Getting the Corporate Ears of the People Who Rule the World! By Andres Agostini at www.linkedin.com/in/andresagostini
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Los Alamos National Laboratory and Procter & Gamble, talk to them through the notions of and by Process Re-engineering.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at GE, talk to them through the notions of and by Six Sigma.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at RAND Corporation, talk to them through the notions of and by Herman Khan’s (Dr. Strangeloves’) Scenario Methodology.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Mitsubishi Motors and Honda, talk to them through the notions of and by Kaisen.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at NASA and DARPA and the Industrial-Military Complex, talk to them through the notions of and by Systems Approach with the Perspective of Applied Non-Theological Omniscience.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Lockheed Martin, talk to them through the notions of and by Six Sigma and Skunk Works.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Toyota, talk to them through the notions of and by Toyota Production System (methodology).
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Royal Dutch Shell, talk to them through the notions of and by Pierre Wack’s Scenario Methodology.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Mayo Clinic, talk to them through the notions of and by Dr. Joseph Juran’s (Total Quality Assurance) Prescription (ISBN: 978–0787900960).
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Google, talk to them through the notions of and by Strong Quantum Supercomputing and Reversing of Human Death.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Xerox, talk to them through the notions of and by PARC (Palo Alto Research Center Incorporated).
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at ExxonMobil, talk to them through the notions of and by Efficiency and Productivity as well as Return On Investment (ROI) per Petroleum Barrel produced (outputted).
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Boeing, talk to them through the notions of and by Aerospace Engineering, Avionics, Systems Engineering, Reliability Engineering, Safety Engineering, Industrial Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering.
If you want to seize the undivided attention of top executives at Loyd’s of London, Swiss RE, Munich RE, talk to them through the notions of and by Minimax, Statistics, Actuarial Science, Predictive Analytic, and Systems Engineering.
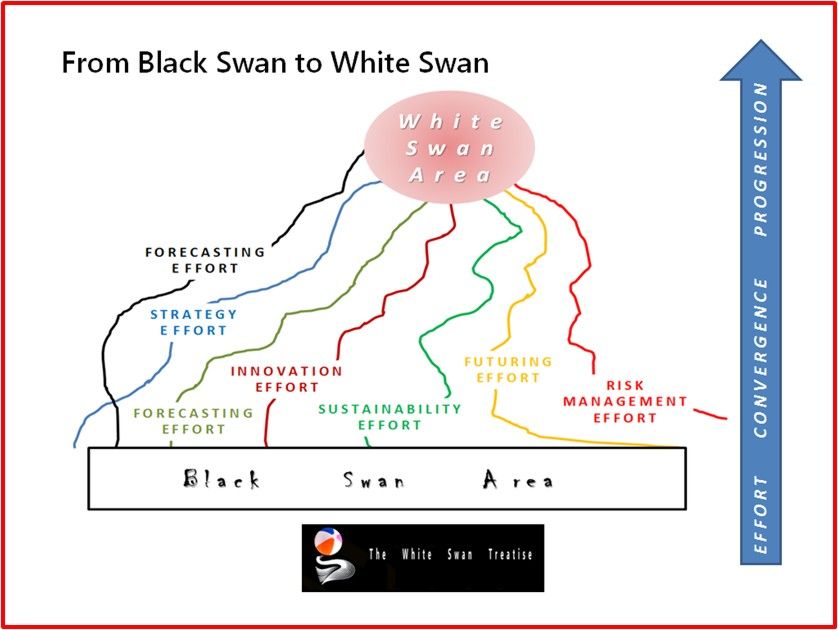
(A Brief Excerpt of the White Swan book).