NASA and aerospace firm Orbital ATK are launching laser equipped satellites into space on Saturday.
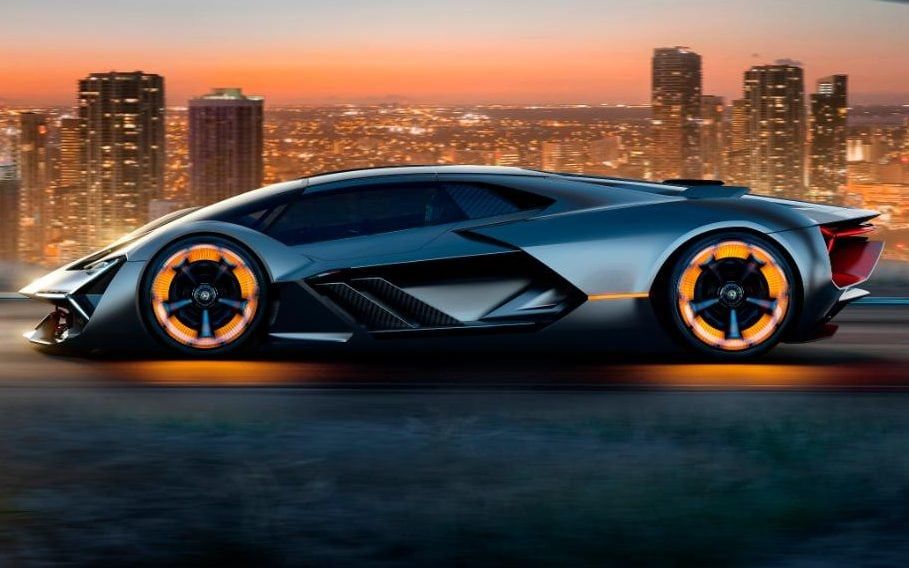



L amborghini has created the world’s first self-healing sports car. The Terzo Millennio, which translates as third millennium in Italian, has the ability to detect and repair cracks in its body work.
Using sensors the car can conduct its own health check to detect any damages and self-repair itself by filling the crack with nanotubes to prevent it spreading.
The super car was created in collaboration with researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Boston.



Air Force lieutenant general Steve Kwast believes a “Kitty Hawk” moment will begin a new era in space. But while the U.S. still leads every other country in space, Kwast cautions that edge is whittling away.
“In my best military judgement China is on a 10-year journey to operationalize space. We’re on a 50-year journey,” Kwast told CNBC.
Kwast, who is also the commander and president of Air University at Maxwell Air Force Base, says the United States must “bring together the right talent to accelerate the journey” in a Manhattan Project-like meeting of minds. He says this would push the space industry to an moment like Wright Brothers had when they completed the first successful airplane flight in 1903, in Kitty Hawk, North Carolina…

And it is on Singles’ Day, automation, robots, AI and machine learning will be widely applied to all aspects of the annual shopping ritual, right from product selection to delivery.
This year’s November 11 shopping ritual will engage a recommendation algorithm, robots, and chatbots capable of understanding human emotion.
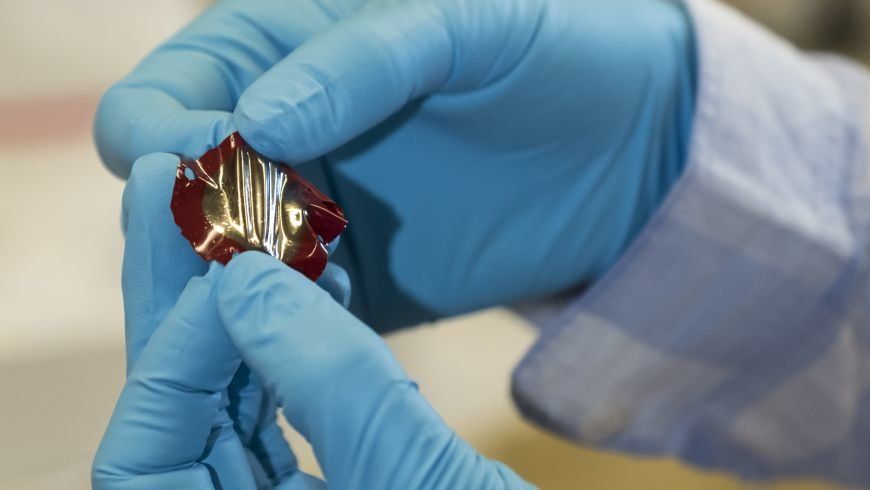
Researchers from Empa have developed a flexible material that generates electricity when stressed. In future, it might be used as a sensor, integrated into clothing or even implanted in the human body, for instance, to power a pacemaker.
Flexible, organic, thin – properties that aren’t usually associated with power plants or sensors. But a new material developed by Empa researchers is exactly that: a thin, organic, flexible film that generates electricity if stretched and compressed. This rubber film could be incorporated into control buttons, clothing, robots or even people, and monitor activities, record touches or generate electricity when stressed to power implanted devices such as pacemakers, for example.
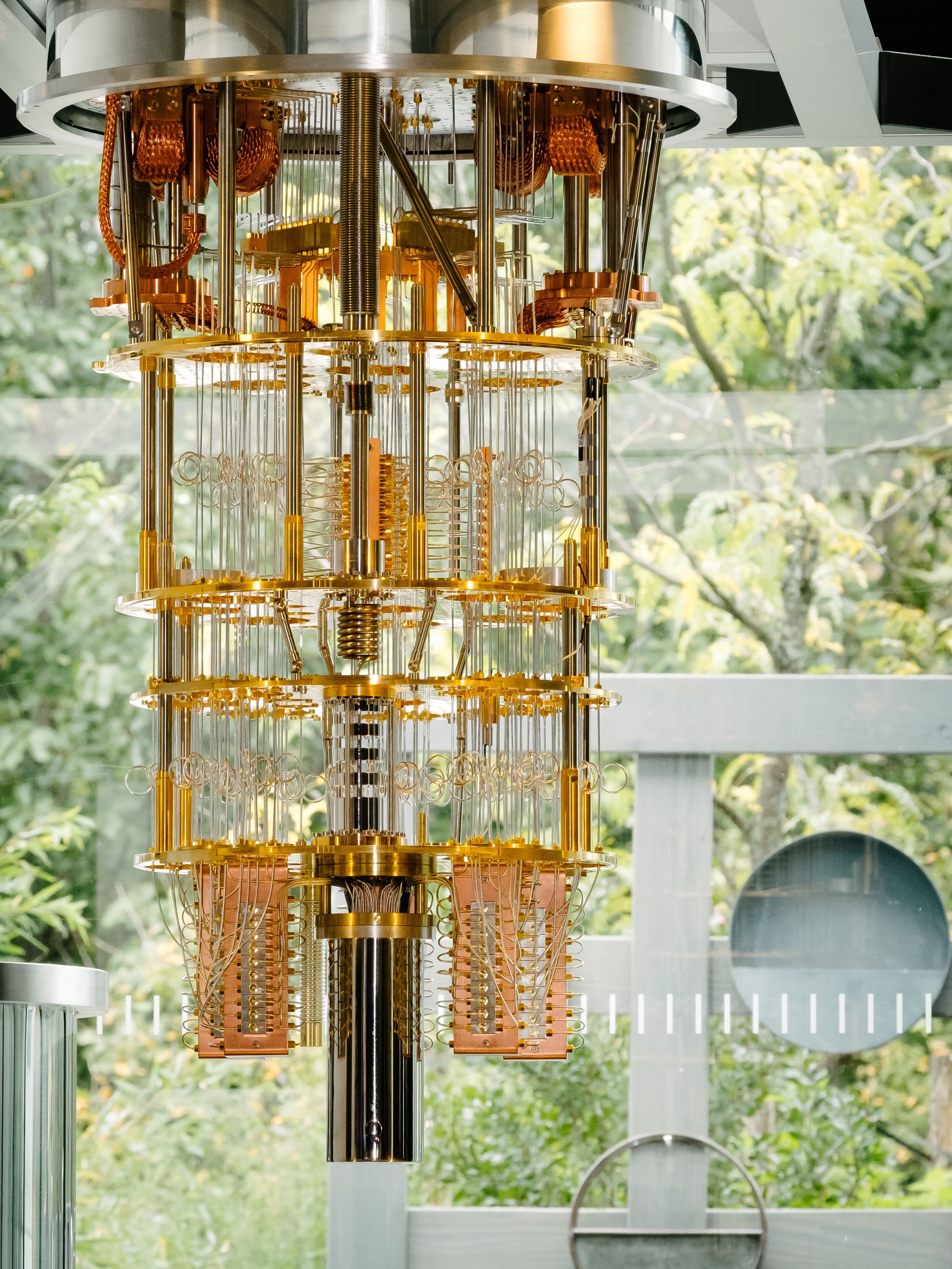

IBM has announced a milestone in its race against Google and other big tech firms to build a powerful quantum computer.
Dario Gil, who leads IBM’s quantum computing and artificial intelligence research division, said Friday that the company’s scientists have successfully built and measured a processor prototype with 50 quantum bits, known as qubits.
Gil says it’s the first time any company has built a quantum computer at this scale.

What happens to roadkill or traffic tickets when our vehicles are in control? Related Article.
Recorded: November 3, 2017
In December 2012, Kurzweil was hired by Google in a full-time position to “work on new projects involving machine learning and language processing”. He was personally hired by Google co-founder Larry Page and Kurzweil agreed on a one-sentence job description: “to bring natural language understanding to Google”.