Scientists working at the observatory have witnessed an astronomical phenomenon that has never been seen before. The details will be released next week.


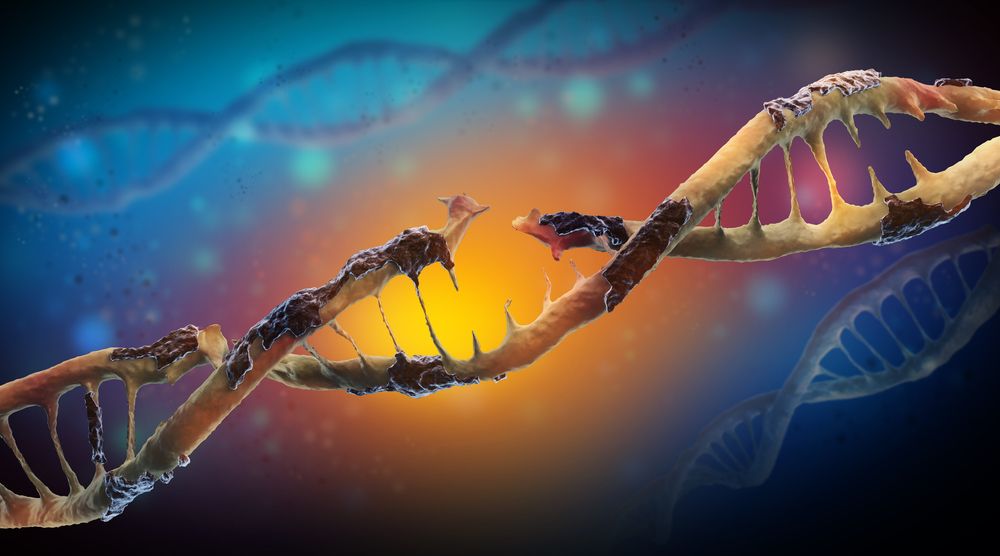
We are doing a series of articles that discuss the Hallmarks of Aging. Published in 2013, this paper is highly regarded in academia and is one of the most cited papers in biology, with an average of being cited once every two days. The paper divides aging into distinct categories (“hallmarks”) of damage to explain how the aging process works and how it causes age-related diseases[1].
Today, we will be looking at one of the primary hallmarks, genomic instability.

Israel notified the NSA, where alarmed officials immediately began a hunt for the breach, according to people familiar with the matter, who said an investigation by the agency revealed that the tools were in the possession of the Russian government.
Israeli spies had found the hacking material on the network of Kaspersky Lab, the global anti-virus firm under a spotlight in the United States because of suspicions that its products facilitate Russian espionage.
Last month, the Department of Homeland Security instructed federal civilian agencies to identify Kaspersky Lab software on their networks and remove it on the grounds that “the risk that the Russian government, whether acting on its own or in collaboration with Kaspersky, could capitalize on access provided by Kaspersky products to compromise federal information and information systems directly implicates U.S. national security.” The directive followed a decision by the General Services Administration to remove Kaspersky from its list of approved vendors. And lawmakers on Capitol Hill are considering a governmentwide ban.
This week, Neill Blomkamp, the Academy Award-nominated director of District 9, unveiled a short film that he made with the Unity Technologies game engine. At Unity’s event in Austin, Texas, Blomkamp’s Oats Studios showed off Adam: The Mirror, a 6-minute film that was a sequel to Adam, a short film that Unity built as an internally produced showcase demo last year.
Evoking the theme of transhumanism, or the notion that we can live beyond our physical bodies, the film shows an android coming to life and realizing that it was a human trapped in a robot’s body. The film was meant to show off the power of the Unity engine when it comes to making high-quality 3D graphics. But to Blomkamp, it’s also an example of how a game engine can help democratize film, making life easier for independent film makers just as Unity has done for indie game developers.
Oats Studios in Vancouver will release a second film, Adam: The Prophet, also built with Unity. And if all goes well, then Blomkamp might be able to get financing for a larger Adam movie, since he has already created a backstory and script for the project. Blomkamp said the game engine helps because it allows him to shoot one scene and then put it into a digital form, like a “3D sandbox.” He shot some scenes in the desert for Adam: The Mirror. And if he needs to re-use that desert scenery, he can do so very easily because it exists in a digital format. So he only has to go out to the desert once to shoot actors.



Building a house by hand can be both time-consuming and expensive. Numerous homebuilders have chosen to automate part of the construction (i.e., by printing the home’s parts) instead.
A new Ukrainian homebuilding startup called PassivDom uses a 3D printing robot that can print parts for tiny houses. The machine can print the walls, roof, and floor of PassivDom’s 380-square-foot model in about eight hours. The windows, doors, plumbing, and electrical systems are then added by a human worker.
When complete, the homes are autonomous and mobile, meaning they don’t need to connect to external electrical and plumbing systems. Solar energy is stored in a battery connected to the houses, and water is collected and filtered from humidity in the air (or you can pour water into the system yourself). The houses also feature an independent sewage system.

Your face is your password, but will this become a mainstream feature for the social network?