Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
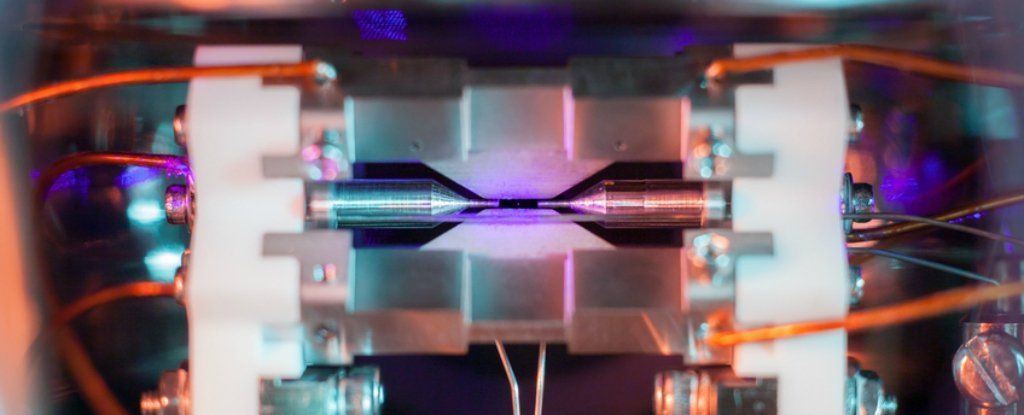
Scientists Have Found a New Way of Storing Information in a Single Atom
Humanity is producing so much data every single minute that we either need to slow down, or scientists need to crack the problem of finding better ways of storing that data ASAP. Now, new research has taken us one step closer to the ultimate in compact data storage: putting data on a single atom.
As the basic building blocks of all matter, atoms are the smallest object we could possibly store a bit (a 1 or a 0) on, potentially shrinking down the size of existing hard drives by about a thousand times or so, if we can figure out how to get it to work.
Scientists have already made progress in storing bits on atoms, but only on a small scale and in tightly controlled lab conditions, which usually means extremely cold setups.
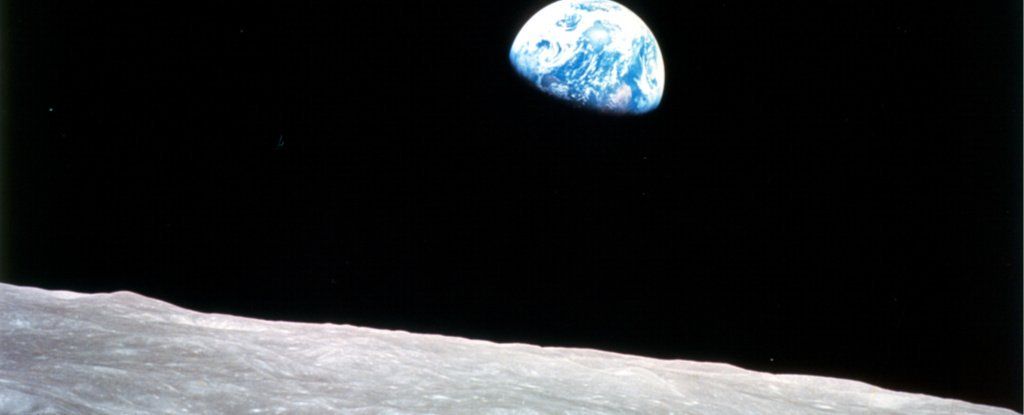

It’s Official: NASA Just Announced a Bold 3-Part Plan to Send Humans to The Moon And Mars
NASA’s got a whole new plan. It wants boots on the Moon in 10 years and on Mars in 20. Give or take.
On Wednesday, the space agency announced its detailed National Space Exploration Plan to achieve the President’s lofty goals set out in his December 2017 Space Policy Directive-1.
Those bold plans include: planning a new Moon landing, long-term human deployment on and around the Moon, reassertion of America’s leadership in space, strengthening private space companies, and figure out how to get American astronauts to the surface of Mars.

5 Sci-Fi Books Biotech Geeks Should Read Right Now
From space colonization to resurrection of dinosaurs to machine intelligence, the most awe-inspiring visions of humanity’s future are typically born from science fiction.
But among an abundance of time travel, superheroes, space adventures, and so forth, biotech remains underrepresented in the genre.
This selection highlights some outstanding works (new and not so new) to fill the sci-fi gap for biotech aficionados.




DARPA high-resolution neural interfaces for controlling drones and cybertech
DARPA seeks to achieve high levels of brain-system communications without surgery, in its new program, Next-Generation Nonsurgical Neurotechnology (N3).
What If a Coin-Sized Black Hole Appeared On Earth
What trouble could a coin-sized black hole cause?
More Cancers Occur
Two-thirds of all cancers are caused by DNA replication errors, according to Johns Hopkins researchers. But don’t light a celebratory cigarette just yet.