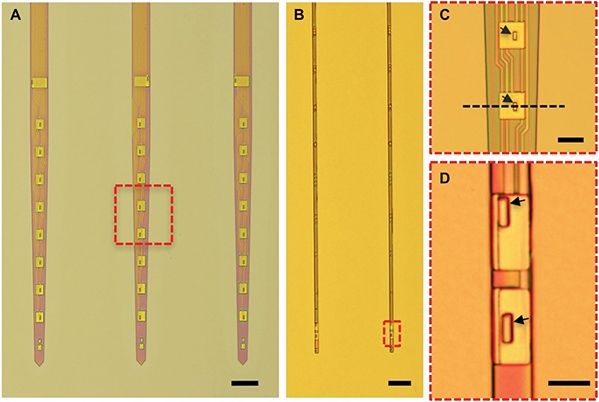
BMI is coming fast and will replace many devices we have today. Advances we making in deep brain development are huge markers that pushes the BMI needle forward for the day when IoT, Security, and big data analytics is a human brain’s and a secured Quantum Infrastructure and people (not servers sitting somewhere) owns and manages their most private of information. I love calling it the age of people empowerment as well as singularity.
Small study in 16 people suggests technique is safe and might help improve mood, anxiety and wellbeing, while increasing weight.
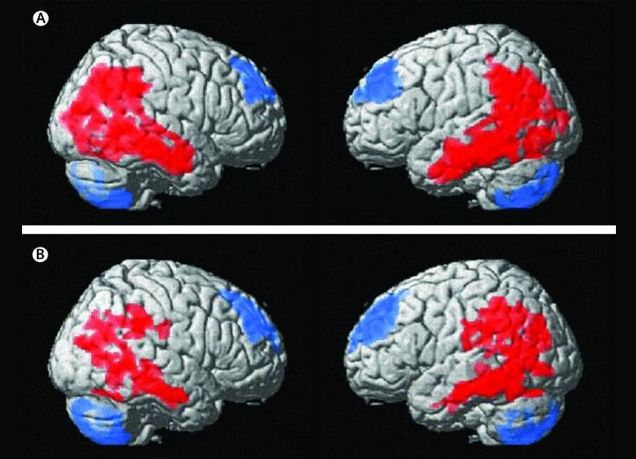
Deep brain stimulation might alter the brain circuits that drive anorexia nervosa symptoms and help improve patients’ mental and physical health, according to a small study published in The Lancet Psychiatry.