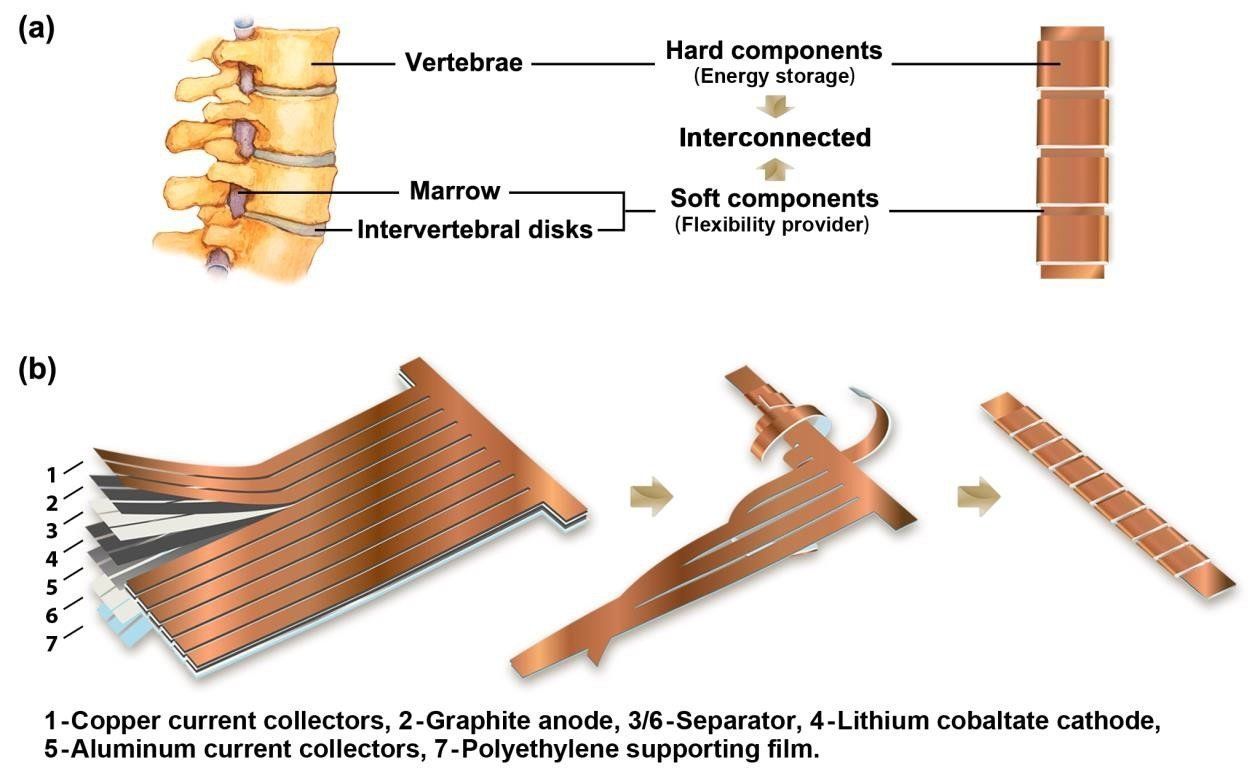
The rapid development of flexible and wearable electronics is giving rise to an exciting range of applications, from smart watches and flexible displays—such as smart phones, tablets, and TV—to smart fabrics, smart glass, transdermal patches, sensors, and more. With this rise, demand has increased for high-performance flexible batteries. Up to now, however, researchers have had difficulty obtaining both good flexibility and high energy density concurrently in lithium-ion batteries.
A team led by Yuan Yang, assistant professor of materials science and engineering in the department of applied physics and mathematics at Columbia Engineering, has developed a prototype that addresses this challenge: a Li-on battery shaped like the human spine that allows remarkable flexibility, high energy density, and stable voltage no matter how it is flexed or twisted. The study is published today in Advanced Materials.
“The energy density of our prototype is one of the highest reported so far,” says Yang. “We’ve developed a simple and scalable approach to fabricate a flexible spine-like lithium ion battery that has excellent electrochemical and mechanical properties. Our design is a very promising candidate as the first-generation, flexible, commercial lithium-ion battery. We are now optimizing the design and improving its performance.”