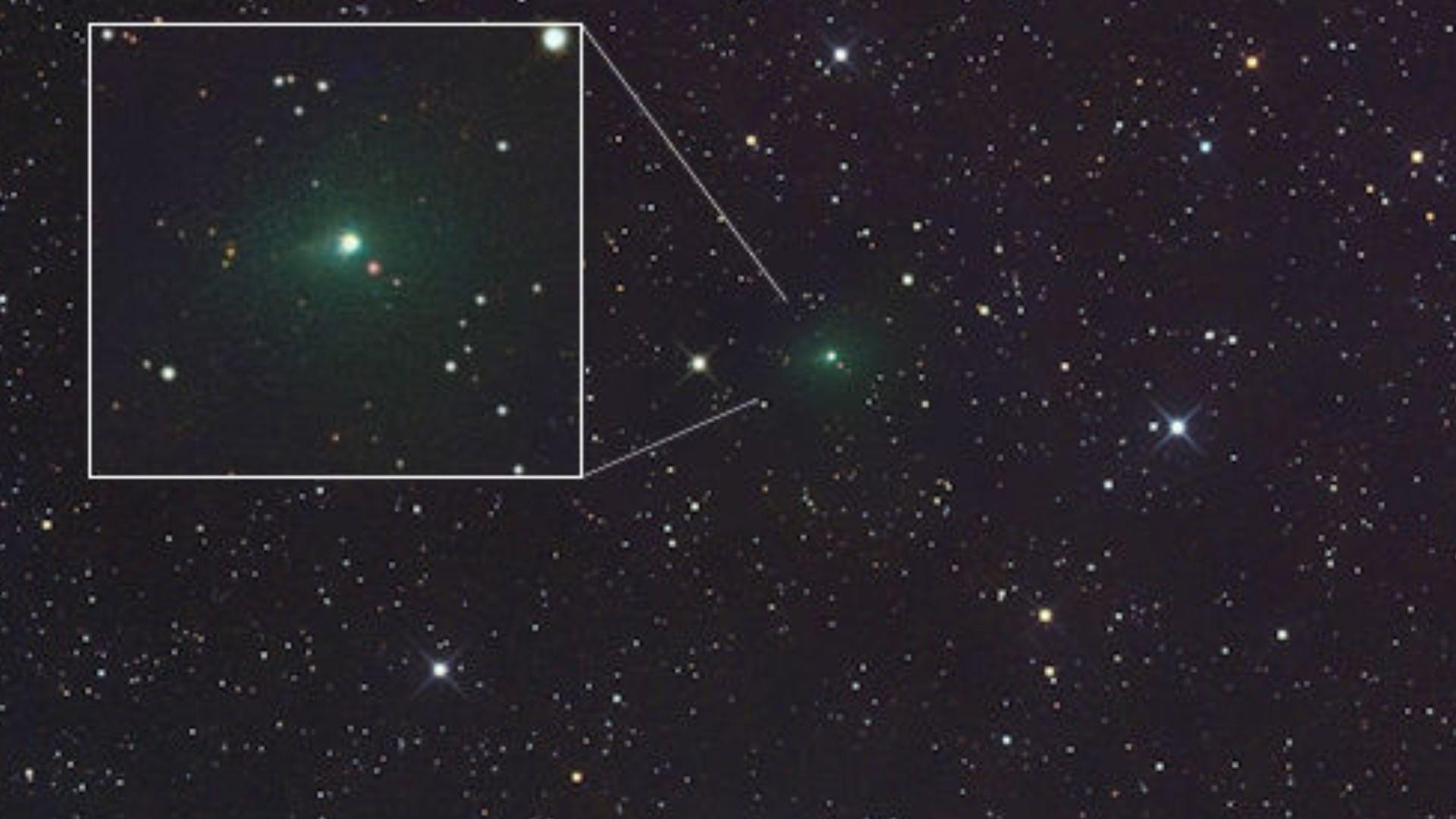
This unexpected color raises new questions about the alien chemistry of comets from beyond our solar system.




To study such patterns of early AI adoption, we extend the Anthropic Economic Index along two important dimensions, introducing a geographic analysis of Claude.ai conversations and a first-of-its-kind examination of enterprise API use. We show how Claude usage has evolved over time, how adoption patterns differ across regions, and—for the first time—how firms are deploying frontier AI to solve business problems.
“Surface charging may occur on satellite components, drag may increase on low-Earth-orbit satellites, and corrections may be needed for orientation problems,” the NOAA explains of G3 storms, adding “Intermittent satellite navigation and low-frequency radio navigation problems may occur, HF radio may be intermittent, and aurora has been seen as low as Illinois and Oregon (typically 50° geomagnetic lat.).”
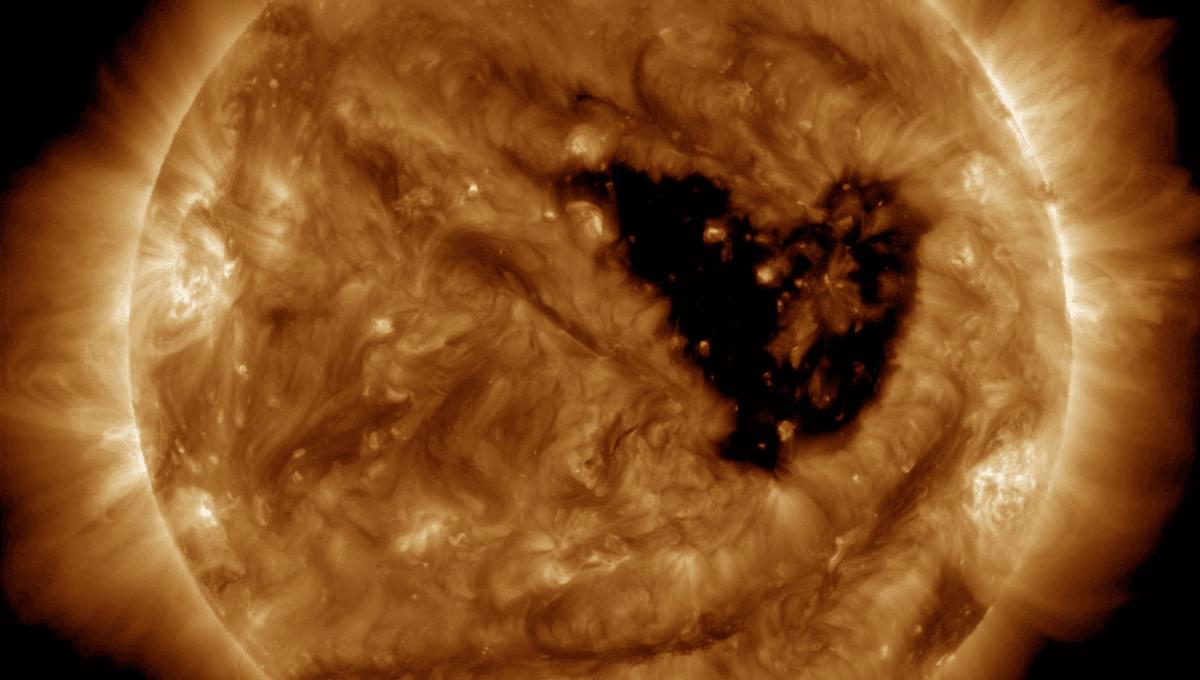
Sun activity increases and decreases in an 11-year cycle known as the Schwabe cycle. From 1826 to 1843, German amateur astronomer Heinrich Schwabe observed the Sun, discovering that it rotates on its axis once every 27 days. He noticed the Sun goes from quiet periods, where no sunspots can be seen, to the maximum phase where 20 or more groups of sunspots can be seen.
During the solar cycle, storms can reach up to level G5, classified as “extreme”, around four times on average. While G3-strength storms are more common, with around 200 per solar cycle, they can still produce powerful aurora around the equinoxes due to something known as the “Russell-McPherron Effect”

Endogenous bioelectrical patterns are an important regulator of anatomical pattern during embryogenesis, regeneration, and cancer. While there are three known classes of instructive bioelectric patterns: directly encoding, indirectly encoding, and binary trigger, it is not known how these design principles could be exploited by evolution and what their relative advantages might be. To better understand the evolutionary role of bioelectricity in anatomical homeostasis, we developed a neural cellular automaton (NCA). We used evolutionary algorithms to optimize these models to achieve reliable morphogenetic patterns driven by the different ways in which tissues can interpret their bioelectrical pattern for downstream anatomical outcomes. We found that: All three types of bioelectrical codes allow the reaching of target morphologies; Resetting of the bioelectrical pattern and the change in duration of the binary trigger alter morphogenesis; Direct pattern organisms show an emergent robustness to changes in initial anatomical configurations; Indirect pattern organisms show an emergent robustness to bioelectrical perturbation; Direct and indirect pattern organisms show a emergent generalizability competency to new (rotated) bioelectrical patterns; Direct pattern organisms show an emergent repatterning competency in post-developmental-phase. Because our simulation was fundamentally a homeostatic system seeking to achieve specific goals in anatomical state space (the space of possible morphologies), we sought to determine how the system would react when we abrogated the incentive loop driving anatomical homeostasis. To abrogate the stress/reward system that drives error minimization, we used anxiolytic neuromodulators. Simulating the effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors diminished the ability of artificial embryos to reduce error between anatomical state and bioelectric prepattern, leading to higher variance of developmental outcomes, global morphological degradation, and induced in some organisms a bistability with respect to possible anatomical outcomes. These computational findings were validated by data collected from in vivo experiments in SSRI exposure in planarian flatworm regeneration.
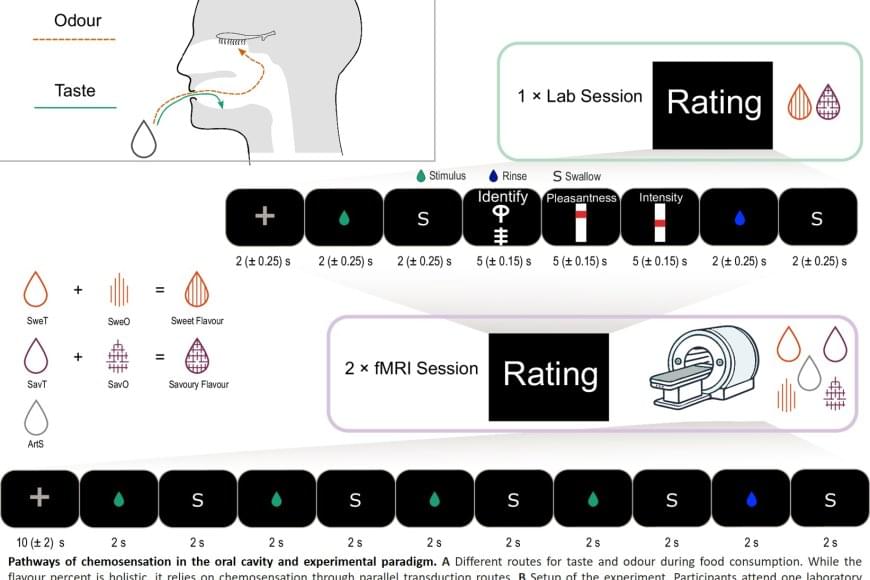
When we eat or drink, we don’t just experience taste, but rather a ‘flavor’. This taste experience arises from a combination of taste and smell, where aromas from food reach the nose via the oral cavity, known as retronasal odor. Researchers have now shown that the brain integrates these signals earlier than previously thought – already in the insula, a brain region known as the taste cortex – before the signals reach the frontal cortex, which controls our emotions and behavior.
“We saw that the taste cortex reacts to taste-associated aromas as if they were real tastes,” explains the lead author. “The finding provides a possible explanation for why we sometimes experience taste from smell alone, for example in flavored waters. This underscores how strongly odors and tastes work together to make food pleasurable, potentially inducing craving and encouraging overeating of certain foods.”
The study involved 25 healthy adults who were first taught to recognize both a sweet taste and a savory taste through combinations of taste and smell. This was followed by two brain imaging sessions using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), in which the participants were given either a tasteless aroma or a taste without smell. The researchers trained an algorithm to recognize patterns in brain activity for sweet and savory tastes, and then tested whether the same patterns could be identified when the participants were only given aromas.
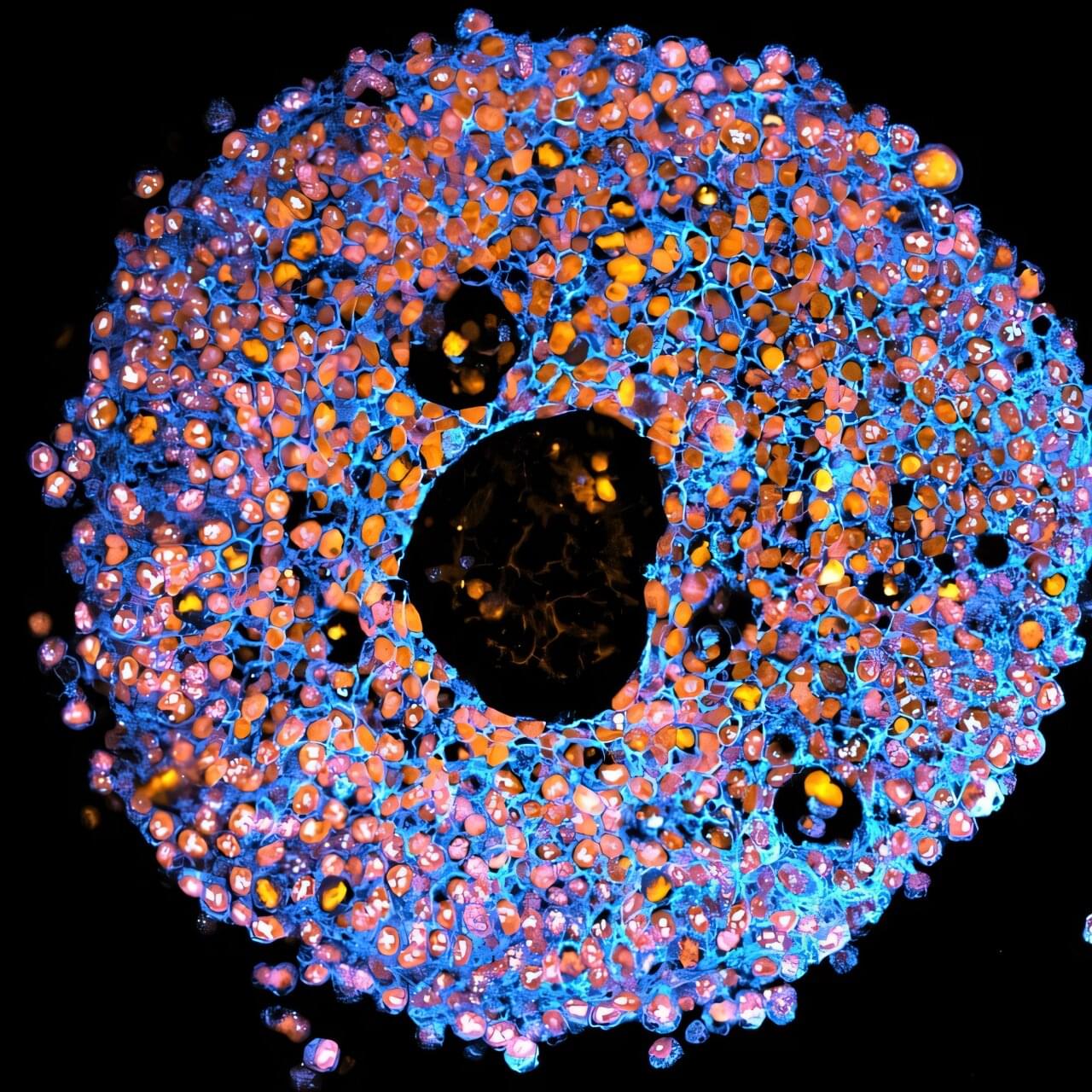
Pregnancy complications lead to more than 260,000 maternal deaths and millions of infant deaths globally. One serious condition in pregnancy linked to placental dysfunction is preeclampsia, which affects 5%–8% of pregnancies.
The study, led by Associate Professor Lana McClements and first author Dr. Claire Richards, from the UTS School of Life Sciences, has just been published in the journal Nature Communications.
Thanks to some longstanding relationships with senior executives in the prepaid and gift card industry has provided us with some unprecedented opportunities.
Our engineers are hard at work building more AI tools and utilities into the user interface and our administrative management dashboard as well.
It won’t be more than a few weeks before our first distributor is interconnected and starting to sell My Instant AI e-PIN codes.
There are many different ways to sell this product. Some will be selling it in their online stores, using their own sales and payment engines, while pulling PINs from our API in real-time as they are sold.
Others will have carded product that has a value applied to it and then activated at the checkout in a retail environment.
Some mobile phone and wireless network providers are including a card in the box, and preloading a shortcut to our platform as an app on the phone’s home screen.