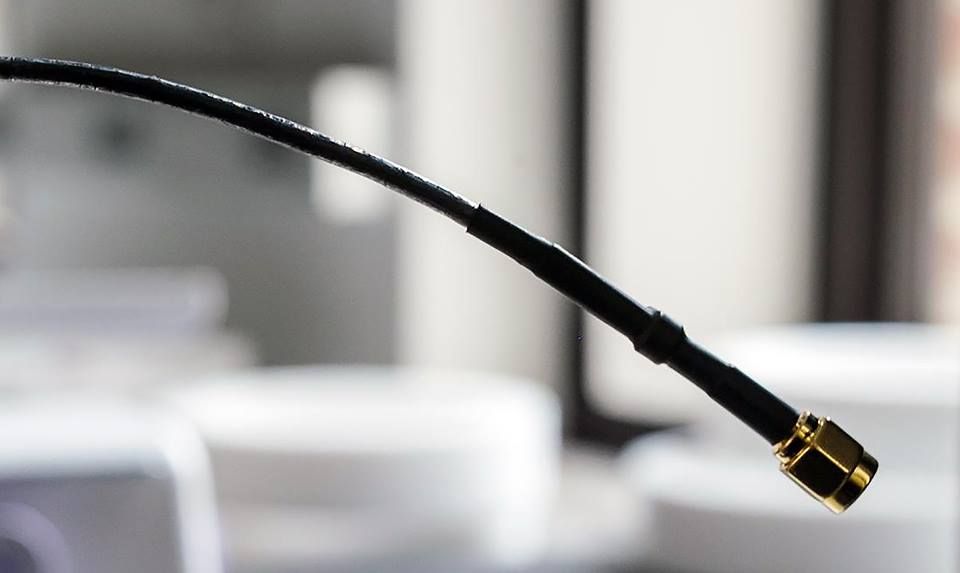
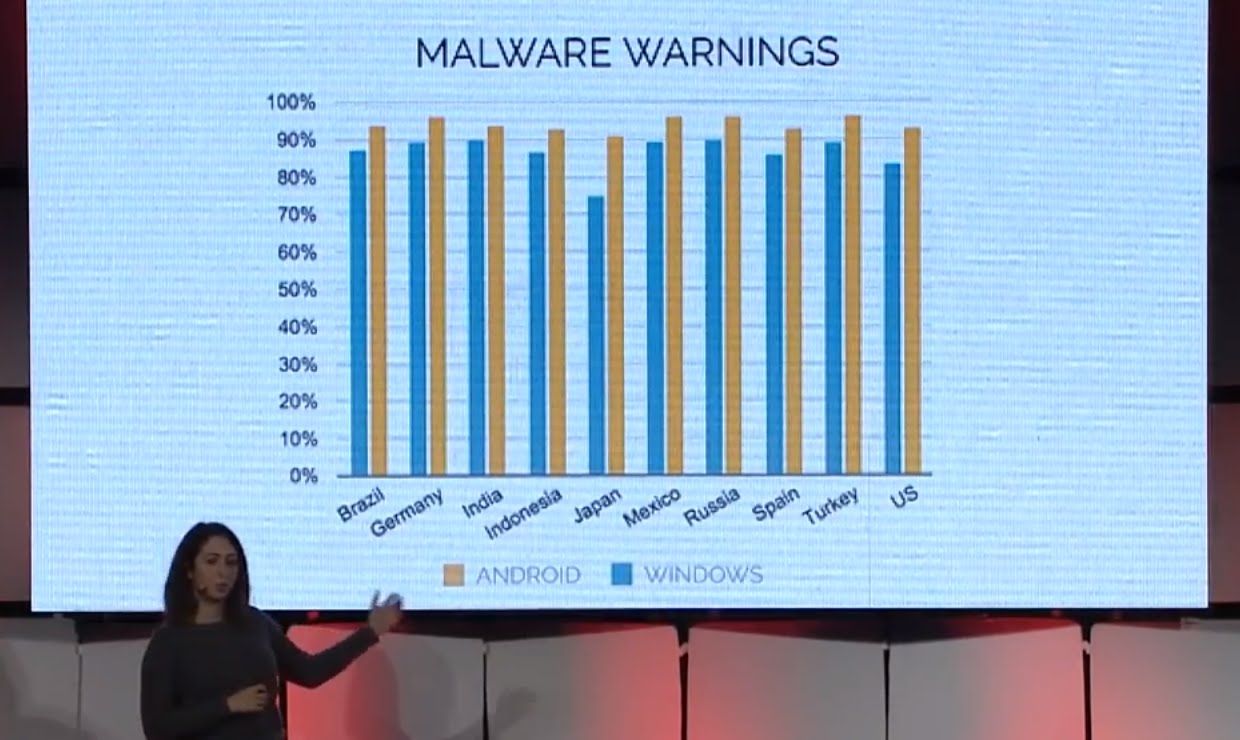
But a carbon nanotube coating (shown in clear jacket) replaces the tin-coated copper braid that serves as the outer conductor, ordinarily the heaviest component. Created by researchers at Rice University, the coating was tested by a collaborative group including NIST, which has more than 10 years of expertise in characterizing and measuring nanotu…bes. The coating, only up to 90 microns (millionths of a meter) in thickness, resulted in a total cable mass reduction of 50 percent (useful for lowering the weight of electronics in aerospace vehicles) and handled 10,000 bending cycles without affecting performance. And even though the coating is microscopically thin, the cable transmitted data with a comparable ability to ordinary cables, due to the nanotubes’ favorable electrical properties.
Credit: J. Fitlow/Rice University See More