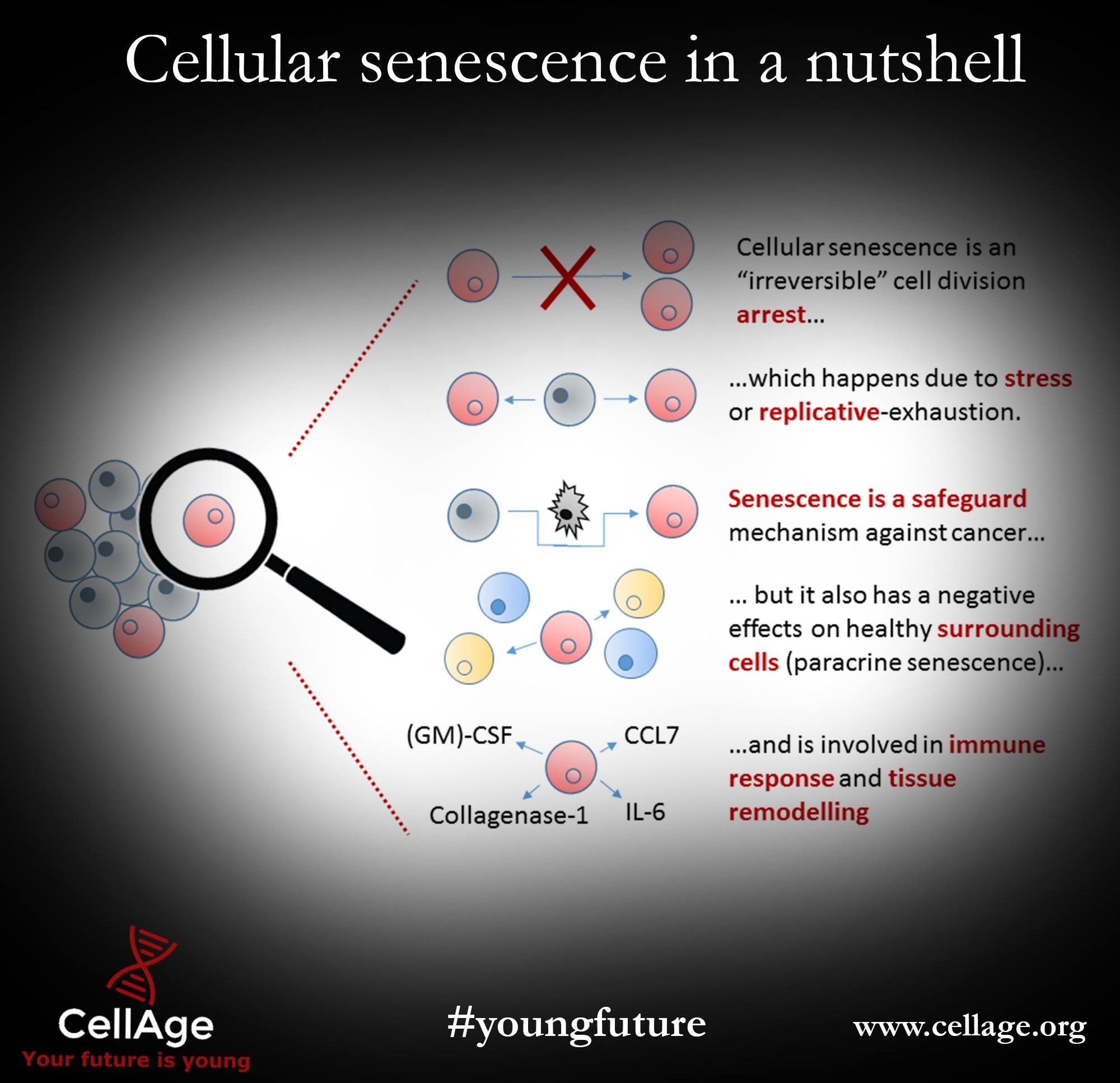
Designing synthetic promoters for safe and precise targeting of dysfunctional “senescent” cells, with the aim of developing senolytic gene therapies to remove them.
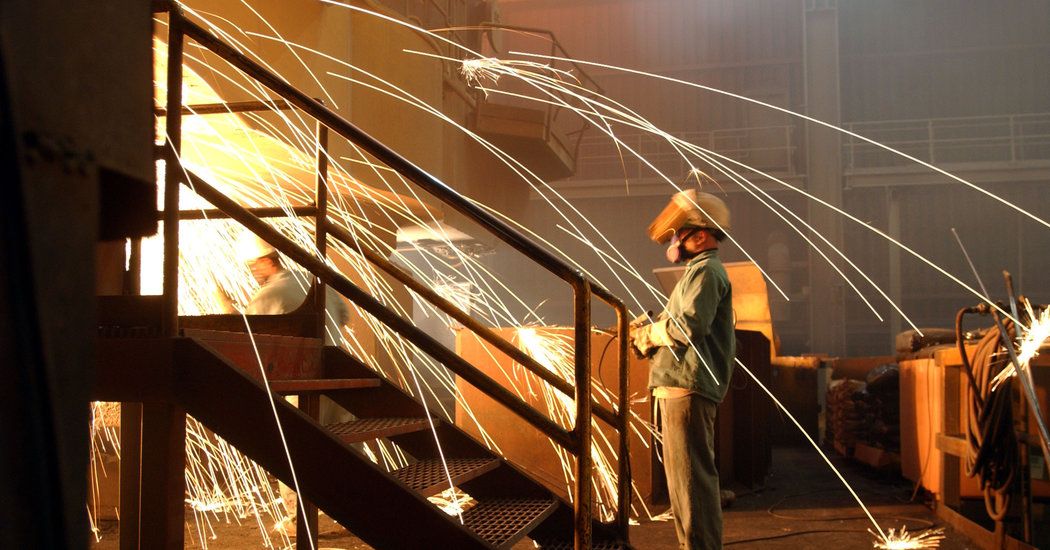


Even in the best case, automation leaves the first generation of workers it displaces in a lurch because they usually don’t have the skills to do new and more complex tasks, Mr. Acemoglu found in a paper published in May.
Robert Stilwell, 35, of Evansville, Ind., is one of them. He did not graduate from high school and worked in factories building parts for tools and cars, wrapping them up and loading them onto trucks. After he was laid off, he got a job as a convenience store cashier, which pays a lot less.
“I used to have a really good job, and I liked the people I worked with — until it got overtaken by a machine, and then I was let go,” he said.
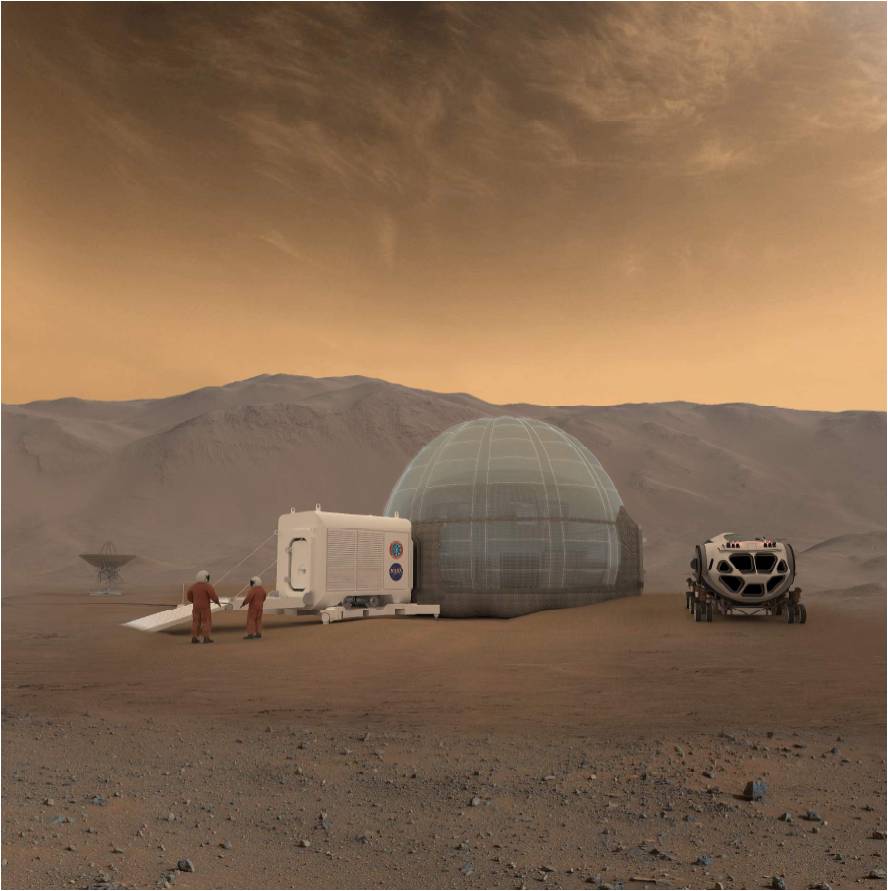

The first pioneers on Mars may build their homes using the ice beneath their feet.
In November, a University of Texas research team reported that Mars’ Utopia Planitia region contains about as much water, in the form of buried ice, as Lake Superior does here on Earth.
This ice layer, which spans a greater area than the state of New Mexico, lies in Mars’ mid-northern latitudes and is covered by just 3 feet to 33 feet (1 to 10 meters) of soil, the scientists determined. [Photos: The Search for Water on Mars].
Dr. Chen Yue, Director of Commercial Satellite Technology for the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) announced on December 10, 2016 that not only has China successfully tested EmDrives technology in its laboratories, but that a proof-of-concept is currently undergoing zero-g testing in orbit (according to the International Business Times, this test is taking place on the Tiangong 2 space station).
‘The establishment of an experimental verification platform to complete the milli-level micro thrust measurement test, as well as several years of repeated experiments and investigations into corresponding interference factors, confirm that in this type of thruster, thrust exists.’
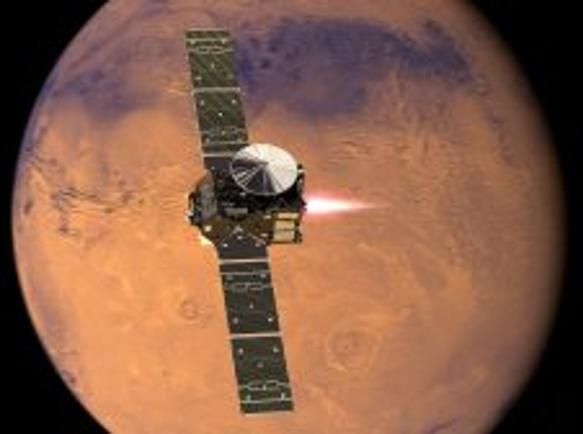

ExoMars will soon start aerobraking in Mars orbit in a years-long effort to sample Mars super-thin lower atmosphere in the ongoing search for trace gases indicative of life and active geology.
ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter is preparing to aerobrake into parts of the unexplored Martian lower atmosphere in search of methane, water vapor and other possible signatures of life on the Red Planet.
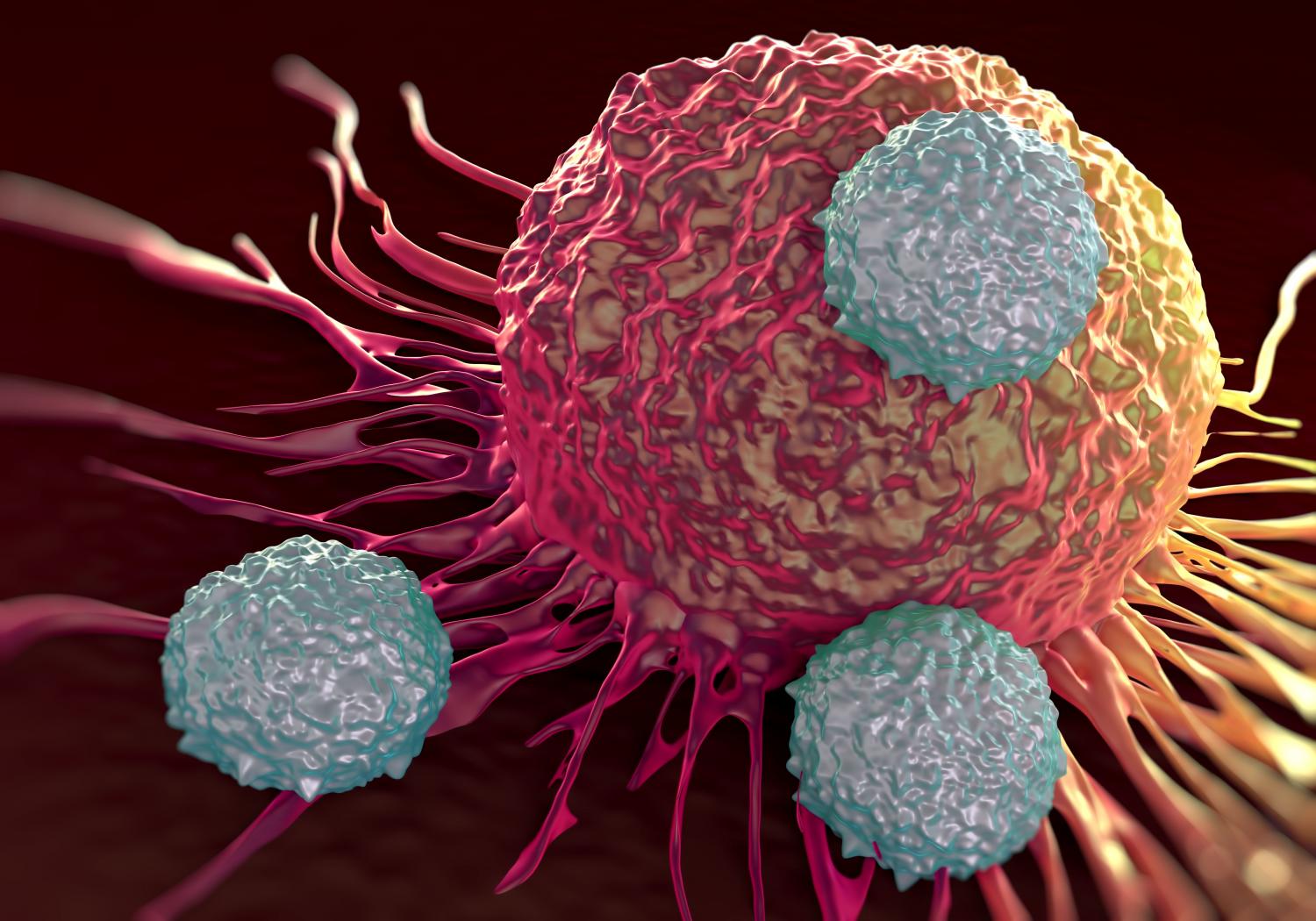
New study provides deeper insight into the immune system.
In a bid to better understand the gene expression patterns that control T cell activity, researchers at the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology mapped genome-wide changes in chromatin accessibility as T cells respond to acute and chronic virus infections. Their findings, published in the Dec. 20, 2016 issue of Immunity, shed light on the molecular mechanisms that determine the fate of T lymphocytes and open new approaches to clinical intervention strategies to modulate T cell activity and improve immune function.
“Identifying the different factors that determine different T cell states and therefore their function helps us understand if T cells will be able or not to fight viral infections or tumor growth, and if they will be able or not to provide long-term protection,” says the study’s first author James Scott-Browne, a postdoctoral fellow in the laboratory of Anjana Rao, a professor in the Division of Signaling and Gene Expression. “We may be able to revert the exhaustion phenotype of T cells and render them better able to fight tumors or chronic viral infections such as HIV, or generate better memory cells in response to vaccines.”
When viruses invade or cells turn malignant, the immune system mobilizes a small cohort of naïve or immature CD8 T cells, a crucial subdivision of the immune system charged with killing virus-infected and cancerous cells. Upon activation, they mature and proliferate exponentially into highly specific effector T cells that eliminate virus-infected or otherwise compromised cells. After their job is done, most effector T cells die leaving behind only a small contingent of memory T cell that confer long-term protection.
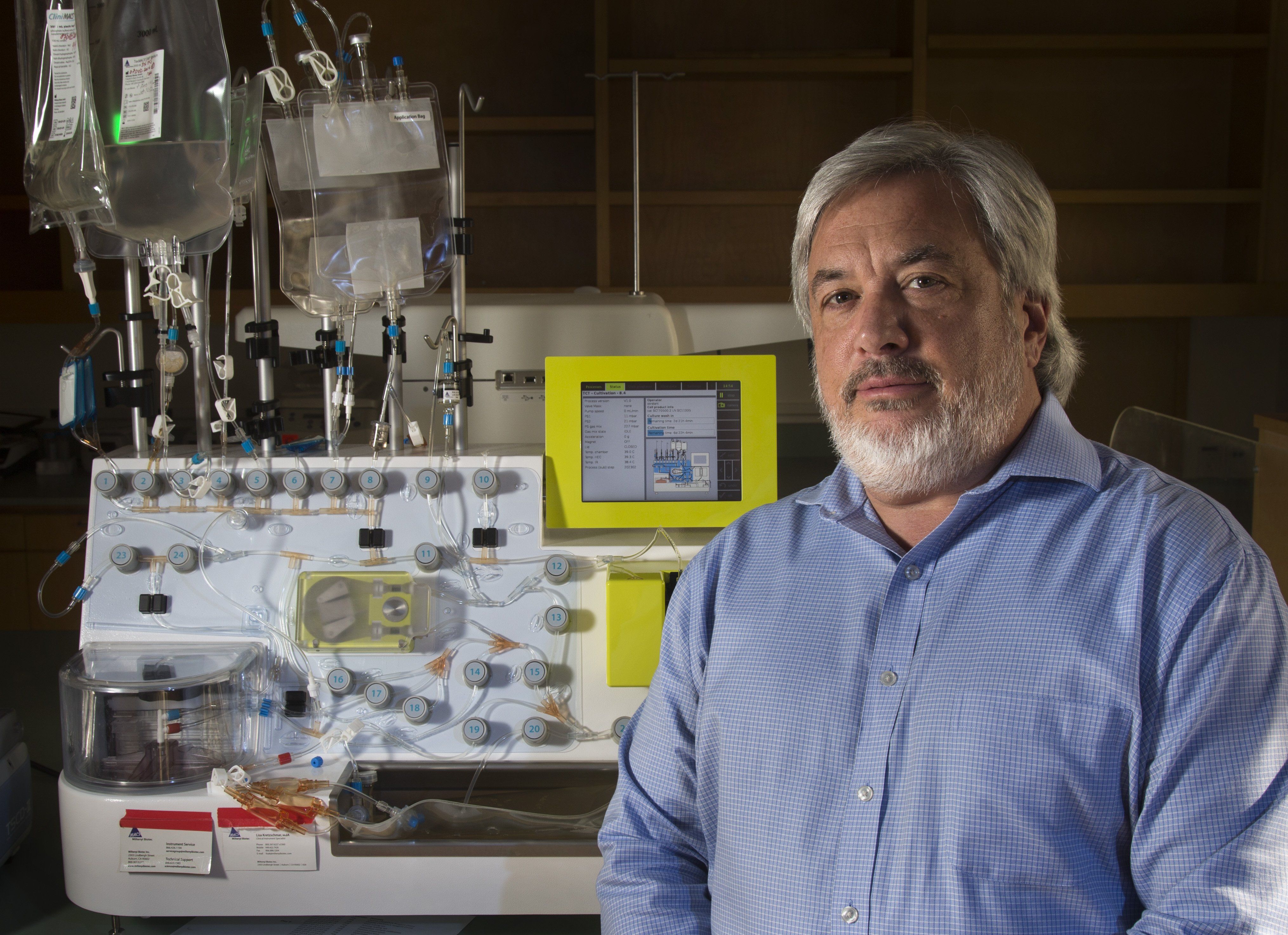

Stanford University’s amazing new regenerative medicine facility where the impossible is becoming possible.
The 25,000-square-foot facility, which opened last September, puts Stanford at the forefront of one of medicine’s most important and promising trends: regenerative medicine, which aims to refurbish diseased or damaged tissue using the body’s own healthy cells.
“We’re curing the incurable,” said laboratory director David DiGiusto, who holds a doctorate.
Critics complain that no one makes anything in Silicon Valley anymore except mobile apps and plug-in cars, a decades-long gripe that dates back to the shuttering of chip fabrication plants.
Smile Vector is a Twitter bot that can make any celebrity smile. It scrapes the web for pictures of faces, and then it morphs their expressions using a deep-learning-powered neural network. Its results aren’t perfect, but they’re created completely automatically, and it’s just a small hint of what’s to come as artificial intelligence opens a new world of image, audio, and video fakery. Imagine a version of Photoshop that can edit an image as easily as you can edit a Word document — will we ever trust our own eyes again?