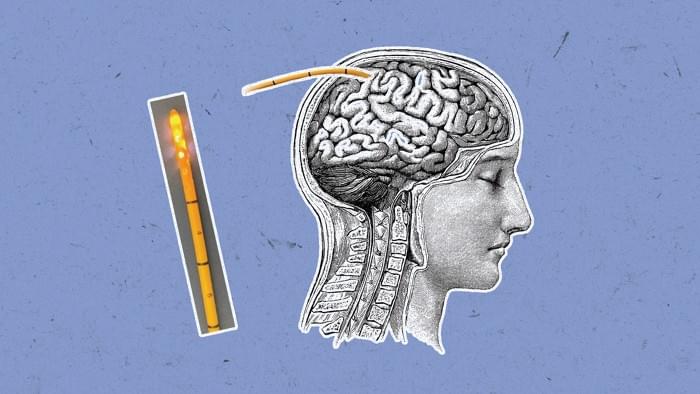
Researchers have developed a device that can simultaneously measure six markers of brain health. The sensor, which is inserted through the skull into the brain, can pull off this feat thanks to an artificial intelligence (AI) system that pieces apart the six signals in real time.
Being able to continuously monitor biomarkers in patients with traumatic brain injury could improve outcomes by catching swelling or bleeding early enough for doctors to intervene. But most existing devices measure just one marker at a time. They also tend to be made with metal, so they can’t easily be used in combination with magnetic resonance imaging.
Simultaneous access to measurements could improve outcomes for brain injuries.