We all know that real space travel and space colonization will not be achieved without the hard work, passion, and courage of people willingly taking risks for the greater good of humanity.
However, we can put all our hearts into deep space missions but won’t succeed unless we also provide the technological innovations needed. Let’s say, that thermal radiation isn’t our biggest enemy in space (literally roasting and melting our astronauts), speed and time are still affecting us the most. Mars, which is only a mere six months of travel time away from Earth, is certainly manageable, but getting to the outer parts of our own solar system already took some 10 years to accomplish.
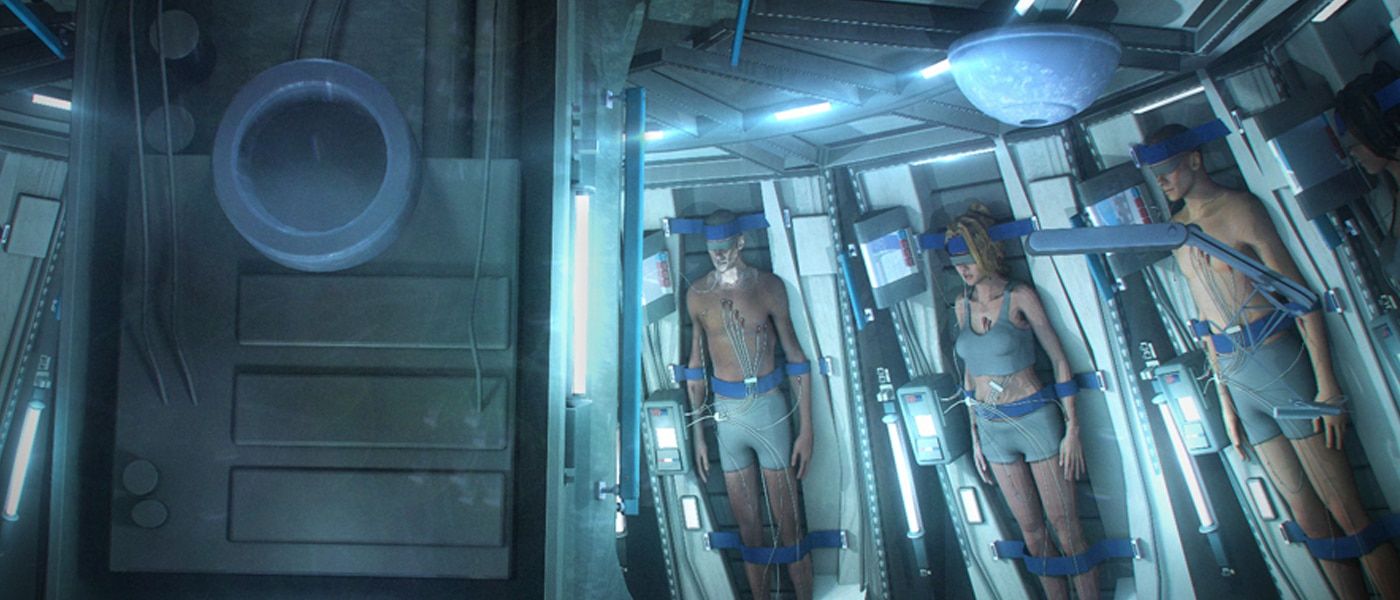
So, it’s obvious why sci-fi avoids any further questioning by putting space explorers in sleep mode. In reality, shutting down humans is hard to do, whereas keeping a body alive in suspension mode is tricky, to say the least.