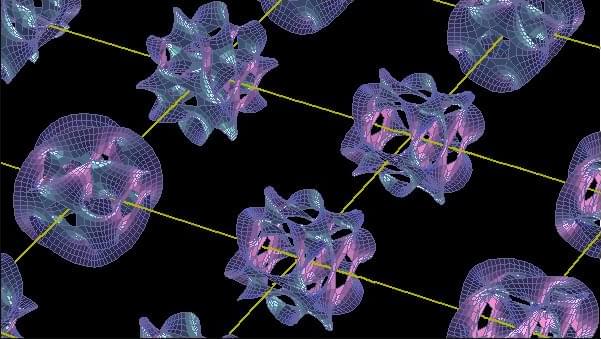
Catenanes are organic compounds with ring-like molecules that are mechanically interlocked. The mechanical locking system in such molecules is so robust that they can only be disentangled via covalent bond cleavage. A recent study has presented a new strategy for controlling the chirality—the property where a molecule has non-superimposable mirror images—of mechanically interlocked molecules (MIMs) like catenanes, without changing its overall shape via non-covalent means.
The researchers successfully demonstrated the synthesis of a compact catenane, BPHC4+ with tunable mechanical chirality, as reported in Nature Synthesis.
Unlike traditional chirality that originates from covalent bonds forming asymmetric centers, in MIMs the chirality can arise from the way parts of the molecule are mechanically linked and not the chirality of the individual rings that are interlocked together. This is known as mechanical chirality.
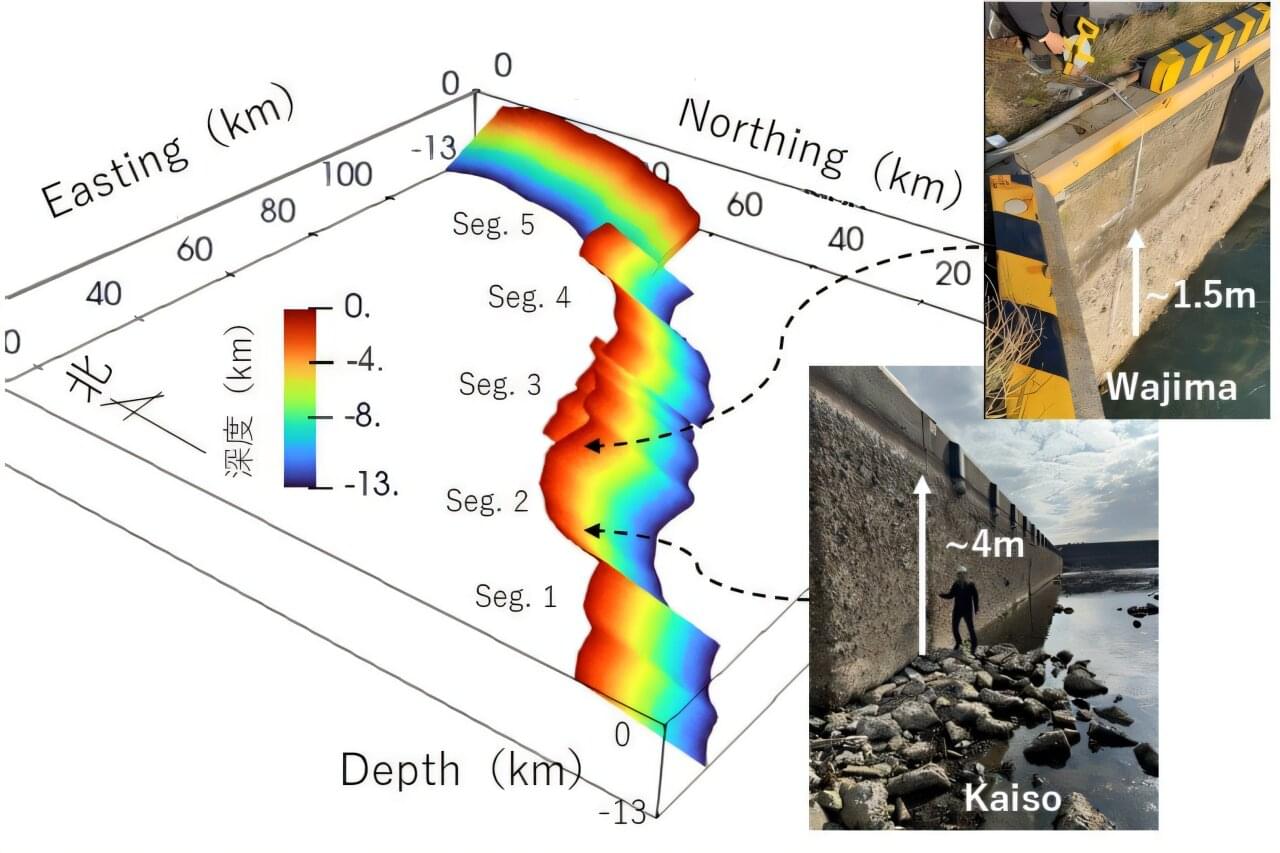
On New Year’s Day 2024, a massive 7.5-magnitude earthquake struck the Noto Peninsula in north central Japan, resulting in extensive damage in the region caused by uplift, when the land rises due to shifting tectonic plates. The observed uplift, however, varied significantly, with some areas experiencing as much as a 5-meter rise in the ground surface.
To better understand how the characteristics of the affected fault lines impact earthquake dynamics, researchers in Japan used recently developed simulations to make a detailed model of the fault. The findings could help develop models to simulate scenarios of different earthquakes and mitigate disasters in the future.
The results were published in the journal Earth, Planets and Space.
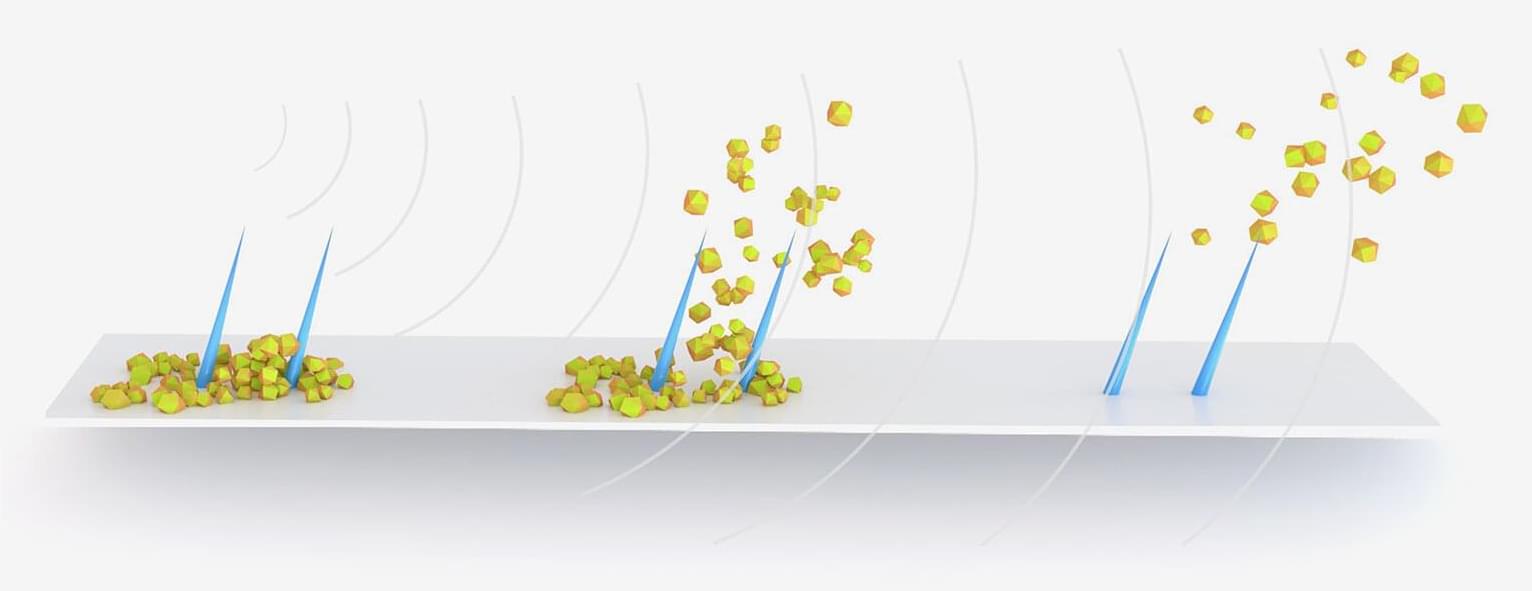
Urinary stents and catheters are implanted medical tubes that are widely used in human and veterinary medicine to drain urine to/from the bladder. Ureteral stents are used when the ureter, the duct between the kidney and bladder, is blocked by tumors, pregnancy, stones or anatomical narrowing.
Biofilm, produced by bacteria, and crystalline deposits, called encrustation, grow on the inner and outer walls of such stents and catheters soon after implantation and are among the main causes of failure of these devices because they lead to painful blockages and urinary infections.
To mitigate these issues, urinary stents and catheters therefore must be replaced every two to six months, which not only considerably restricts the quality of life of those affected but also leads to high hospital load and costs.
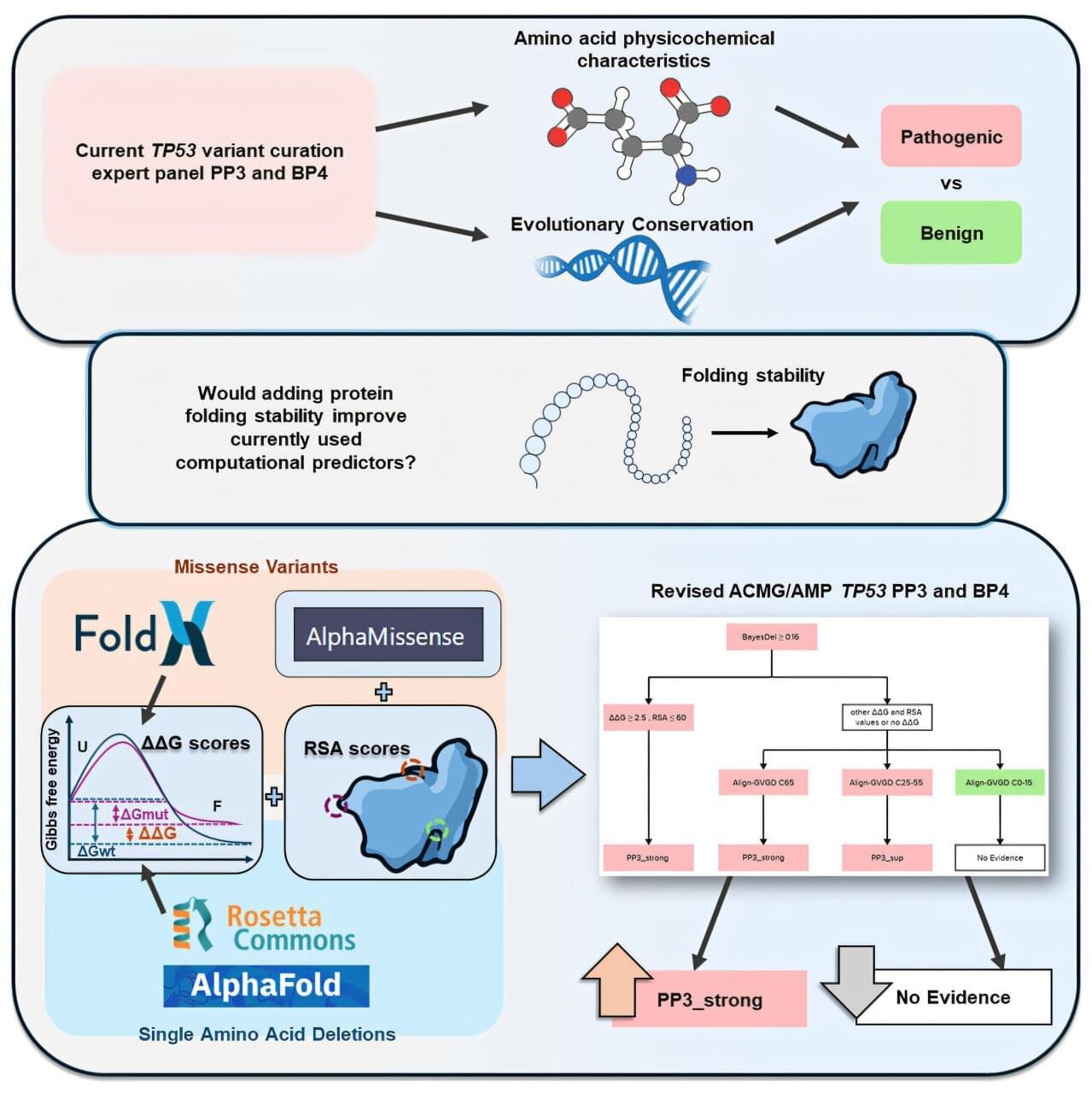
QIMR Berghofer-led research has shown that new advanced computational prediction tools can improve the accuracy of genetic testing for families affected by an inherited condition that significantly increases their risk of developing cancer, paving the way to better targeted care.
The findings have been published in the American Journal of Human Genetics alongside complementary studies by international collaborators, which together show how incorporating the new computational biology tools with existing modeling methods improved the predictive power of genetic test results.
Computational tools are used to predict if and how a genetic variant is likely to impact the function of the protein encoded by the gene.
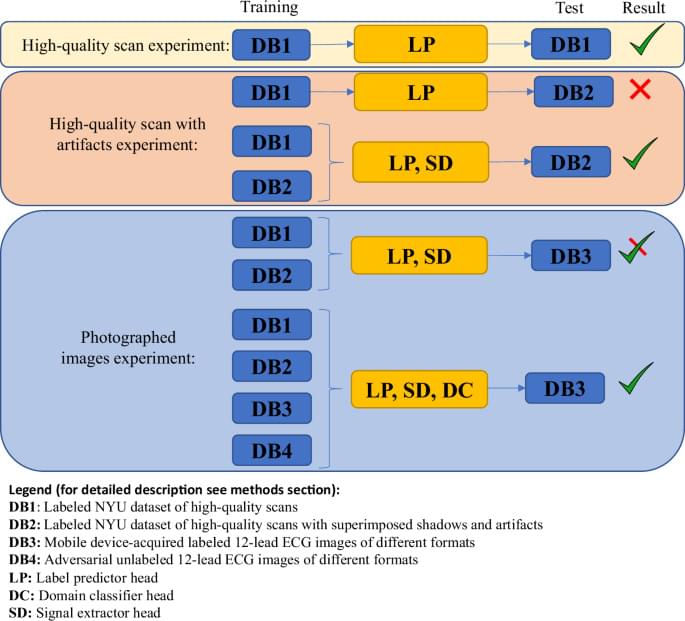
Gliner, V., Levy, I., Tsutsui, K. et al. Clinically meaningful interpretability of an AI model for ECG classification. npj Digit. Med. 8, 109 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-01467-8