AI may be limited by a lack of taste, touch and smell which prevents it from fully understanding concepts in the same way as humans — suggesting that more advanced models may need to have a robot body



Sometimes I watch videos on YouTube. There was this fun Veritasium video with an interesting interview question from Google. It goes something like this.
You are shrunk down to the size of a nickel and put in a blender. How do you escape before the blender is turned on?
The answer is apparently that you just jump out. The idea is that a 5 centimeter tall person could jump just as high as a normal sized person. I mean, it sort of makes sense — there are many dogs that can jump as high as a horse, right?

For decades, we’ve thought the control center of life lies in DNA. But a new scientific framework is emerging that challenges that idea, and suggests that vast portions of the genome are immaterial and lie outside the physical world. Today, physicist Dr. Brian Miller shares his perspective on the cutting-edge, potentially revolutionary research of mathematical biologist Dr. Richard Sternberg on the immaterial aspects of the genome. In this exchange, Dr. Miller shares several examples of the immaterial nature of life. These ideas point towards the earliest stages of the next great scientific revolution and have significant implications for the intelligent design debate.
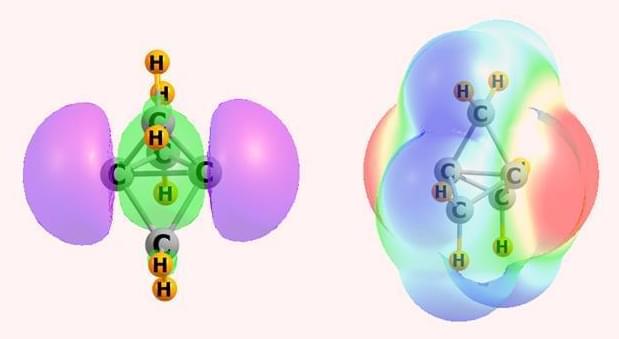
Scheiner and Zierkiewicz, however, have been studying apical carbon atoms in propellane and pyramidane molecules, where the bonding situation is rather different. Along with Mariusz Michalczyk, also at Wrocław University of Science and Technology, they’ve identified an electron-donating orbital – or pseudo lone pair – on these tetrahedral carbons.
While it clearly has a negative charge, Scheiner acknowledges that the nature of this electron-donating orbital could be up for debate. Nonetheless, it appears that this region of negative electrostatic potential can attract the σ-hole of an electrophile to form various non-covalent interactions including hydrogen, halogen, chalcogen, pnictogen and tetrel bonds.

Women who have already passed through the menopause may be able to have children following a blood treatment usually used to heal wounds
What if the most powerful organ in your body isn’t your brain, but your heart? In this deeply revealing compilation from Gaia’s MISSING LINK Series 👉 https://www.gaia.com/lp/mindful-maste…, Gregg Braden uncovers a forgotten truth buried in both science and ancient wisdom—that your heart holds 40,000 brain-like cells capable of memory, emotion, and thought.
Learn how you can unlock total recall, deep intuition, and spontaneous healing through harmonizing two forgotten systems: your heart and your brain.
00:00 – The Nightmare That Solved a Murder.
03:15 – Human Chromosome 2: Engineered Evolution?
07:30 – The Brain in the Heart: 40,000 Neurites.
11:00 – Transferred Memories in Organ Transplants.
16:20 – Little Girl’s Memory Solves a Crime.
21:15 – Heart Intelligence vs Brain Intelligence.
25:00 – Ancient Cultures & Heart-Based Education.
28:40 – Unlocking Superhuman Abilities.
32:20 – Total Recall & Intuition on Demand.
36:10 – Reprogramming the Subconscious.
39:00 – Heart-Brain Harmony Triggers 1,300 Biochemical Reactions.
Cherck Out Gregg’s latest book Pure Human: The Hidden Truth of Our Divinity, Power, and Destiny here 👉 https://hayhs.com/ph_pp_hc_az.
👍 LIKE if you enjoyed this video!
🔄 SHARE with your friends and spread the knowledge!
🔔 SUBSCRIBE for more amazing content!
👉 Hit the BELL Icon on our HOME Page to stay updated with our latest releases!
Stay Connected.
Official website: https://greggbraden.com/about-gregg-braden/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/GreggBraden.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/GreggBraden.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/Gregg.Braden/
This channel is managed by:
Zohar Entertainment Group International Inc, USA
YouTube Certified Enterprise Partner — FAM Networks, USA
Facebook: / greggbraden.
Twitter: / greggbraden.
Instagram: / gregg.braden
