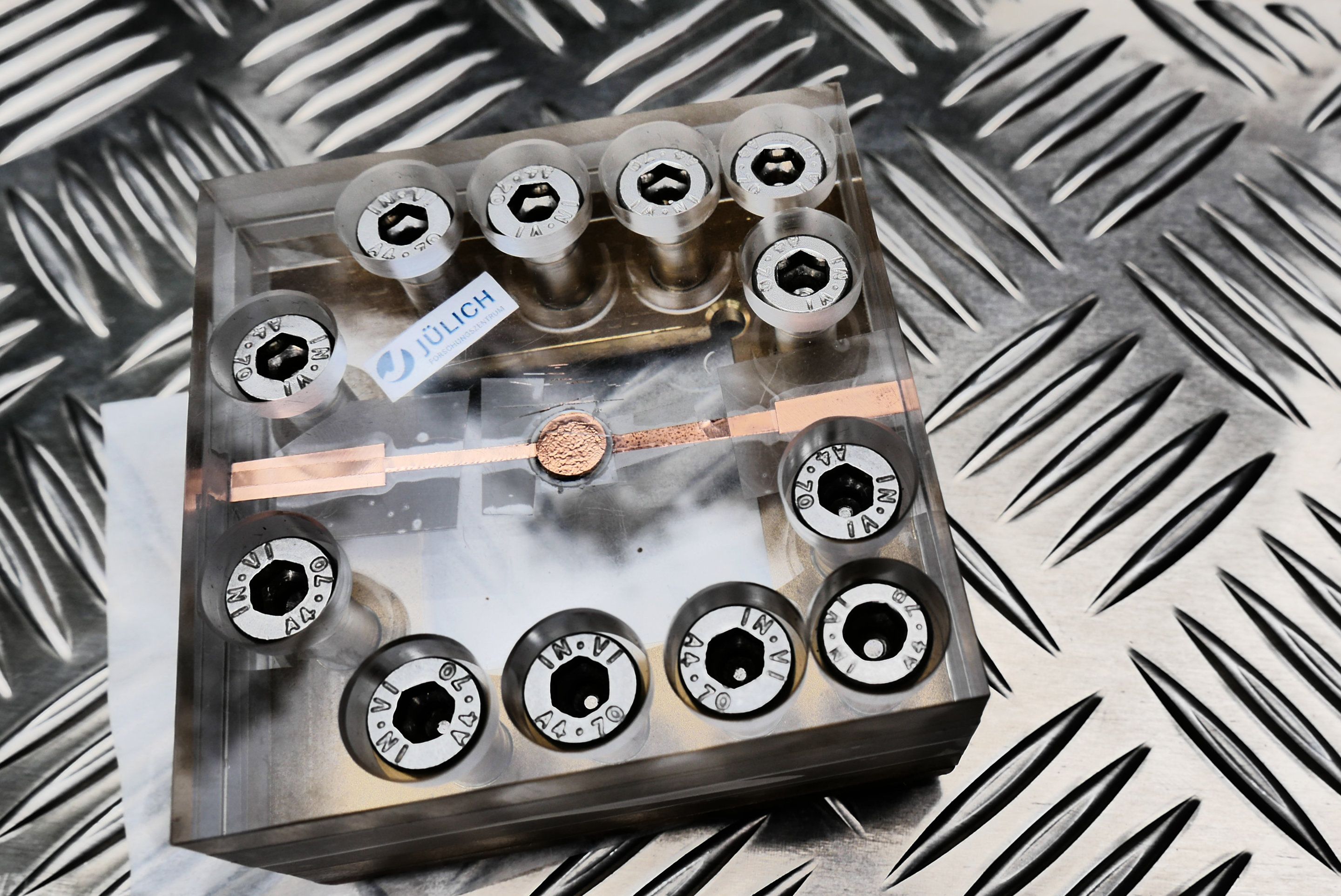
Solid-state batteries contain no liquid parts that could leak or catch fire. For this reason, they do not require cooling, and are considered to be much safer, more reliable, and longer lasting than traditional lithium-ion batteries. Juelich scientists have now introduced a new concept that allows currents up to 10 times greater during charging and discharging than previously described in the literature.
Low current is considered one of the biggest hurdles in the development of solid-state batteries because the batteries take a relatively long time to charge, usually about 10 to 12 hours in the case of a fully discharged battery. The new cell type that Jülich scientists have designed, however, takes less than an hour to recharge.
“With the concepts described to date, only very small charge and discharge currents were possible due to problems at the internal solid-state interfaces. This is where our concept based on a favourable combination of materials comes into play, and we have already patented it,” explains Dr. Hermann Tempel, group leader at the Juelich Institute for Energy and Climate Research (IEK-9).