Exotic properties suggested by recent DESI collaboration data are more likely to apply to dark energy than dark matter, argues Harvard astronomer Avi Loeb.
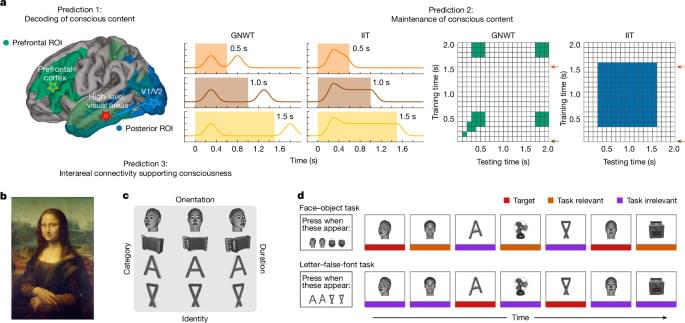
Multimodal results (iEEG, fMRI and MEG) of predictions from integrated information theory and global neuronal workspace theory align with some predictions of both theories on visual consciousness, but also critically challenge key tenets of both theories.
Everything related to the human brain and neuroscience has always been an area in which specialists have said that there is much to discover, learn and investigate. In fact, the generation of memory in human beings, memories, and the different diseases that are clustered around the CPU of the body have always been constantly evolving.
Now, Dr. Tomas Ryan of Trinity College Dublin, a neuroscientist who has explored the issues of brain learning by tracking the cells involved in this process, has found new findings suggesting that memory formation depends on the connections between groups of engram cells, neurons thought to capture and store distinct experiences.
In this new research, the experts indicate that each experience leaves a pattern of neuronal activation that can be activated later, which would mean the creation of a memory. To reach this conclusion, the neuroscientists tracked two sets of engram cells, each linked to a different memory.
Xiaomi Corp. unveiled its own open-source AI model, joining the growing ranks of Chinese tech leaders hoping to make a splash in a burgeoning field endorsed by Beijing.
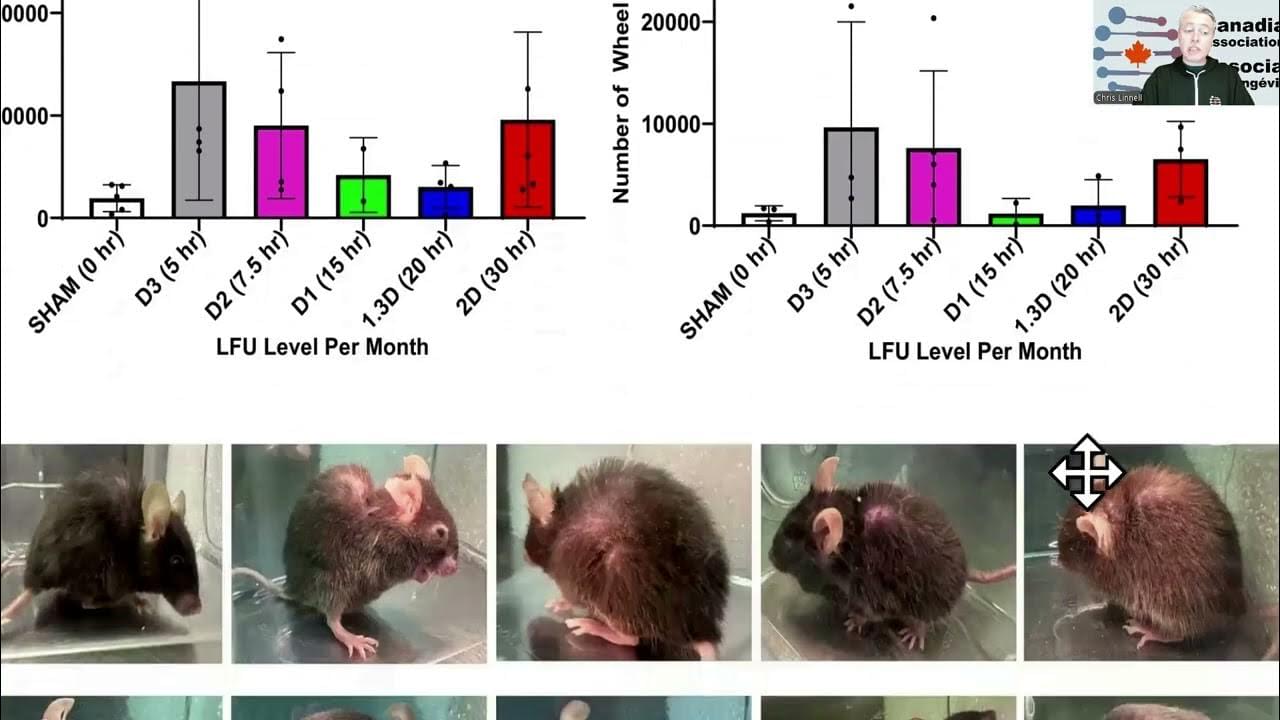
A review of the most interesting and impactful longevity related studies from March, with a look at how low frequency ultrasound can reverse cellular senesce…
An accurate diagnosis of ADHD is crucial in bringing clarity and the right support to people who need it, but current diagnosis methods are time-consuming and inconsistent. A new study suggests AI could help.
Researchers in South Korea trained machine learning models to connect characteristics in photos of the fundus at the back of the eye to a professional diagnosis of ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder).
Of four machine learning models tested in the study, the best achieved a 96.9 percent score for predicting ADHD accurately, based on image analysis alone.
A quantum computer can solve optimization problems faster than classical supercomputers, a process known as “quantum advantage” and demonstrated by a USC researcher in a paper recently published in Physical Review Letters.
The study shows how quantum annealing, a specialized form of quantum computing, outperforms the best current classical algorithms when searching for near-optimal solutions to complex problems.
“The way quantum annealing works is by finding low-energy states in quantum systems, which correspond to optimal or near-optimal solutions to the problems being solved,” said Daniel Lidar, corresponding author of the study and professor of electrical and computer engineering, chemistry, and physics and astronomy at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering and the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.
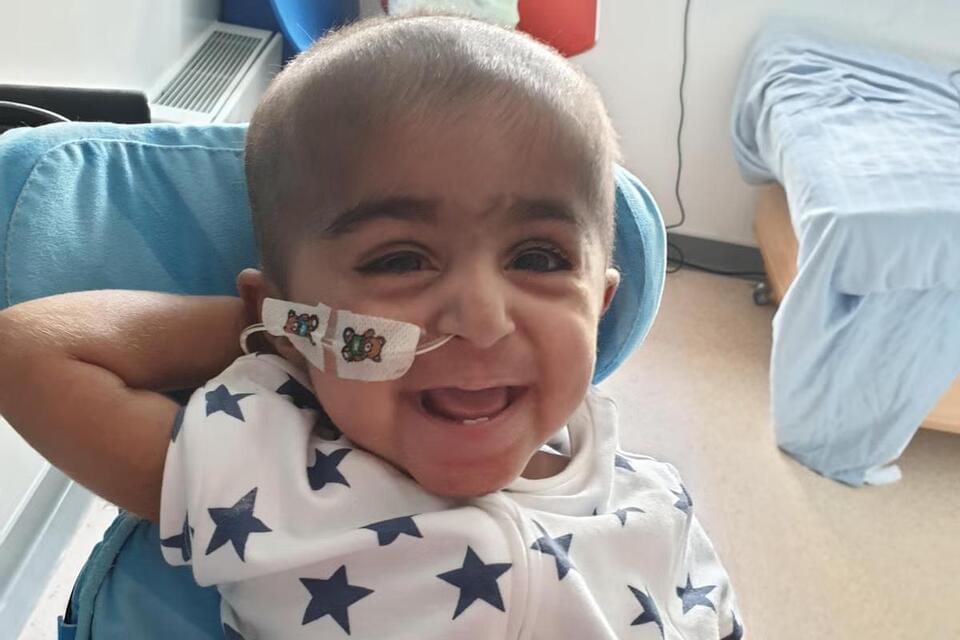
A four-year-old boy with a life-threatening immune disease is now living a normal life thanks to a pioneering gene therapy trial.
Eisa Hussain, who suffers from a severe form of leukocyte adhesion deficiency 1 (LAD-1), can now play football and attend school – milestones his family once thought impossible.
LAD-1 cripples the immune system, leaving children vulnerable to infections. Without treatment, the most severe cases are often fatal before the age of two.
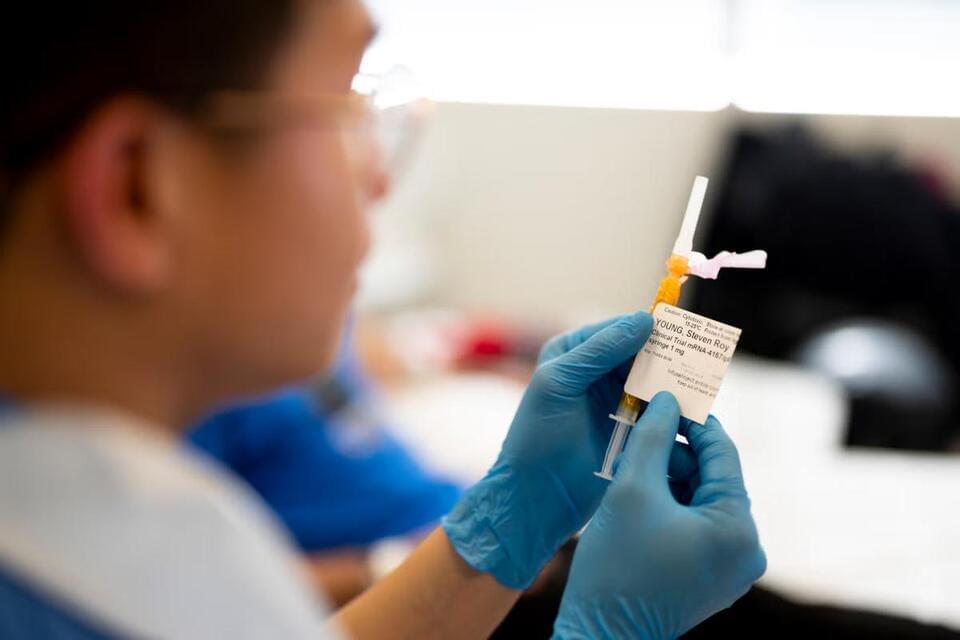
A new jab which allows cancer patients to be treated with just one injection is set to be rolled out by the NHS for 15 different types of the disease.
Patients will be able to receive the immunotherapy in a vaccine, called nivolumab, in a treatment that will take just 15 minutes rather than spending an hour on an IV drip.
Around 1,200 patients a month will receive it for 15 different types of cancer, including skin, bladder and oesophageal cancer as England becomes the first country in Europe to offer it.
Japanese scientists have created all-organic solar cells made of carbon-based materials with a record efficiency of 8.7% for this type of cell.
It is noted that the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth every day is 10 times higher than all the existing needs of humanity. Over the past 6 years, there has been a rapid development of cells for solar panels. However, there are still a number of challenges to their widespread use, including high production costs, efficiency, and environmental impact.
Silicon is currently the most widely used material in solar cells. However, such cells often also contain potentially hazardous materials that are difficult to dispose of in an environmentally friendly manner.