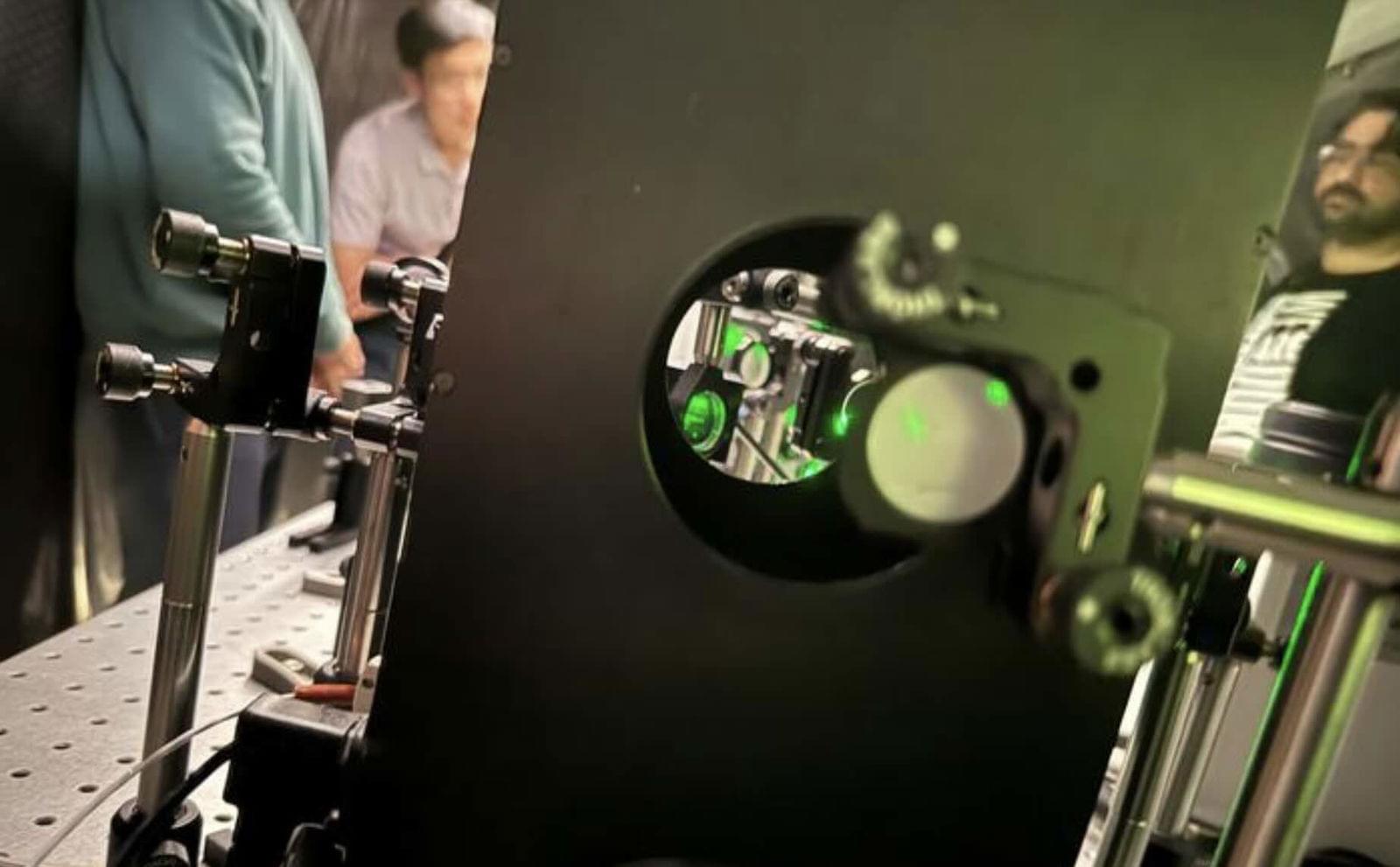
Engineers at Duke University have successfully manipulated laser beams to create intricate 3D patterns known as ‘optical knots.’


After confirming the potential historic observation, the results were evaluated for several possible errors. The work was also analyzed independently. Each time, the team came back to the conclusion that they may have found the first potential signs of life outside our solar system.
“It was an incredible realisation seeing the results emerge and remain consistent throughout the extensive independent analyses and robustness tests,” said co-author Måns Holmberg, a researcher at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore.
Notably, the concentrations of either DMS or DMDS spotted by JWST were thousands of times higher than concentrations found on Earth. According to the Cambridge astronomers, detecting high levels of either of these chemicals on Hycean (ocean) worlds due to large amounts of biological activity was previously predicted.
Consumer electronic devices are made from materials that we have been using for more than 60 years, mainly silicon, germanium and copper. Why have semiconductor electronics become increasingly fast over this time?
I would argue that this is due to miniaturization, or the ability to stack an increasingly large number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (microchip). Some may argue that we are starting to reach limits in that miniaturization, as thin films approach a thickness of just about 10 nanometers, or even lower.
These nearly two-dimensional (2D) materials could be used to build the next-generation electronics. However, as electronic materials like silicon are miniaturized, they become less energy efficient.
A car accident, football game, or even a bad fall can lead to a serious or fatal head injury. Annually, traumatic brain injuries (TBI) cause half a million permanent disabilities and 50,000 deaths. Monitoring pressure inside the skull is key to treating TBI and preventing long-lasting complications.
Most of these monitoring devices are large and invasive, requiring surgical emplacement. But Georgia Tech researchers have recently created a sensor smaller than a dime. The miniature size offers huge benefits.
“Surgery means extensive recovery time and can significantly impact patient health. Our system doesn’t require surgery because we use a conventional stent, the catheter, as a delivery vehicle,” said W. Hong Yeo, the Harris Saunders Jr. Endowed Professor and an associate professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering.
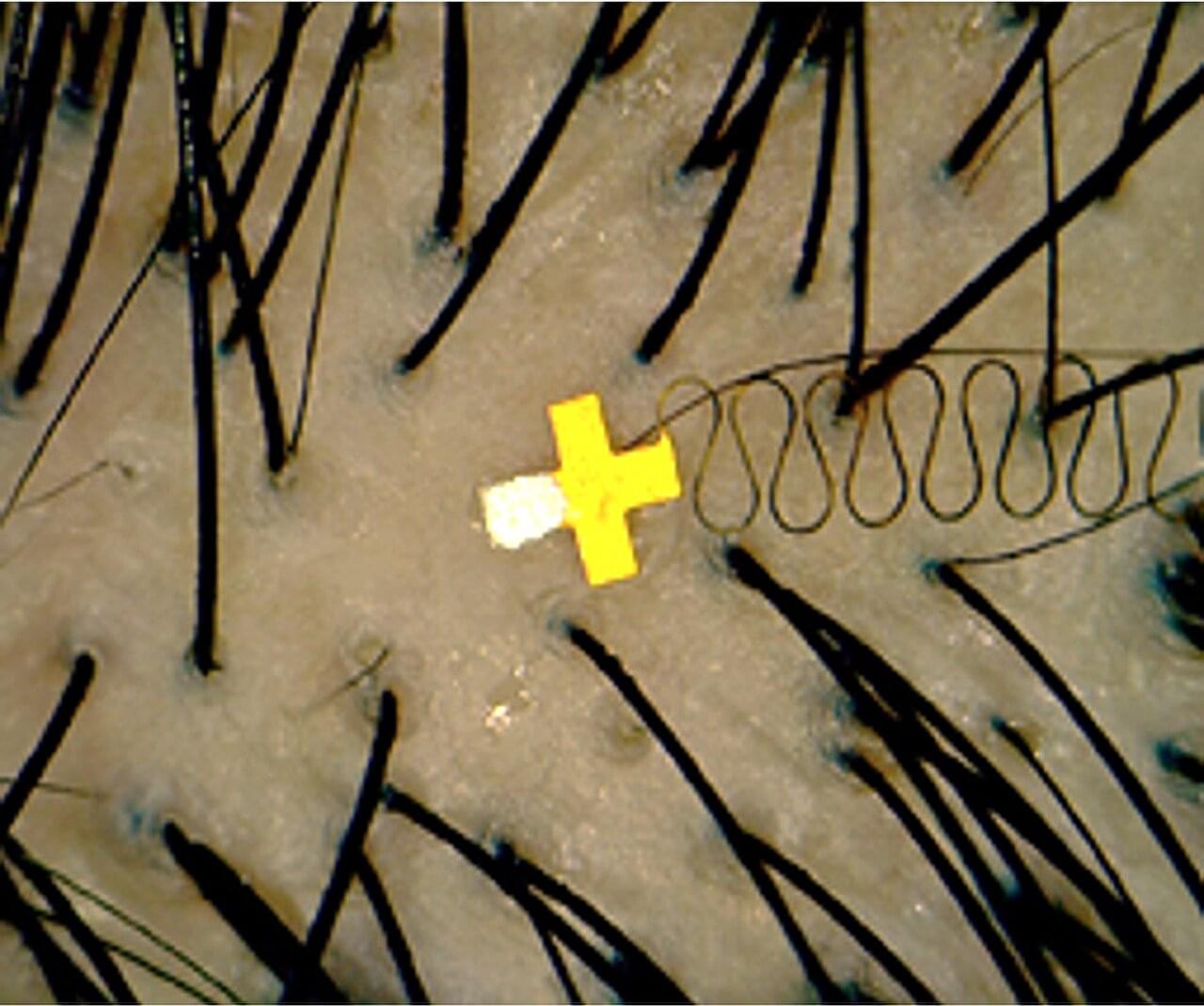

Georgia Tech researchers have developed an almost imperceptible microstructure brain sensor to be inserted into the minuscule spaces between hair follicles and slightly under the skin. The sensor offers high-fidelity signals and makes the continuous use of brain-computer interfaces (BCI) in everyday life possible.
BCIs create a direct communication pathway between the brain’s electrical activity and external devices such as electroencephalography devices, computers, robotic limbs, and other brain monitoring devices. Brain signals are commonly captured non-invasively with electrodes mounted on the surface of the human scalp using conductive electrode gel for optimum impedance and data quality. More invasive signal capture methods such as brain implants are possible, but this research seeks to create sensors that are both easily placed and reliably manufactured.
Hong Yeo, the Harris Saunders Jr. Professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering, combined the latest microneedle technology with his deep expertise in wearable sensor technology that may allow stable brain signal detection over long periods and easy insertion of a new painless, wearable microneedle BCI wireless sensor that fits between hair follicles. The skin placement and extremely small size of this new wireless brain interface could offer a variety of benefits over traditional gel or dry electrodes.
Developing humanoid robots, unravelling the complexities of AI, and the mysteries of consciousness.
Welcome to the North of Patient podcast — conversations on health[beyond]care — where we paint an inspired landscape of healthcare’s future through dialogues with creative and unconventional thinkers from around the world.
For a summary of the episode, visit the blog post on North of Patient:
https://open.substack.com/pub/northofpatient/p/episode-13-dr…Share=true.
This week’s guest is the remarkable Dr. Suzanne Gildert. She’s a physicist, artist, and AI tech executive based in Vancouver on a mission to uncover the mysteries of consciousness and innovate unconscious AI.
In this episode, we dive into the groundbreaking advancements and pressing challenges in quantum computing, examining the transformative potential of these technologies to reshape our world. Beyond the science, we also explore the philosophical dimensions of AI consciousness, questioning whether AI can ever truly replicate human experience and identity.
Learn more about Nirvanic AI:

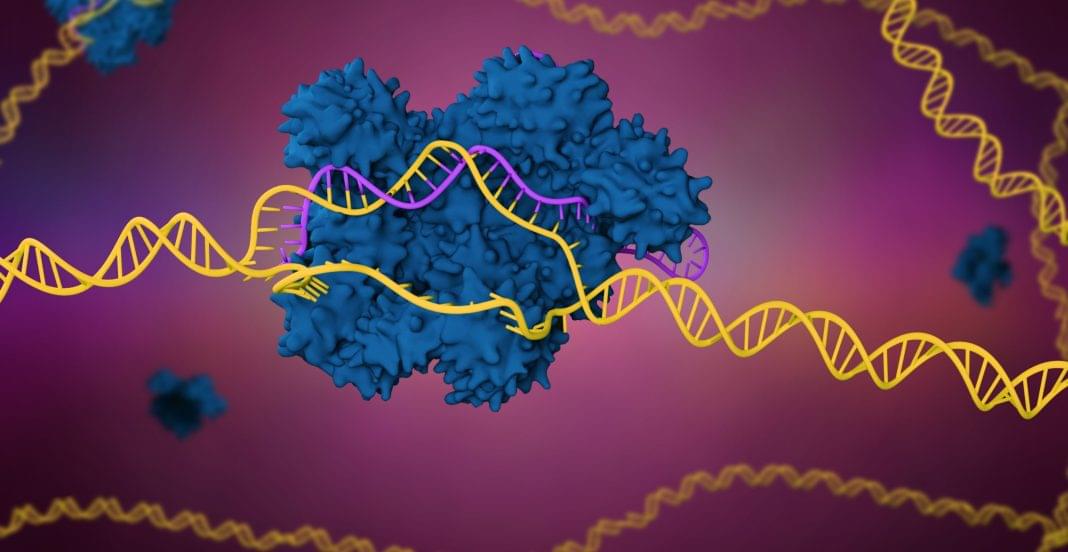
Scientists from Mass General Brigham and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center have developed a novel gene editing tool called STITCHR. Unlike traditional CRISPR, STITCHR inserts entire genes at precise locations, minimizing unintended mutations. This gene editing tool simplifies use and offers potential as a one-time treatment for genetic disorders.
The technology uses retrotransposons, naturally occurring “jumping genes” found in all eukaryotic organisms, which can move and integrate into genomes. Using computational screening, the researchers identified and reprogrammed a specific retrotransposon to work with the nickase enzyme from CRISPR, forming the complete STITCHR system that allows a precise, seamless gene insertion into the genome.
STITCHR offers the potential to replace or supplement entire genes, creating a more universal treatment option for various genetic diseases. The research team is now working to improve its efficiency and move it toward clinical use. Their study, published in Nature, highlights how insights from basic cellular biology can drive innovation in genetic medicine and lead to new therapeutic tools.
Our brain’s ability to absorb fresh information — whether that means mastering a new task at work, memorizing the refrain of a song, or navigating unfamiliar streets — depends on a remarkable talent for neural self‑reinvention.
Every time we practice something novel, millions of tiny contacts between nerve cells subtly adjust their strength and neurons use multiple mechanisms to store knowledge.
Some connections, called synapses, amplify their signals to stamp in crucial details; others turn down the volume to clear away noise. Collectively these shifts are known as synaptic plasticity and for decades neuroscientists have cataloged dozens of molecular pathways that can nudge a synapse up or down.
Whar may happen when the first truly smart robots appear, based on brain emulations or ems. Scan a human brain, then run a model with the same connections on a fast computer, and you have a robot brain, but recognizably human.
Train them to do some job and copy it a million times: an army of workers is at your disposal. When they can be made cheaply.
within perhaps a century, they will displace humans in most jobs.
In this new economic era, the world economy may double in size every few weeks.
Applying decades of expertise in physics, computer science, and economics.
and use ofstandard theories indicate a detailed picture of a world dominated by ems.
Associate Professor of Economics, and received his Ph.D in 1997 in social sciences from Caltech. Joined George Mason’s economics faculty in 1999 after completing a two year post-doc at U.C Berkely. His major fields of interest include health policy, regulation, and formal political theory. Recent book: The Age of Em: Work, Love and Life When Robots Rule The Earth. Oxford University Press, 2016.
This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.
While CRISPR-mediated gene editing has led to powerful advances across biology, medicine, and agriculture, challenges persist in optimizing the editing efficiency of enzymes, such as the widely used Cas9 nuclease. This is especially true in therapeutic use cases, where the goal is to attain high rates of editing via a relatively low and transient enzyme dose.
In a new study published in the April 2025 issue of The CRISPR Journal titled, “Hairpin Internal Nuclear Localization Signals in CRISPR-Cas9 Enhance Editing in Primary Human Lymphocytes,” researchers from the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) at the University of California (UC), Berkeley, present a strategy to improve editing efficiency in human immune cells for therapeutic applications by leveraging new constructs for nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequences.
“Efficient CRISPR enzyme production is essential for translation. This is one element that allowed the rapid clinical evaluation of Casgevy, the world’s first genome editing drug. Unfortunately, this aspect tends to be overlooked in the basic research performed in academia,” said Ross Wilson, PhD, assistant adjunct professor of molecular and cell biology at UC Berkeley, who led the new study.