The first phase of the 107-acre site is set to begin construction early next year.
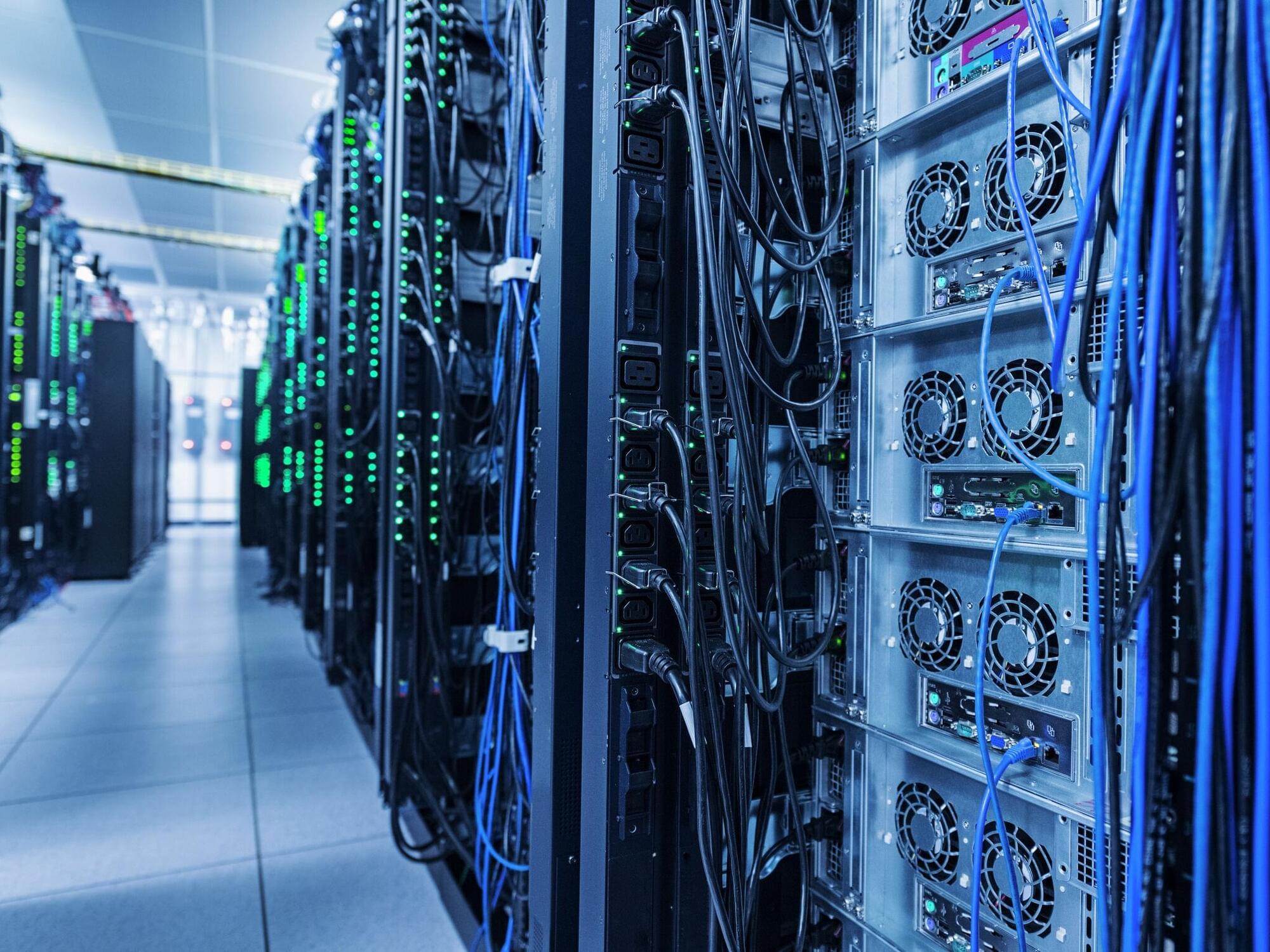
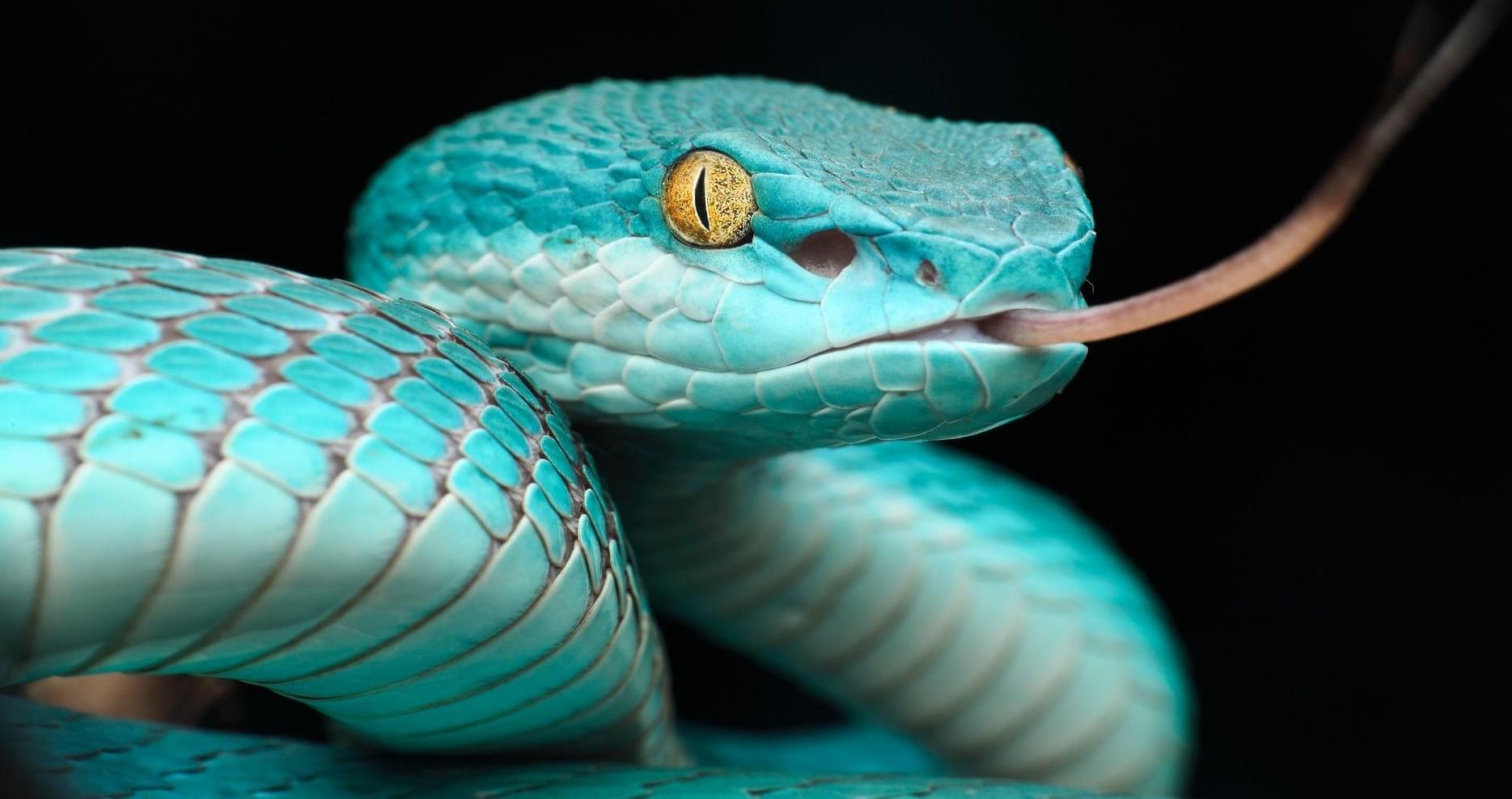



Scientists in China have developed a first-of-its-kind artificial imaging system inspired by snakes that are able to “see” heat coming off their prey in total darkness. The sensor captures ultra-high-resolution infrared (IR) images in 4K resolution (3,840 × 2,160 pixels) — matching the image quality of the iPhone 17 Pro’s camera.
Any object with a temperature above absolute zero (−460 degrees Fahrenheit or-273 degrees Celsius) emits some electromagnetic radiation. For normal body heat, this has a wavelength in the IR range. The human eye can only pick up shorter wavelengths that are in the visible light range.

(EUVL, also known simply as EUV) is a technology used in the semiconductor industry for manufacturing integrated circuits (ICs). It is a type of photolithography that uses 13.5 nm extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light from a laser-pulsed tin (Sn) plasma to create intricate patterns on semiconductor substrates.
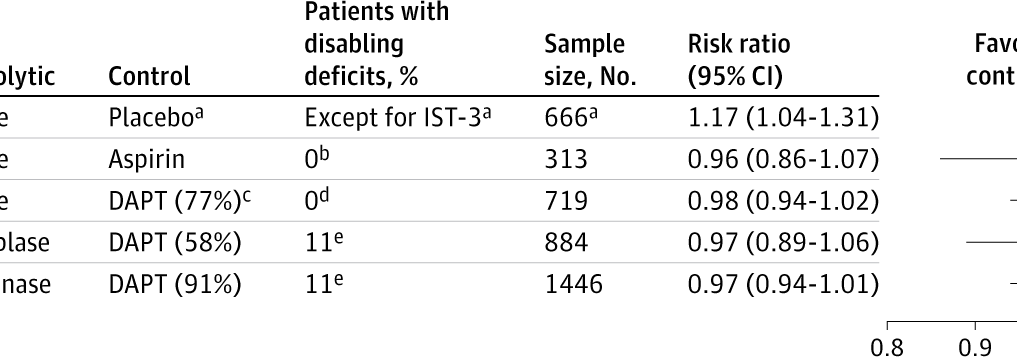
A secondary analysis of the TEMPO-2 RCT found no significant improvement in outcomes for minor ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous tenecteplase, regardless of the presence of disabling deficits.
Question Did outcomes following intravenous tenecteplase for minor ischemic stroke vary based on the presence of disabling deficits?
Findings In this secondary analysis of the TEMPO-2 randomized clinical trial including 884 patients with minor ischemic stroke and proven intracranial occlusion, both patients with and without disabling deficits defined according to US National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)–based criteria showed a neutral treatment effect from intravenous tenecteplase, with no significant effect modification.
Meaning Current definitions of disabling stroke did not modify the neutral treatment effect of intravenous tenecteplase in patients with minor stroke and intracranial occlusion.
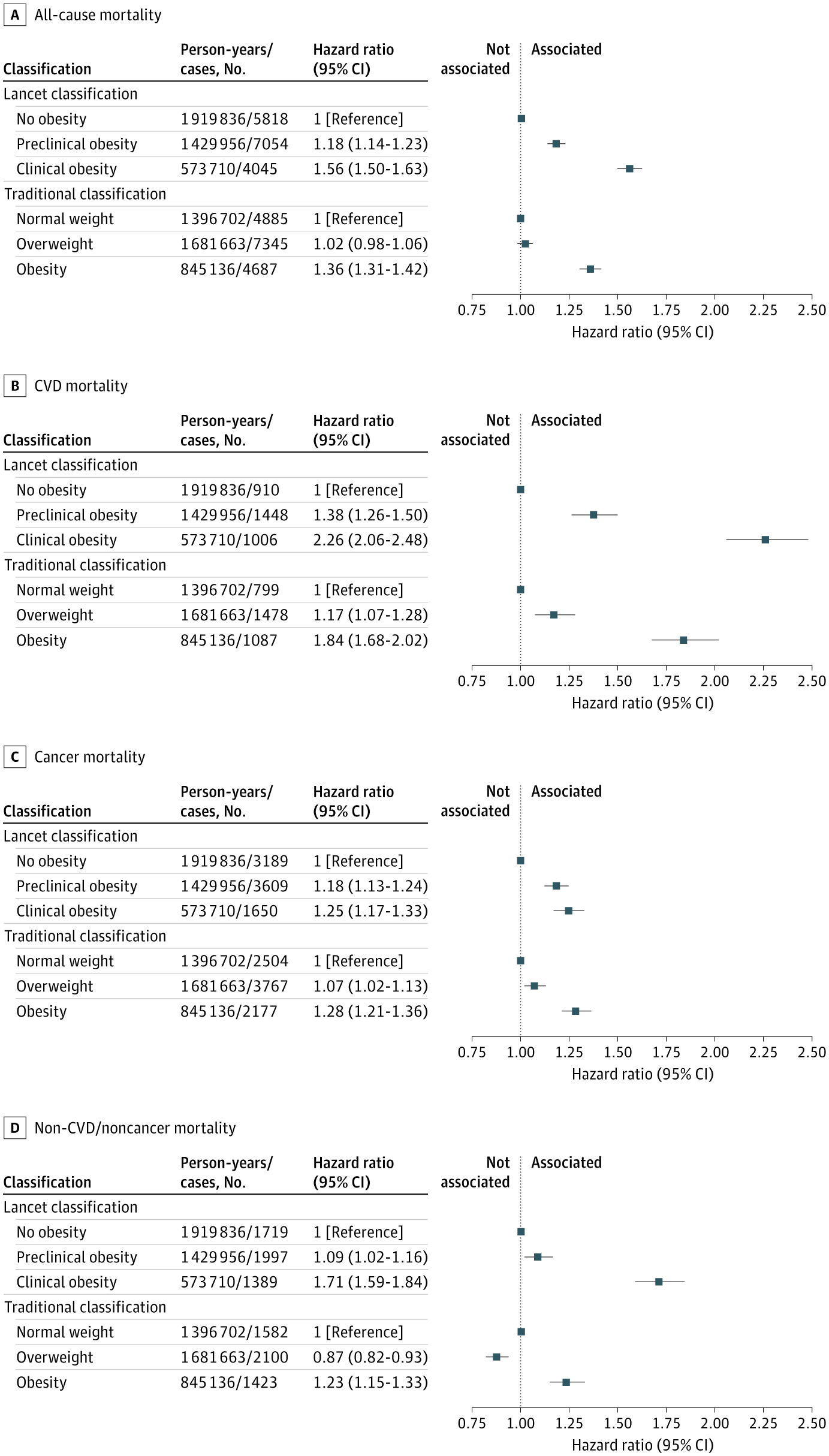
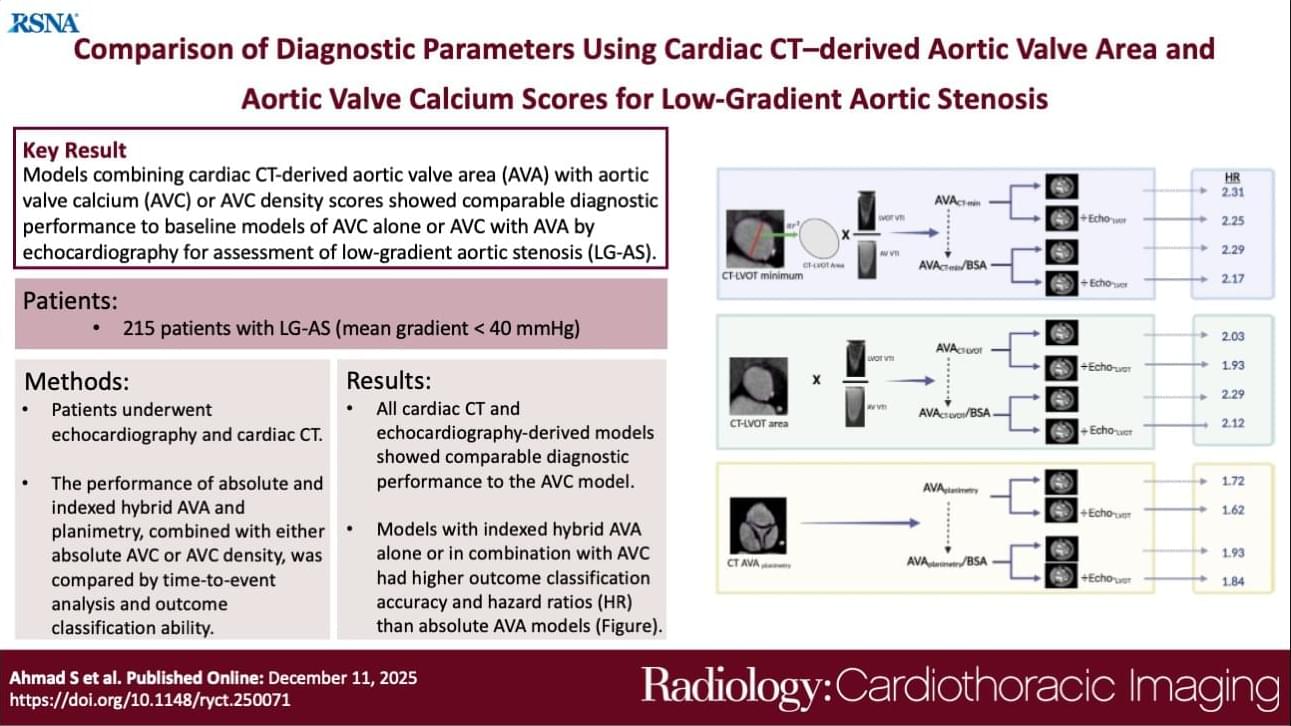
Comparing performance of cardiac CT–derived hybrid aortic valve area and planimetry, in combination with aortic valve calciumor AVC density, for assessing low-gradient aortic stenosis.
To compare the performance of cardiac CT–derived hybrid aortic valve area (AVA) and planimetry, in combination with aortic valve calcium (AVC) or AVC density (AVCd), for assessing low-gradient aortic stenosis (LGAS).
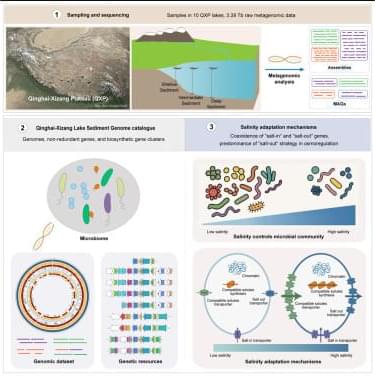
Zhang et al. construct a comprehensive microbial genome catalog from the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau lakes, with 80.78% of genomes representing previously undescribed taxa. Their research provides not only a holistic genomic resource for bioprospecting, but also suggests key salinity adaptation strategies, particularly the dominant role of glycine betaine uptake in hypersaline environments.
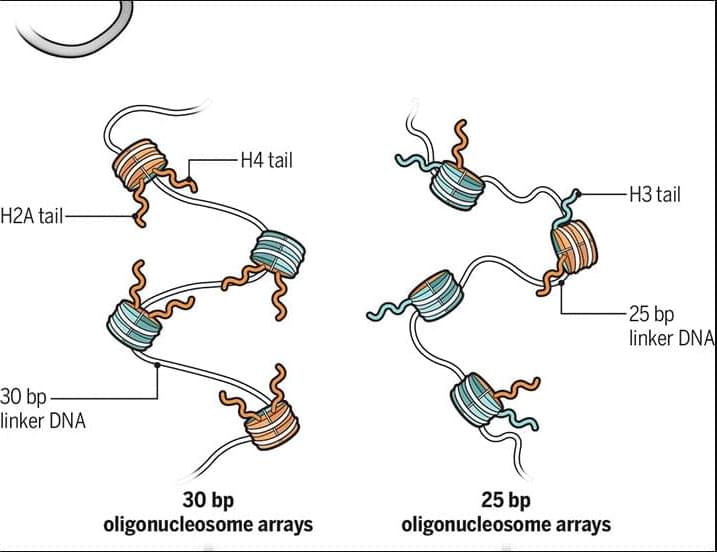
The DNA of eukaryotic organisms is packaged by histone proteins into chromatin. The structural organization of chromatin is tied to its function. Loosely packed, more transcriptionally active regions of chromatin are known as euchromatin, whereas highly condensed, less transcriptionally active regions are known as heterochromatin.
Despite advances in the study of chromatin structure over the past 100 years, a biochemical understanding of how basic structural motifs beget higher-order chromatin organization remains lacking.
In a new Science study, researchers present an approach that enables imaging and analysis of the structure of chromatin condensates in situ, which moves the field much closer toward defining the structural chromatin motifs that underpin its nuclear functions.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
Cryogenic electron tomography of condensed chromatin enables multiscale analysis of its structure.