A privately built spacecraft is hours from attempting to land on the moon, a feat that only one other company has accomplished in spaceflight history.
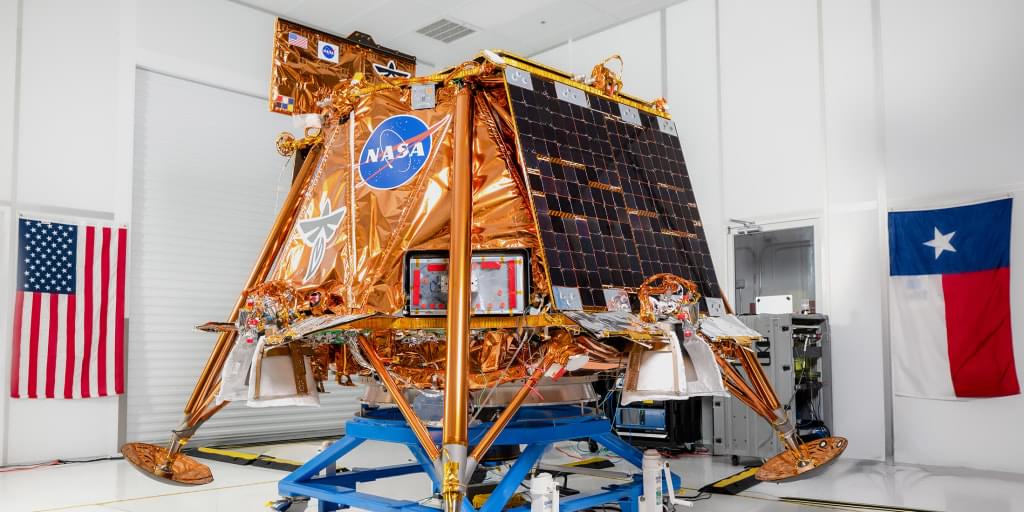
The robotic lander, dubbed Blue Ghost, has been in orbit around the moon for roughly two weeks, preparing for its daring descent. Texas-based company Firefly Aerospace developed the spacecraft, which aims to touch down on the lunar surface early Sunday at around 3:34 a.m. ET.
If all goes according to plan, Blue Ghost will become the second privately built vehicle to land on the moon successfully. In February 2024, another Texas-based company, Intuitive Machines, made history when its Odysseus lander pulled off a nail-biting touchdown near the moon’s south pole.