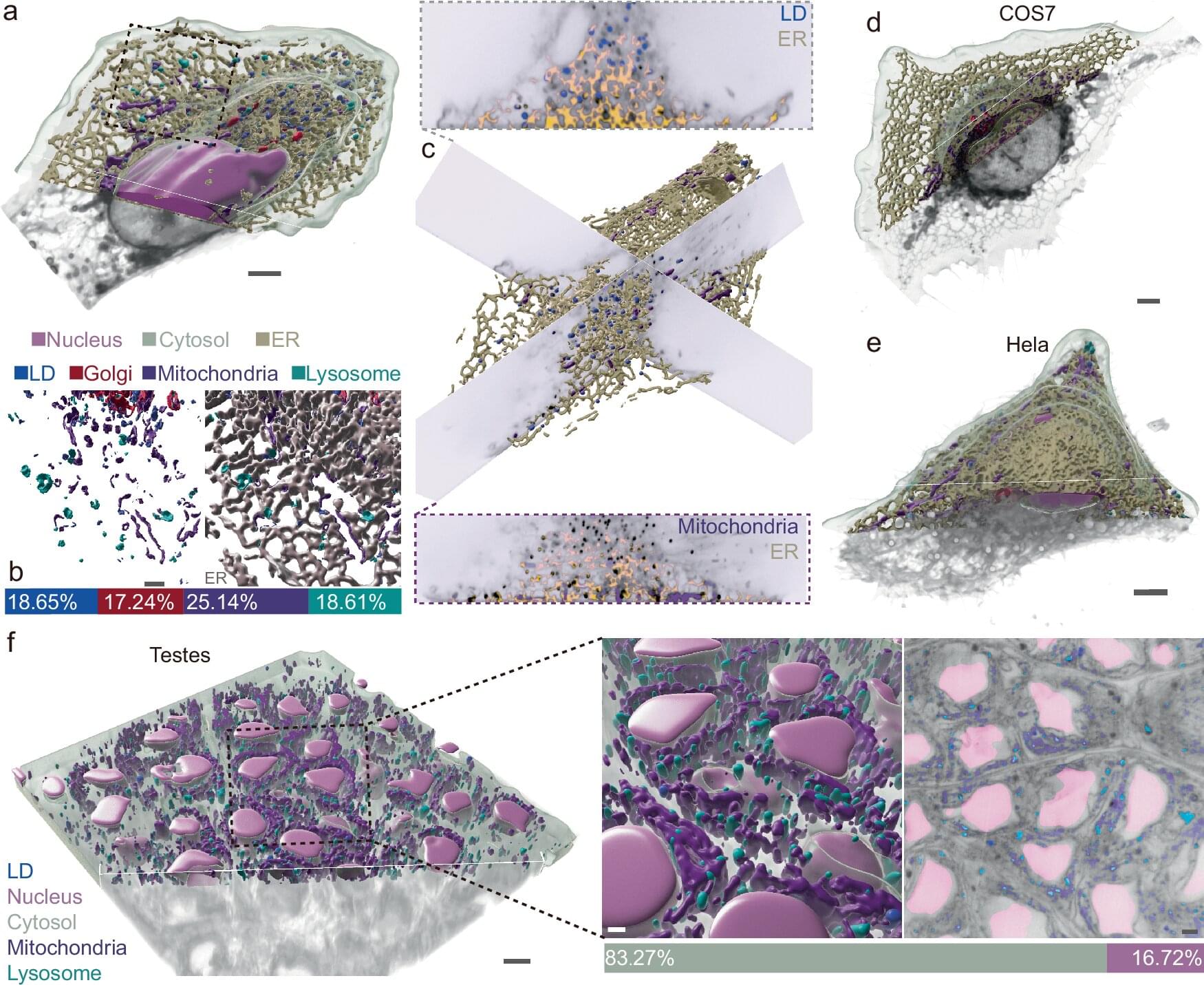
A breakthrough in imaging technology promises to transform our understanding of the inner workings of living cells, and provide insights into a wide range of diseases.
The study, recently published in the journal Nature Communications, unveils an innovative approach that combines super-resolution imaging with artificial intelligence and deep learning to reveal subcellular structures and dynamics. It was led by researchers from Peking University, Ningbo Eastern Institute of Technology and the University of Technology Sydney.
“It’s like taking an airplane over a city at night and watching all the live interactions,” said UTS Distinguished Professor Dayong Jin. “This cutting-edge technology will open new doors in the quest to understand the intricate world within our cells.”