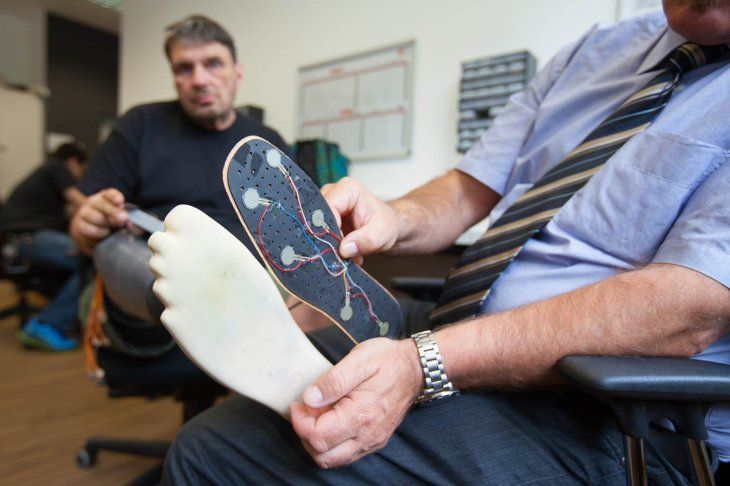
Austrian researchers develop artificial limb which can solve problem of phantom pain.
The case for transhumanism
Posted in futurism, transhumanism
I’m excited to see transhumanism getting this broadly out there in major media. This 4-minute interview is the Financial Times “Video of the Day”, and has also been picked up by AOL, MSN, Nasdaq news, and Toshiba news, among others:http://video.ft.com/4332303826001/The-case-for-transhumanism/world and http://www.ft.com/fastft/353931/firstft-mario-brothers-beats
Google, as a search engine, had built a fine business by “indexing” all of these documents and making them searchable. The company was built on a principle of centralization: If you take the chaotic Web and bestow order upon it, merge it into a single consolidated index, make it make sense, you can make users very, very happy. And upon that index, and that shared happiness, and the willingness of some users to click on targeted advertising, Google could construct a tremendous enterprise. An empire, if you will. Except empires are not traditionally constructed from indexing documents. But maps are.

“The first marketable, personal computers in the late 70s came about after almost 40 years of research and development, which created the technology at public expense. One of the peculiarities, if you’d like, of our system of innovation and development is that it’s radically anti-capitalist in many ways…People who paid taxes in the 50s and 60s may not have known it, but they were creating what was ultimately marketed by Apple. But they don’t get any of the profit. I think that’s a social pathology and the same carries over into space.” Read more
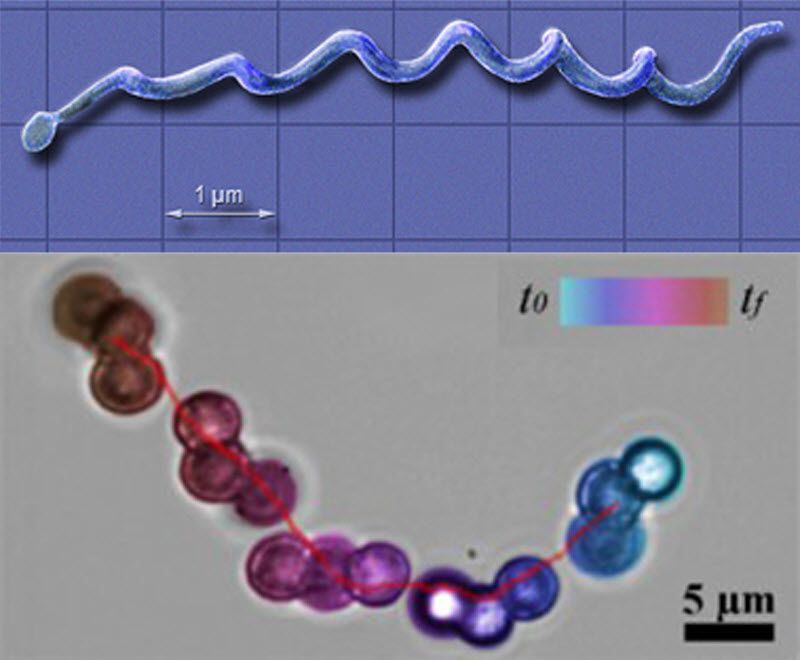
Drexel’s microswimmer robots (bottom) are modeled, in form and motion, after spiral-shaped Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria (top), which cause Lyme Disease (credit: Drexel University)
Lurking 8,000 light years from Earth is a black hole 12 times more massive than our sun. It’s…
Lately, media around the web has been bracing for robots — not time-traveling robots per se, but robot workers. Specifically, the increased sophistication of artificial intelligence and improved engineering of robotics has spurred a growing concern about what people are going to do when all the regular jobs are done by robots.
A variety of solutions have been proposed to this potential technological unemployment (we even had an entire Future of Work series dealing with this topic in March), many of which suggest that there will still be things that humans can do that robots can’t, but what are they? Read more