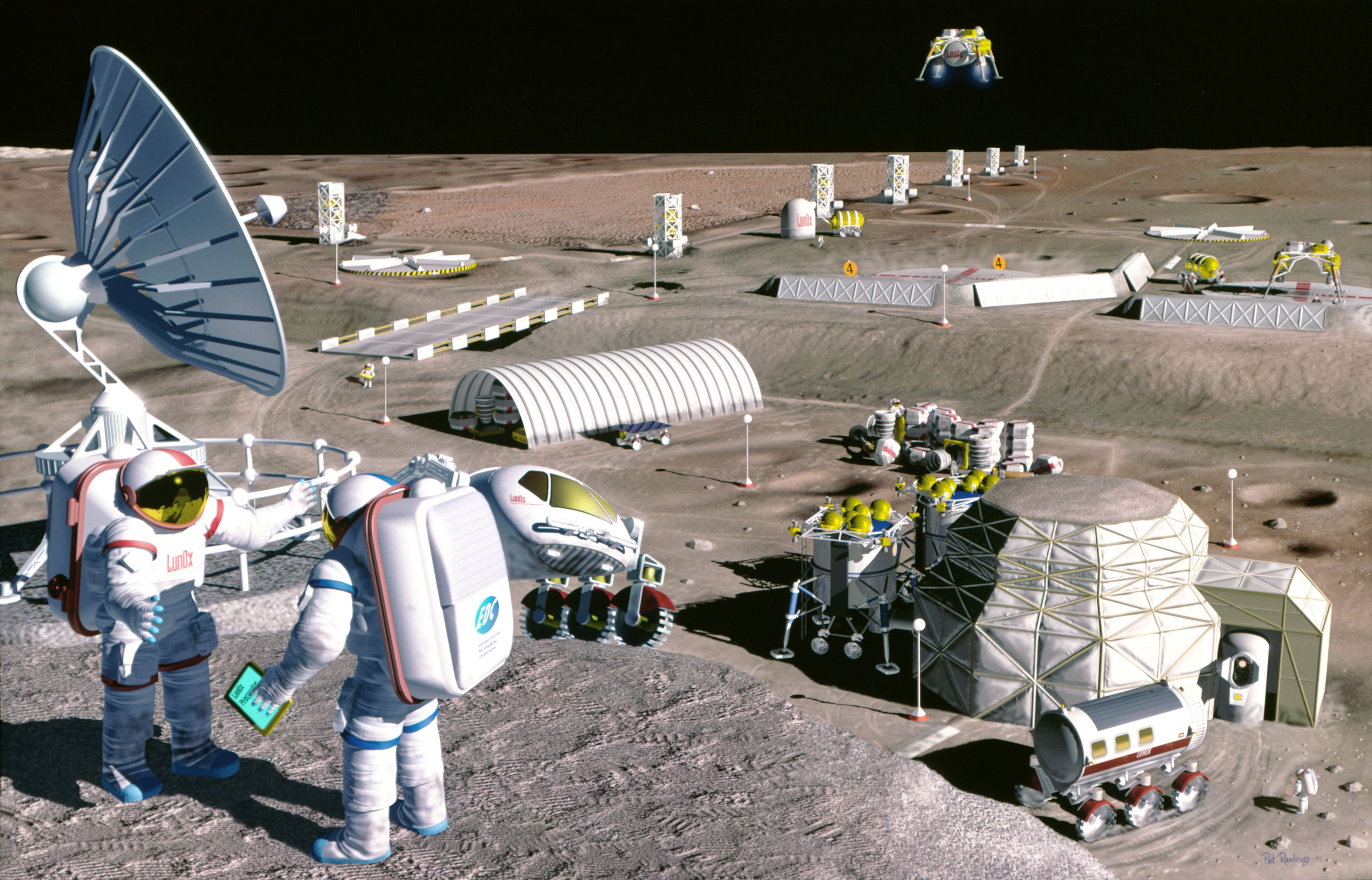
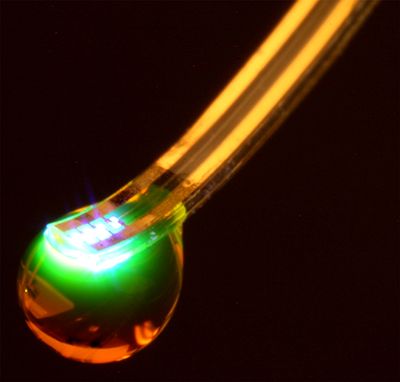
And that in turn could help us get to Mars, says NASA-commissioned study.
University of Wisconsin-Madison engineers have created a nanoscale device that can emit light as powerfully as an object 10,000 times its size. It’s an advance that could have huge implications for everything from photography to solar power.

On Monday, famed physicist Stephen Hawking and Russian tycoon Yuri Milner held a news conference in London to announce their new project: injecting $100 million and a whole lot of brain power into the search for intelligent extraterrestrial life, an endeavor they’re calling Breakthrough Listen.
“We believe that life arose spontaneously on Earth,” Hawking said at Monday’s news conference, “So in an infinite universe, there must be other occurrences of life.” Read more
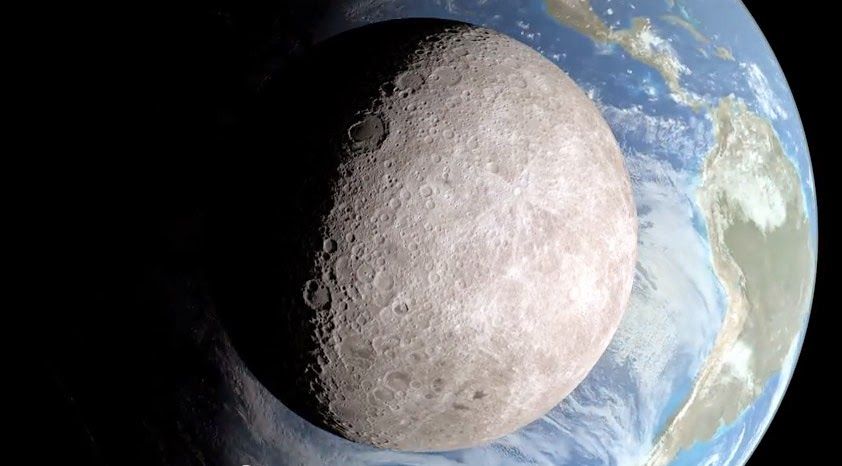
A View of Moon From The Other Side
Posted in space
We know how moon looks form Earth but what does it look like form the other side? Here is a view of our Moon from The Other Side.
My latest article for the Huff Post. I’ve been speaking a lot on transhumanism and business recently, so here’s a story on those two fields growing together:.
“Nunes demonstrated this with a tablet in the augmented reality lab and a small 3D-printed duplicate of a piece of well hardware. The maintenance manual app used the tablet’s camera to figure out what kind of hardware it was looking at, and then was able to track the component as the tablet moved around it. The operator could look up installation procedures and see steps demonstrated in 3D on the parts each step involves, rather than having to refer to static printed diagrams.” Read more
“An analysis of the history of technology shows that technological change is exponential, contrary to the common-sense “intuitive linear” view. So we won’t experience 100 years of progress in the 21st century — it will be more like 20,000 years of progress (at today’s rate). The “returns,” such as chip speed and cost-effectiveness, also increase exponentially. There’s even exponential growth in the rate of exponential growth. Within a few decades, machine intelligence will surpass human intelligence, leading to The Singularity — technological change so rapid and profound it represents a rupture in the fabric of human history. The implications include the merger of biological and nonbiological intelligence, immortal software-based humans, and ultra-high levels of intelligence that expand outward in the universe at the speed of light.” — Ray Kurzweil.
One of the biggest existential challenges that transhumanists face is that most people don’t believe a word we’re saying, however entertaining they may find us. They think we’re fantasists when in fact we’re talking about a future just over the horizon. Suppose they’re wrong and we are right. What follows? Admittedly, we won’t know this until we inhabit that space ‘just over the horizon’. Nevertheless, it’s not too early to discuss how these naysayers will be regarded, perhaps as a guide to how they should be dealt with now.
So let’s be clear about who these naysayers are. They hold the following views:
1) They believe that they will live no more than 100 years and quite possibly much less.
2) They believe that this limited longevity is not only natural but also desirable, both for themselves and everyone else.
3) They believe that the bigger the change, the more likely the resulting harms will outweigh the benefits.
Now suppose they’re wrong on all three counts. How are we to think about such beings who think this way? Aren’t they the living dead? Indeed. These are people who live in the space of their largely self-imposed limitations, which function as a self-fulfilling prophecy. They are programmed for destruction – not genetically but intellectually. Someone of a more dramatic turn of mind would say that they are suicide bombers trying to manufacture a climate of terror in humanity’s existential horizons. They roam the Earth as death-waiting-to-happen. This much is clear: If you’re a transhumanist, ordinary people are zombies.
Zombies are normally seen as either externally revived corpses or bodies in a state between life and death – what Catholics call ‘purgatory’. In both cases, they remain on Earth beyond their will. So how does one deal with zombies, especially when they are the majority of the population? There are three general options:
1) You kill them, once and for all.
2) You avoid them.
3) You enable them to be fully alive.
The decision here is not as straightforward as it might seem because the prima facie easiest option (2) requires that there are no resource implications. But of course, zombies require living humans (i.e. potential transhumans) in order to exist in the manner they do, which in turn makes the zombies dangerous; hence (1) has always proved such an attractive option for dealing with zombies. After all, it is difficult to dedicate the resources needed to secure the transhumanist goal of indefinite longevity, if there are zombies trying to anchor your existential horizons in the present to make their own lives as easy as possible.
This kind of problem normally arises in the context of ecological sustainability as ‘care for future generations’: Our greedy habits of mass consumption blind us to the long-term damage it does to the environment. However, the relevant sense of ‘care’ in the transhumanist case relates to sustaining the investment base needed to reach a state of indefinite longevity. It may require diverting public resources from seemingly more pressing needs, such as having a strong national defence — as the US Transhumanist Party presidential candidate Zoltan Istvan thinks. It is certainly true that if people routinely lived indefinitely, then the existential character of ‘the horror of war’ would be considerably reduced, which may in turn decrease both the likelihood and cost of war. Well, maybe…
So what about option (3), which is probably the one that most of us would find most palatable, at least in principle?
Here there is a serious public relations problem, one not so different from development aid workers trying to persuade ‘underdeveloped’ peoples that their lives would be appreciably improved by allowing their societies to be radically re-structured so as to double their life expectancy from 40 to 80. While such societies are by no means perfect and may require significant change to deliver what they promise their members, nevertheless the doubling of life expectancy would mean a radical shift in the rhythm of their individual and collective life cycles – which could prove quite threatening to their sense of identity.
Of course, the existential costs suggested here may be overstated, especially in a world where even poor people have decent access to more global trends. Nevertheless the chequered history of development aid since the formal end of Imperialism suggests that there is little political will – at least on the part of Western nations — to invest the human and financial capital needed to persuade people in developing countries that greater longevity is in their own long-term interest, and not simply a pretext to have them work longer for someone else.
The lesson for us lies in the question: How can we persuade people that extending their lives is qualitatively different from simply extending their zombiehood?
Immersive virtual reality is the vision of a computer-generated reality that looks, sounds, smells and feels so authentic that it psychologically tricks our brain into accepting that it is real.