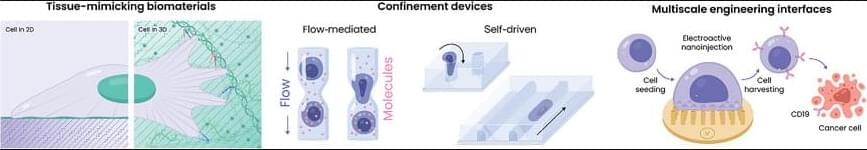
The rise of cell-based therapies, regenerative medicine, and synthetic biology, has created an urgent need for efficient cell engineering, which involves the manipulation of cells for specific purposes. This demand is driven by breakthroughs in cell manufacturing, from fundamental research to clinical therapies. These innovations have come with a deeper understanding of developmental biology, continued optimization of mechanobiological processes and platforms, and the deployment of advanced biotechnological approaches. Induced pluripotent stem cells and immunotherapies like chimeric antigen receptor T cells enable personalized, scalable treatments for regenerative medicine and diseases beyond oncology. But continued development of cell manufacturing and its concomitant clinical advances is hindered by limitations in the production, efficiency, safety, regulation, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of current manufacturing routes. Here, recent developments are examined in cell engineering, with particular emphasis on mechanical aspects, including biomaterial design, the use of mechanical confinement, and the application of micro-and nanotechnologies in the efficient production of enhanced cells. Emerging approaches are described along each of these avenues based on state-of-the-art fundamental mechanobiology. It is called on the field to consider mechanical cues, often overlooked in cell manufacturing, as key tools to augment or, at times, even to replace the use of traditional soluble factors.
Current manufacturing workflows for CAR-based immunotherapies, particularly CAR T, and the emerging CAR NK and CAR macrophage platforms, generally involve four key stages: (i) isolation of primary immune cells or their precursors, (ii) cell activation or differentiation, (iii) genetic modification with CAR constructs, most often via viral vectors or electroporation (EP), and (iv) expansion or preparation for reinfusion. Among these, transfection remains the most critical and technically challenging step, directly influencing the functionality, safety, and scalability of the final product.
In clinical-scale production, EP remains the most widely used non-viral method for gene delivery into immune cells, yet it is increasingly recognized as suboptimal, particularly when delivering large or complex CAR constructs. It suffers from inefficient nuclear delivery, high cell toxicity, and poor functional yields of viable, potent CAR-expressing cells.[ 113 ] These limitations are further exacerbated in more fragile or less permissive cell types, such as NK cells and macrophages, which show lower transfection efficiencies and greater sensitivity to electroporation-induced stress.[ 114 ] Viral vectors, while still dominant in clinical manufacturing, present their own challenges: they are constrained by limited cargo capacity, are costly to produce at scale, and raise regulatory and safety concerns, especially when applied to emerging CAR-NK and CAR macrophage therapies that require flexible, transient, or multiplexed genetic programs.[ 115 ]
In contrast to immune-cell engineering, stem cell-based approaches present a different set of challenges and engineering requirements. While immune cells are genetically modified to enhance cytotoxicity[ 116 ] and specificity or to mitigate excessive T-cell activation,[ 117 ] stem cells must be engineered to control self-renewal, lineage commitment, and functional integration, often requiring precise, non-integrative delivery of genetic or epigenetic modulators (e.g., mRNA, episomal vectors) to maintain cellular identity and safety.[ 118 ] Stem cells hold exceptional therapeutic promise due to their capacity for self-renewal and differentiation into specialized cell types, supporting applications in personalized disease modeling, tissue repair, and organ regeneration.[ 119 ] However, engineering stem cells in a safe, efficient, and clinically relevant manner remains a major challenge. Conventional delivery methods, such as viral vectors and EP, can compromise genomic integrity,[ 120 ] reduce viability,[ 118 ] and induce epigenetic instability,[ 121 ] limiting their translational potential.