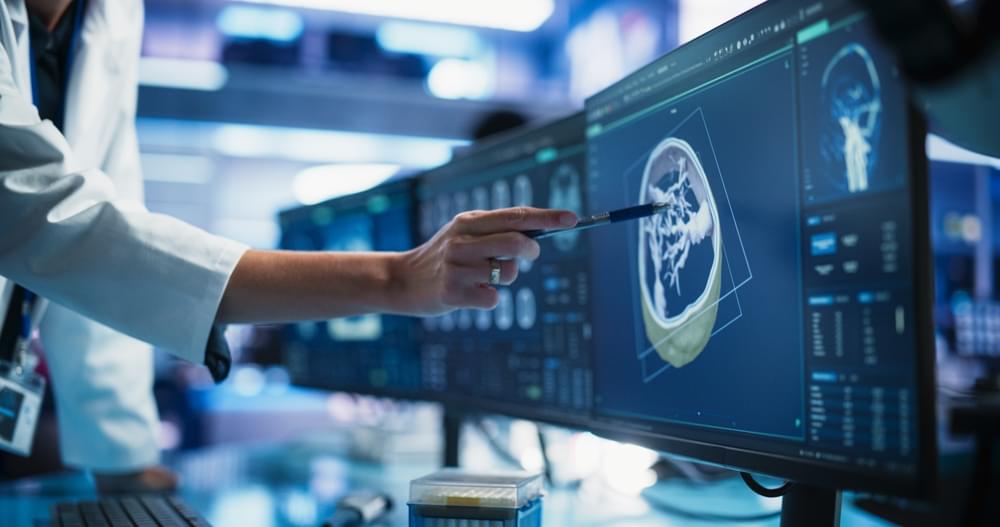
Researchers have long used spatial proteomics, particularly immunofluorescence-based methods, to identify, quantify and map proteins within tumours and their microenvironments. Now, these tools are edging towards the clinic.


Biannual international conference co-organized by Frédéric Barbaresco and Frank Nielsen. Last updated, February 2025.

Figure AI, the robotics company aiming to build the first commercially viable humanoid worker, recently announced it secured a staggering $675 million in funding from some of the biggest names in tech and venture capital, including Jeff Bezos, Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT), Nvidia (NASDAQ:NVDA), OpenAI, and Intel (NASDAQ:INTC). Now valued at $2.6 billion, the San Jose, California-based startup is in talks with United Parcel Service (NYSE:UPS) to integrate its humanoid robots into the global shipping g
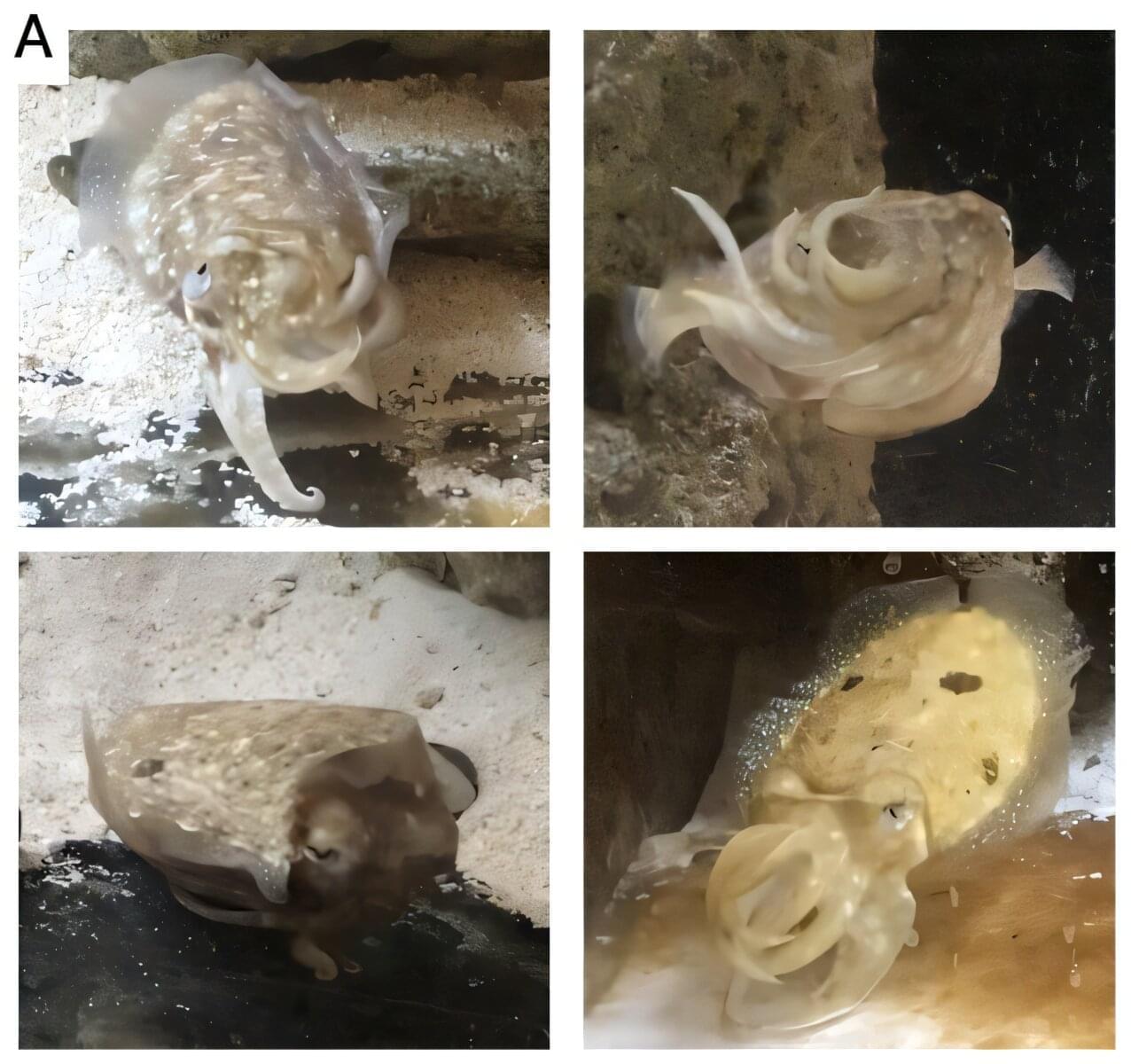


Sophie Cohen-Bodénès and Peter Neri, neuroscientists at École Normale Supérieure, in France, report possible evidence of cuttlefish communicating by waving their ‘arms’ at one another. Their paper is posted on the bioRxiv preprint server.
Prior research has shown that cuttlefish can change their skin color on demand and use that ability as a form of communication. Cuttlefish have also been observed moving their arms in certain ways when confronting other males. They possess eight arms lined with suckers, along with a pair of tentacles situated close to their mouths. In this new effort, the researchers took a closer look at the ways cuttlefish move their arms, possibly as a means of communicating with others of their kind.
The researchers put several specimens in a tank in their lab to observe them as they interacted with one another. They also videotaped several specimens as they moved their arms and played the videos back to the cuttlefish to see how they would react. They found four waving patterns that appeared to be consistent—up, side, roll, and crown.
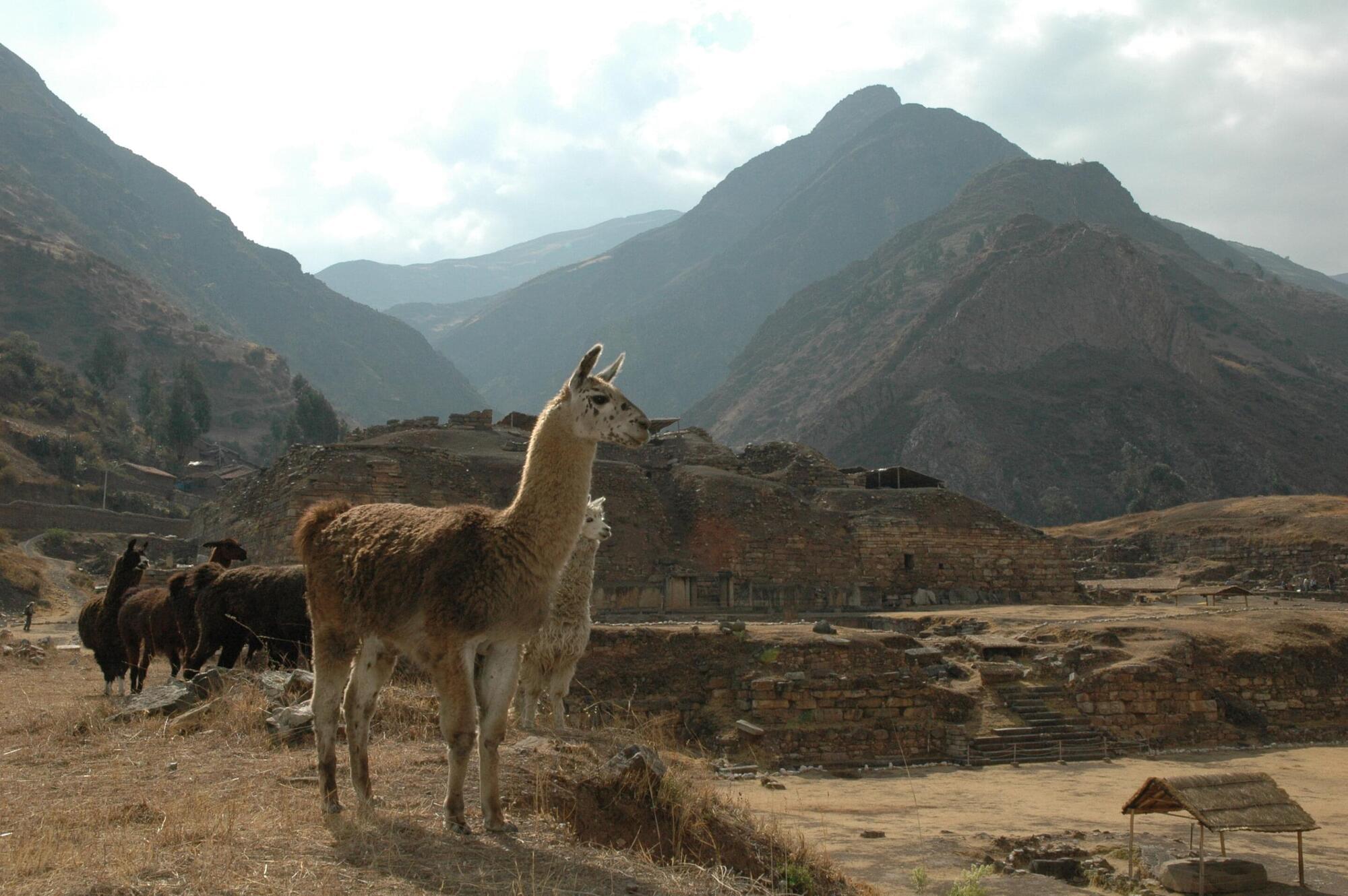

Two thousand years before the Inca empire dominated the Andes, a lesser-known society known as the Chavín Phenomenon shared common art, architecture, and materials throughout modern-day Peru. Through agricultural innovations, craft production, and trade, Chavín shaped a growing social order and laid the foundations for a hierarchical society among the high peaks.
But one of their most powerful tools wasn’t farming. It was access to altered states of consciousness.
That’s according to a new study that uncovered the earliest-known direct evidence of the use of psychoactive plants in the Peruvian Andes. A team of archaeologists from the University of Florida, Stanford University and South American institutions discovered ancient snuff tubes carved from hollow bones at the heart of monumental stone structures at Chavín de Huántar, a prehistoric ceremonial site in the mountains of Peru.
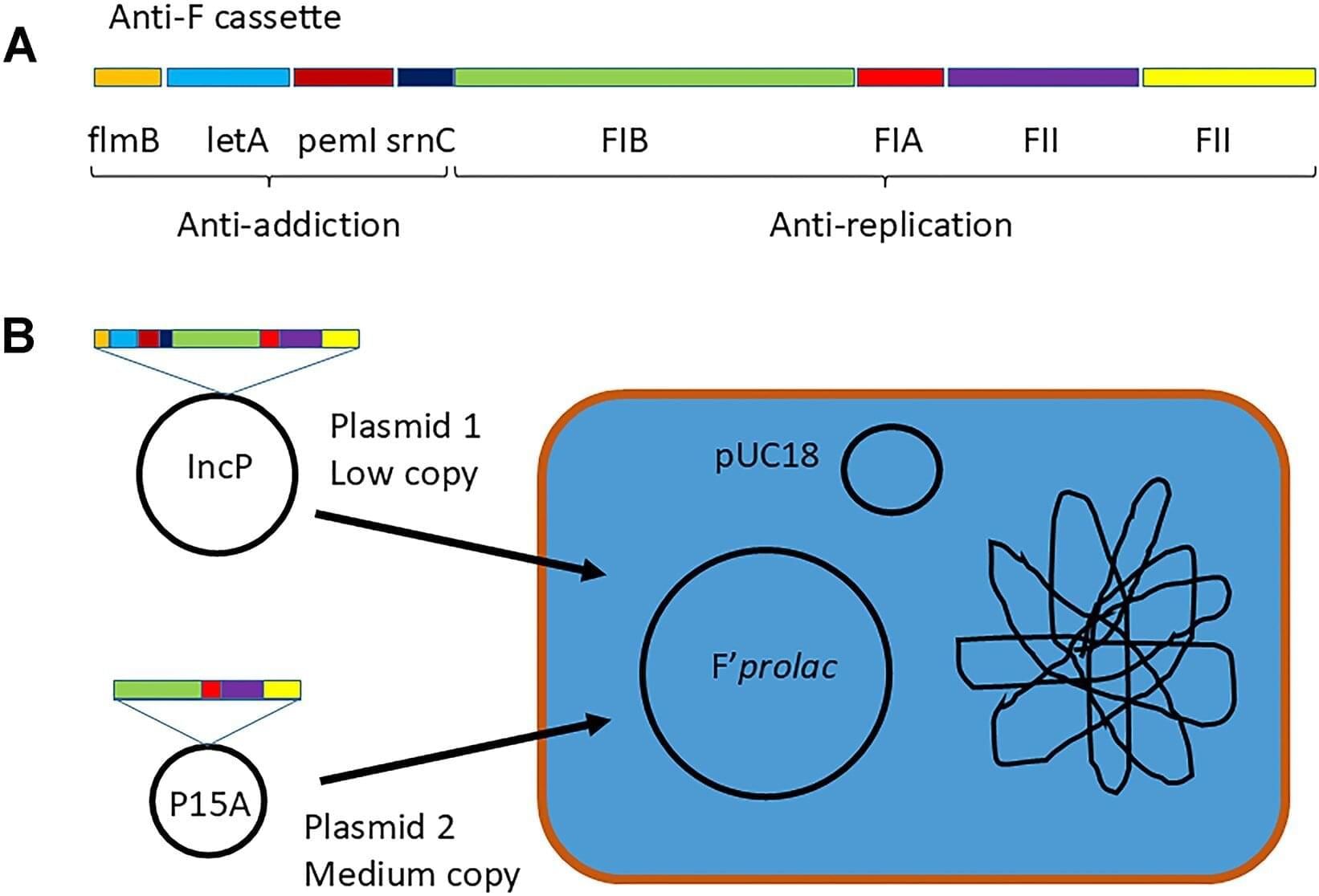
Birmingham scientists have identified an essential genetic code for a method called plasmid curing, which aims to “displace” antibiotic-resistance genes from bacteria.
Plasmids, which are small, circular strands of DNA, play a crucial role in allowing bacteria to share beneficial genes rapidly in a changing environment, most concerningly when they carry genes conferring resistance to antibiotics.
Professor Chris Thomas from Birmingham’s School of Biosciences has investigated plasmid curing for many years, and engineered useful “multi-copy” (many copies in each bacterium) plasmids for this purpose, resulting in a patented, efficient way to displace unwanted plasmids that carry resistance.
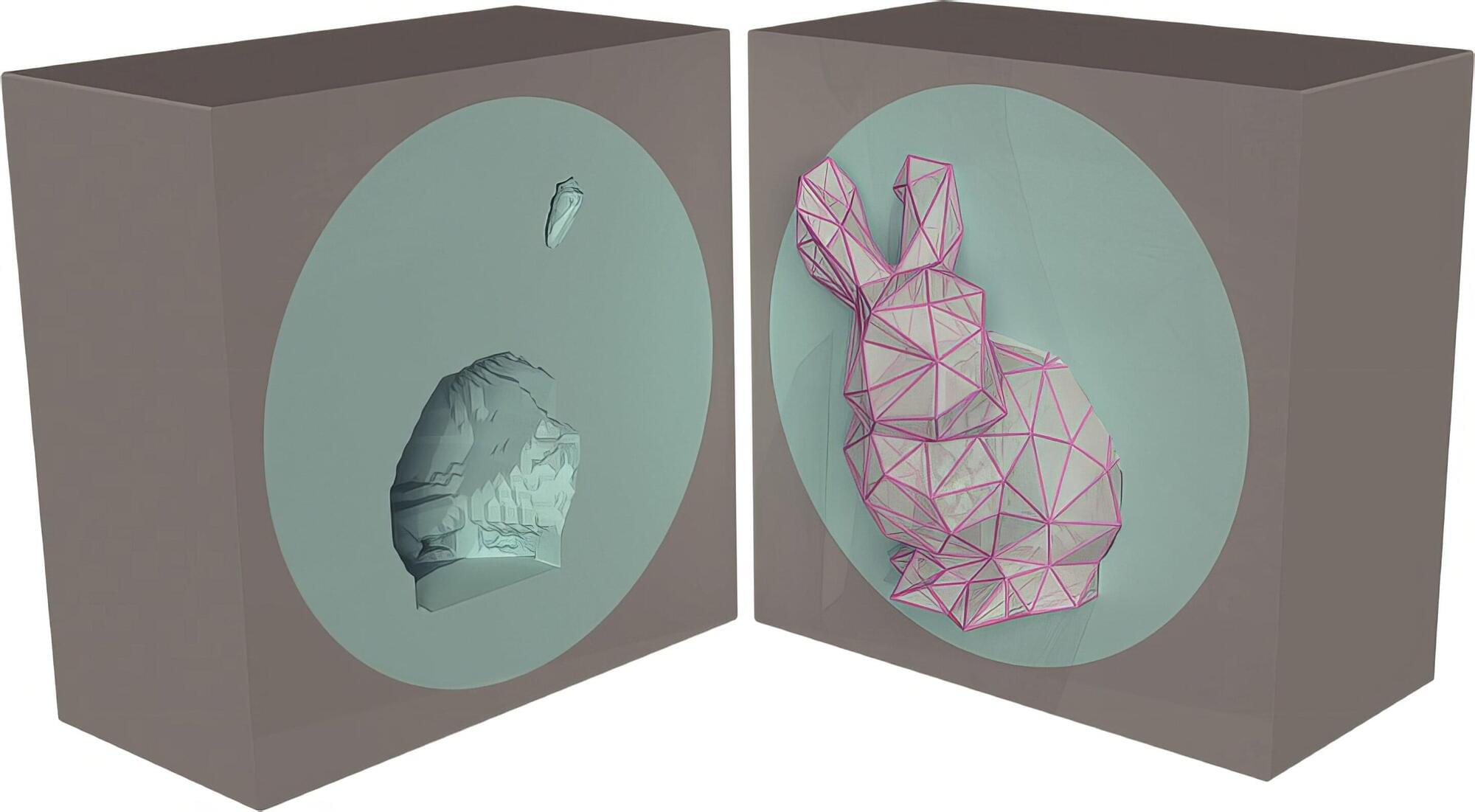
Whether designing a window in an airliner or a cable conduit for an engine, manufacturers devote a lot of effort to reinforcing openings for structural integrity. But the reinforcement is rarely perfect and often creates structural weaknesses elsewhere.
Now, engineers at Princeton and Georgia Institute of Technology have developed a technique that can maintain structural integrity by essentially hiding the opening from the surrounding forces. Rather than reinforcing the opening to protect against a few select forces, the new approach reorganizes nearly any set of forces that could affect the surrounding material to avoid the opening.
In an article, titled “Unbiased Mechanical Cloaks” in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers said they surrounded openings with microstructures designed to protect against many loads—external forces that cause stress, movement or deformation. The microstructures’ shape and orientation are calibrated to work with the most challenging loads facing the structure, allowing designers to counter multiple stresses at once.