The prototype chip it dubs Ocelot follows similar announcements by Microsoft and Google


I believe that dna will be able to answer just about all our genetic coding questions so much that it will lead to even better breakthroughs in the future and use hardly any energy. I believe also that the master algorithm can eventually be derived from DNA as dna seems already a perfect master algorithm for human beings where human beings are the key to all future progress. I say this as quantum computing is still not stable but we already know that dna computers seem already a masterpiece already especially even organoids of the human brain. Really it becomes really quite simple as even the quantum realm is unstable but dna computers that are quantum would stabilize this currently unstable realm.
Riera Aroche, R., Ortiz García, Y.M., Martínez Arellano, M.A. et al. DNA as a perfect quantum computer based on the quantum physics principles. Sci Rep 14, 11,636 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62539-5
Background and ObjectivesN-acetyl-l-leucine (NALL) has been established to improve the neurologic manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) after 12 weeks in a placebo-controlled trial. In the open-label extension phase (EP) follow-up, data were…
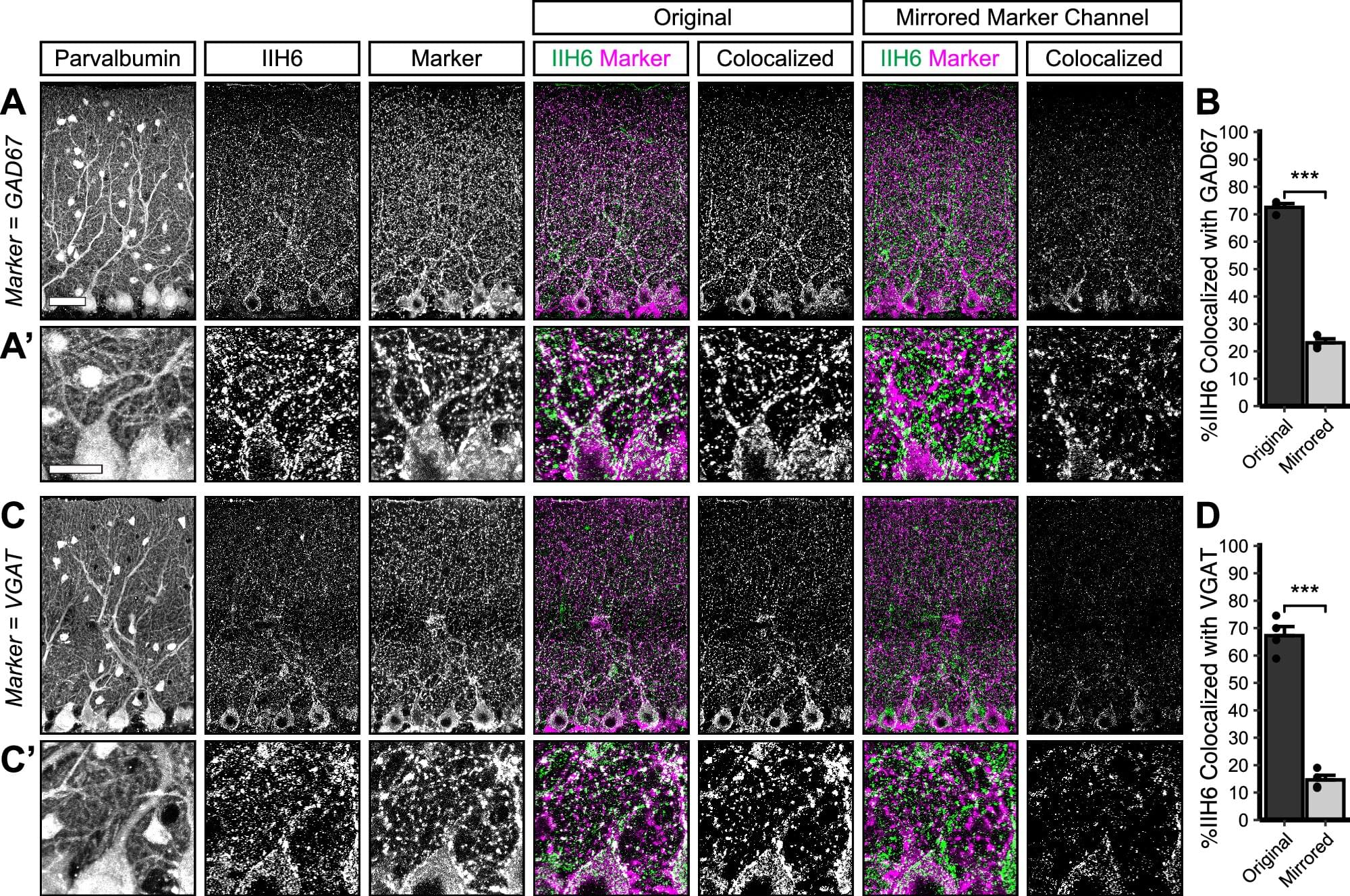
Scientists have uncovered how a protein helps build and maintain vital brain connections, providing insights into the neurological problems experienced by people with a rare form of muscular dystrophy known as dystroglycanopathy.
The research conducted at Oregon Health & Science University and published in Communications Biology reveals that the protein Dystroglycan plays a critical role in forming and maintaining connections between nerve cells in the cerebellum—the part of the brain responsible for movement coordination and motor learning.
In people with dystroglycanopathy, genetic mutations in the protein affect not only muscles but also the brain. The condition is a type of congenital muscular dystrophy, a group of inherited disorders that appear at birth or in early infancy.

Figuring out the ages of stars is fundamental to understanding many areas of astronomy—yet, it remains a challenge since stellar ages can’t be ascertained through observation alone. So, astronomers at the University of Toronto have turned to artificial intelligence for help.
Their new model, called ChronoFlow, uses a dataset of rotating stars in clusters and machine learning to determine how the speed at which a star rotates changes as it ages.
The approach, published recently in The Astrophysical Journal, predicts the ages of stars with an accuracy previously impossible to achieve with analytical models.