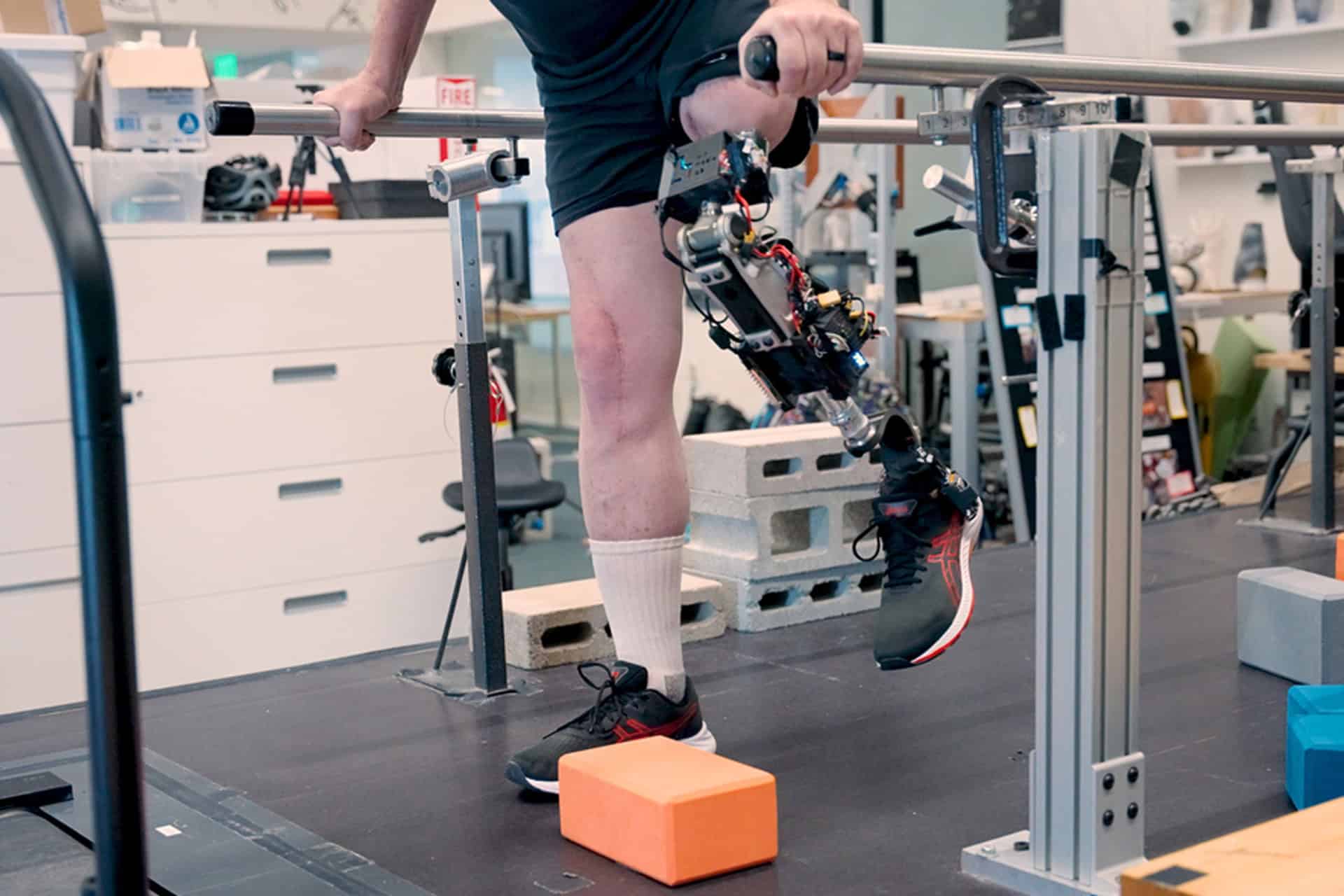
No straps, no sockets: MIT team created a true bionic knee and successfully tested it on humans.




🧑🚀 Q: What are the details of the upcoming Crew-11 mission? A: Crew-11 is set to launch on July 31st, 2025, with NASA astronaut Zena Cartman as commander, for a 6-month stay on the ISS.
Technical Improvements.
🔧 Q: What new system has SpaceX installed at Pad A for Starship? A: SpaceX installed a new Ship Quick Disconnect (QD) system at Pad A, which is smaller, temporary, and designed for static fire tests only.
🪂 Q: What upgrades have been made to the Dragon spacecraft Endeavor? A: Endeavor now features the Drogue 3.1 parachute system with reinforced crown material and a new packing system for more controlled deployment.
Program Challenges.
🚁 Q: What issues is Boeing’s Starliner program facing? A: Starliner is experiencing helium leaks and thermal management problems affecting its thrusters, delaying the next mission.
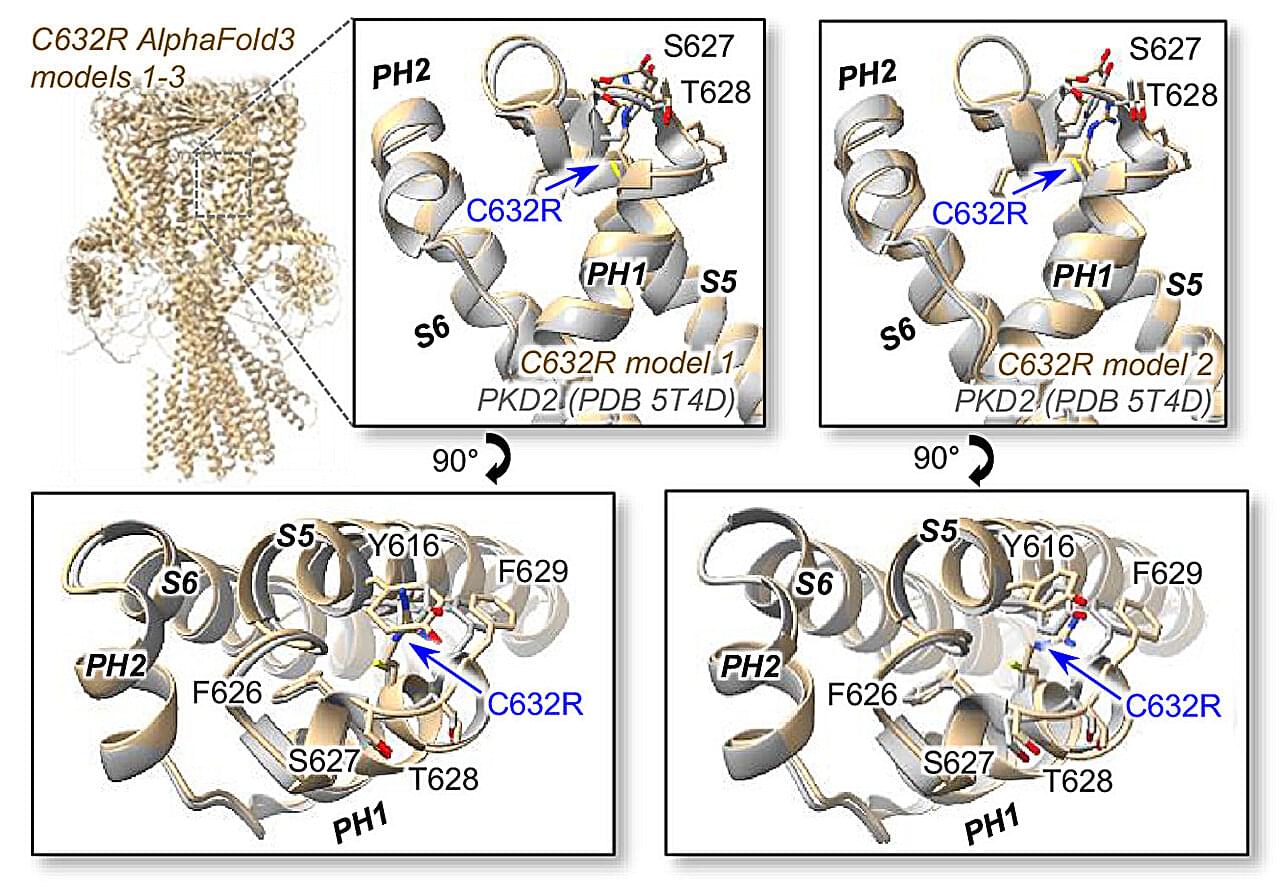
A recent study led by Paul DeCaen, Ph.D., associate professor of Pharmacology, has identified novel molecular mechanisms by which genetic mutations in the PKD2 gene cause the most common form of polycystic kidney disease, according to findings published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
PKD2 encodes an ion channel localized to the primary cilia of cells lining the kidney collecting ducts, a series of tubules and ducts that helps achieve electrolyte and fluid balance in the body. Both inherited and acquired mutations in PKD2 are known to cause autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), a condition characterized by the growth of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys that can lead to kidney failure and other serious complications.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, one in 1000 individuals will develop ADPKD and more than 95% of patients carry disease-causing genetic variants in PKD1 or PKD2. However, there are no available therapies that target these disease-causing variants.
A new Yale study has found a promising target for treating the brain fog that can follow COVID-19 and offers new insight into a hypothesis about the origin of Alzheimer’s disease.
One of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is the presence of plaque formed by the buildup of amyloid beta peptides (short chains of amino acids) in and around brain cells. Some researchers suspect that amyloid beta, which is structurally similar to antimicrobial peptides, protects the brain against bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungal infections. Because the blood-brain barrier tends to lose its integrity in Alzheimer’s disease patients, the accumulation of amyloid beta might be a signal that pathogens are infiltrating the brain.
In a new study published in Science Advances, Yale researchers investigated whether infection by SARS-CoV-2—the virus that causes COVID-19—can trigger Alzheimer’s disease-like amyloid beta buildup, leading to neurological impairments like brain fog.



IN A NUTSHELL 🌟 Rice University researchers developed a groundbreaking glass coating that reflects heat and reduces energy costs. 🔬 The coating is made from a tough layer of boron nitride and carbon, offering resistance to UV light and temperature swings. 💡 This innovation uses pulsed laser deposition at room temperature, making it cost-effective and.