Some go gently into the night. Others die in freak accidents or deadly invasions, or after a showy display.


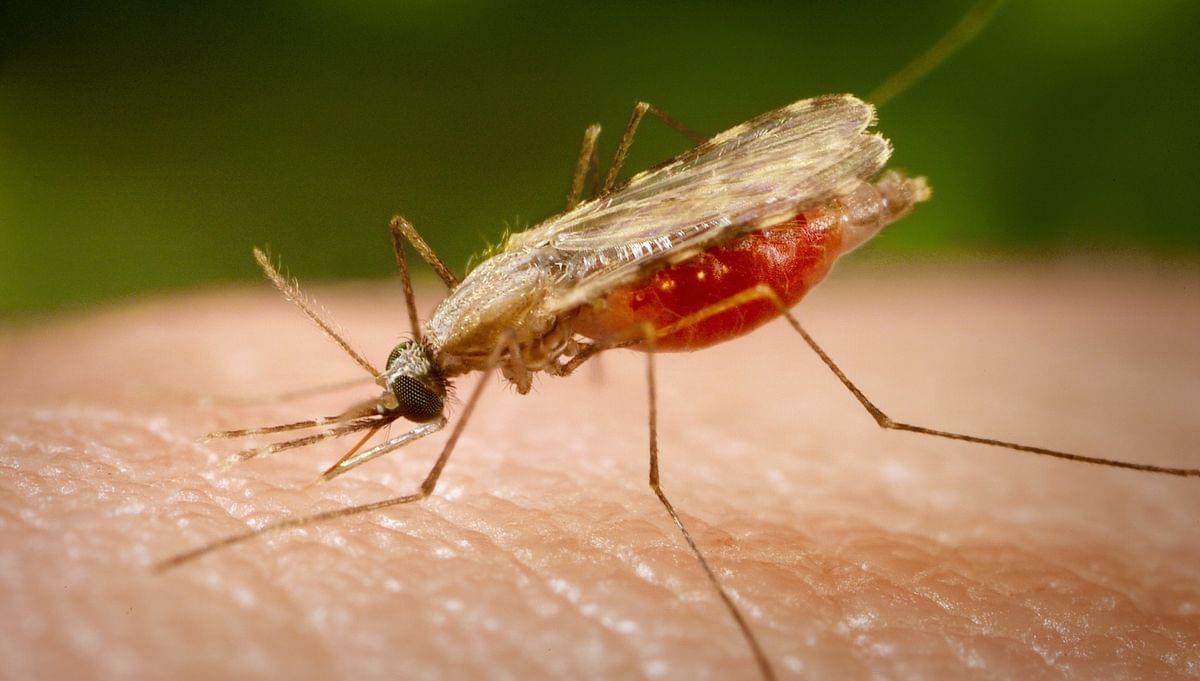
A single dose of nitisinone (approximately 0.1 milligram per kilogram of body weight) could make someone’s blood deadly to mosquitoes for around five days, they found. However, no mosquito mortality was observed for “any single dose of ivermectin,” the team reported.
In a separate analysis, the researchers fed mosquitoes blood samples from three patients with alkaptonuria who regularly took 2 mg of nitisinone a day. All of the mosquitoes died within 12 hours of feeding. Blood from a patient with alkaptonuria who had not started the treatment was not toxic to mosquitoes.
Taken together, these findings suggest that nitisinone therapy could be a promising new malaria-control method. However, the researchers cautioned that there are still many hurdles to overcome before the drug could be used for this purpose.
When we gaze out into the cosmos beyond the borders of the Milky Way, we behold multitudes. Space is teeming with galaxies, speckled across the darkness like stars. If we stopped there, it would be easy to assume that the distribution of galaxies is more or less even throughout space-time.
But there’s some method to the madness: rather than wheeling freely about, galaxies tend to concentrate into clusters and clumps and filaments of the cosmic web, attracted by mutual gravity into matter highways, superhighways and nodes.
The inverse of that is voids – regions of significantly lower density, with relatively few galaxies.
In a jaw-dropping announcement that has sent shockwaves through the automotive and tech industries, Elon Musk has revealed that Tesla’s next-generation vehicles will feature an innovative new capability: the ability to chat with drivers. This game-changing feature will allow Tesla cars to interact with their owners through natural language, responding to commands, engaging in conversation, and even providing real-time assistance to drivers on the road. Musk’s revelation marks another leap forward in Tesla’s mission to redefine the future of transportation and push the boundaries of what cars can do.
The announcement comes on the heels of Tesla’s ongoing efforts to integrate artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced technology into its vehicles, further blurring the lines between traditional cars and cutting-edge, self-driving machines. With this new feature, Tesla is set to revolutionize the driving experience by introducing a level of interactivity and intelligence that has never been seen in a vehicle before. 
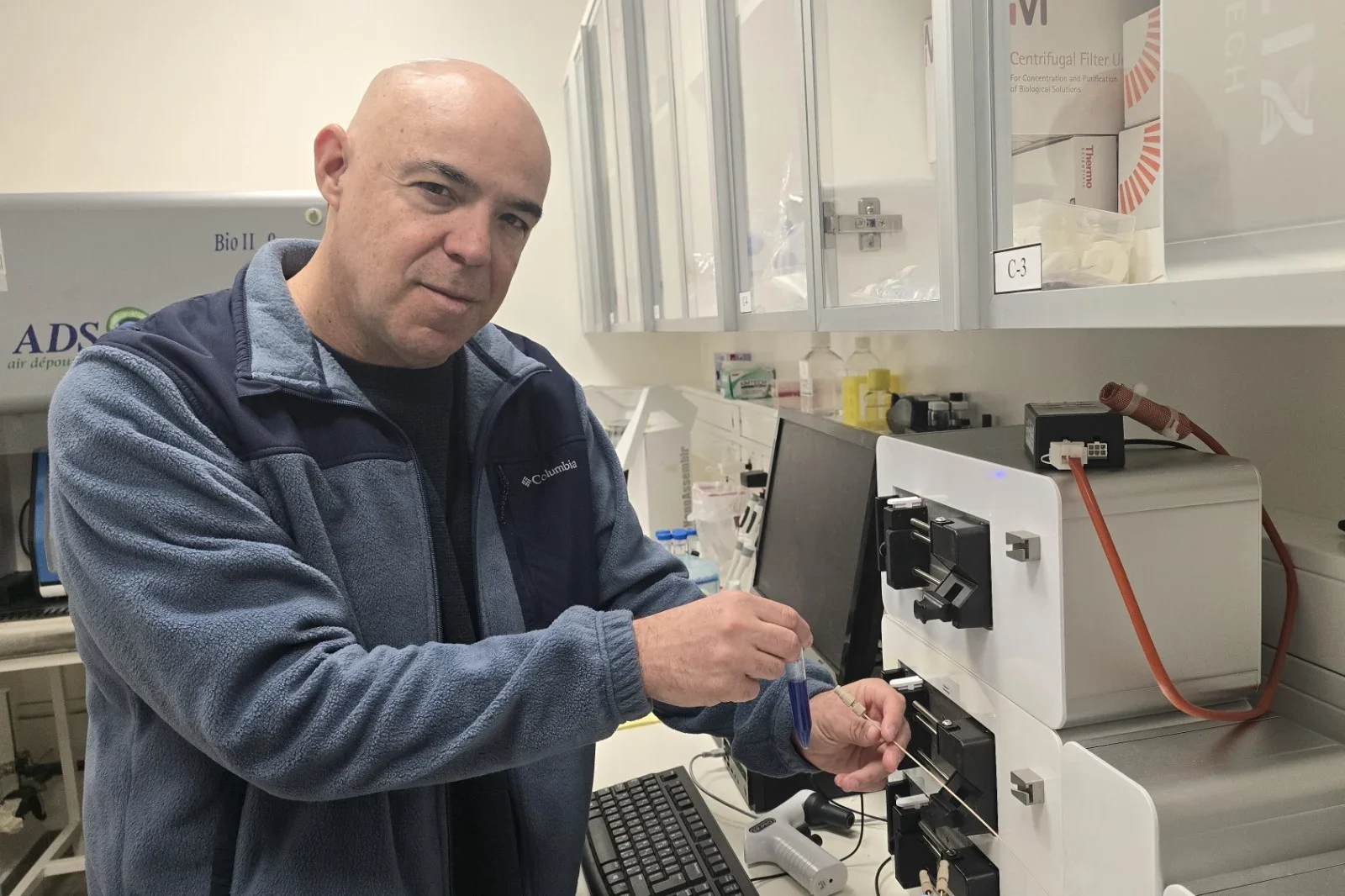

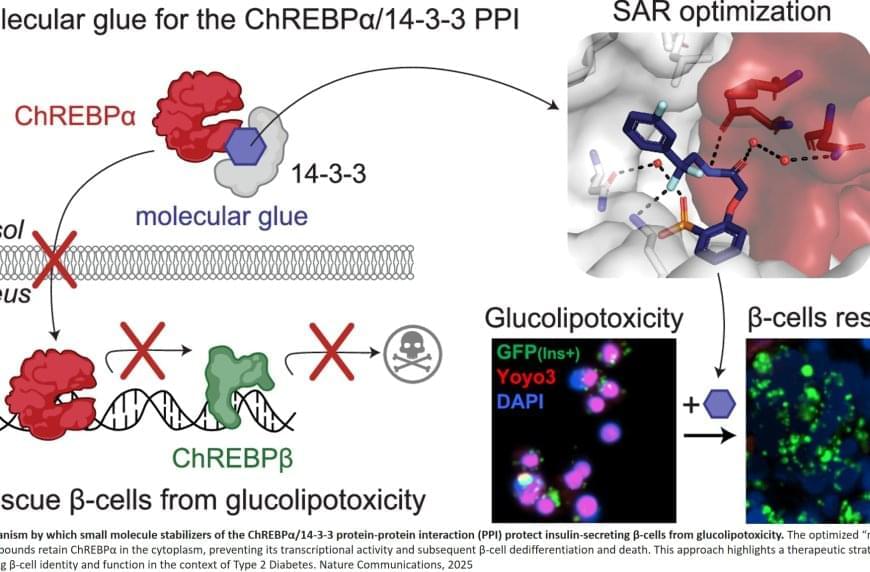
ChREBP is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in regulating glucose metabolism. It exists in two main isoforms: ChREBPα and ChREBPβ. This is the first study to identify and develop small molecules—termed “molecular glues”—that enhance the interaction between ChREBPα and 14−3−3 proteins in pancreatic beta cells.
The molecular glues in this case increase the binding between 14−3−3 proteins and ChREBPα, which is anchored in the cytoplasm of the beta cell by the 14−3−3 proteins. Under conditions of glucolipotoxicity, ChREBPα goes into the nucleus and starts making too much of ChREBPβ, which acts to disable and even kill the patient’s beta cells. By using a molecular glue designed to increase the binding of ChREBPα to 14−3−3 proteins, ChREBPα never leaves the cytoplasm, cannot enter the nucleus, and therefore does not make ChREBPβ
When tested in primary human beta cells, these molecular glues significantly reduced the toxic effects of glucolipotoxicity, thus preserving beta cell function and identity. This discovery represents a major shift in diabetes research, as transcription factors like ChREBP have long been considered “undruggable” targets. The study also highlights the broader potential of molecular glues for modulating similar interactions in other diseases.
The researchers have discovered a novel approach to protecting insulin-producing beta cells from the damaging effects of glucolipotoxicity—a harmful condition linked to the progression of type 2 diabetes (T2D). These findings, published in Nature Communications, could lead to promising treatments targeting beta cell dysfunction.
For patients, this research could lead to new treatments that protect the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, potentially slowing or even preventing the progression of diabetes, thus reducing the need for insulin therapy and improving long-term blood sugar control. Unlike current therapies that primarily manage blood sugar levels, this approach would allow doctors to directly target beta cell loss, which could improve long-term disease outcomes for their patients.
“This is an exciting step forward in our understanding of beta cell protection and the prevention of diabetes deterioration,” said the lead author. “For the first time, we’ve shown that it’s possible to use small molecules to fine-tune carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP) activity in a way that could have major therapeutic implications.”
