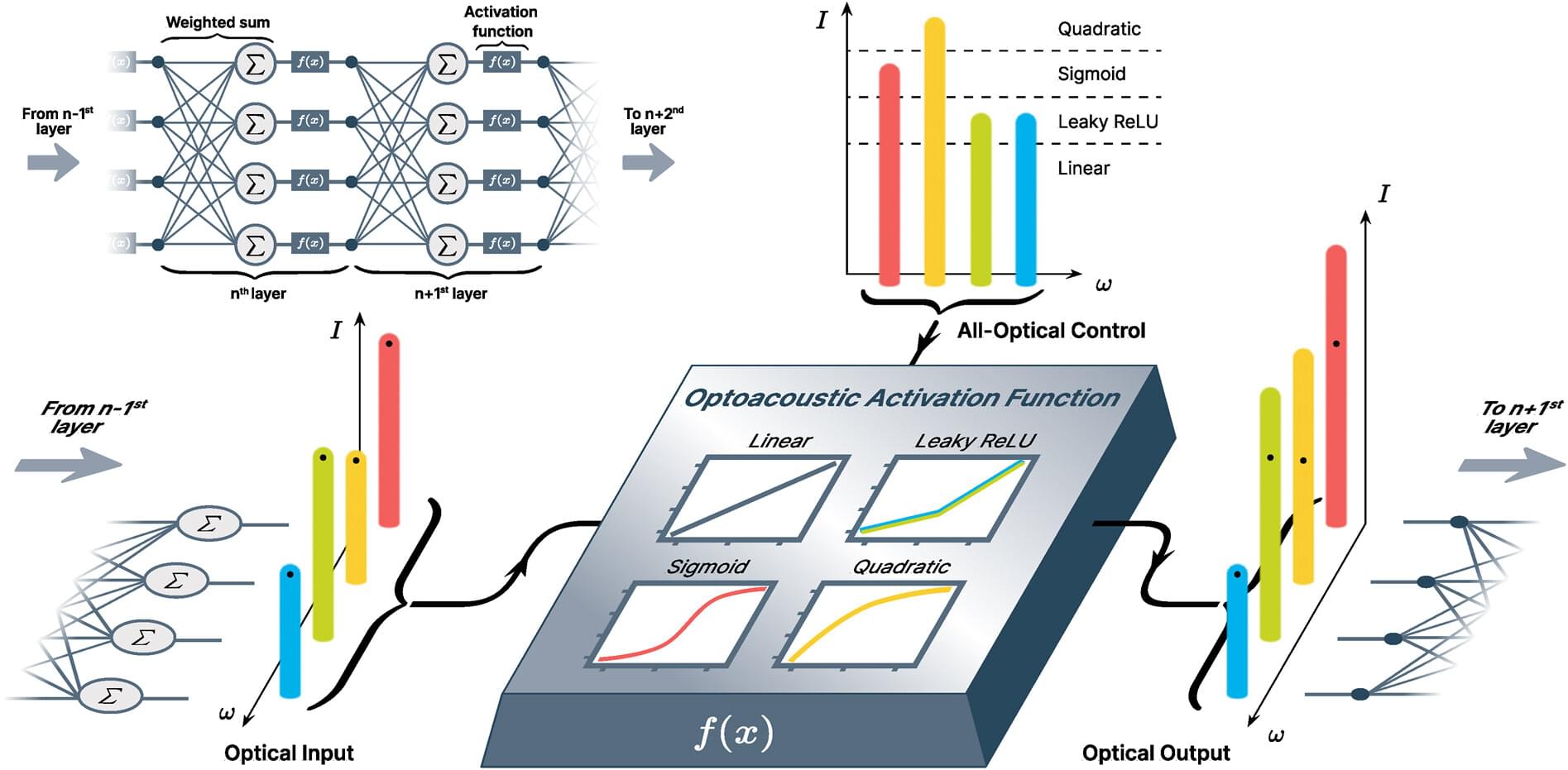
Neural networks are one typical structure on which artificial intelligence can be based. The term “neural” describes their learning ability, which to some extent mimics the functioning of neurons in our brains. To be able to work, several key ingredients are required: one of them is an activation function which introduces nonlinearity into the structure.
A photonic activation function has important advantages for the implementation of optical neural networks based on light propagation. Researchers in the Stiller Research Group at the MPL and LUH in collaboration with MIT have now experimentally shown an all-optically controlled activation function based on traveling sound waves.
It is suitable for a wide range of optical neural network approaches and allows operation in the so-called synthetic frequency dimension. The work is published in the journal Nanophotonics.