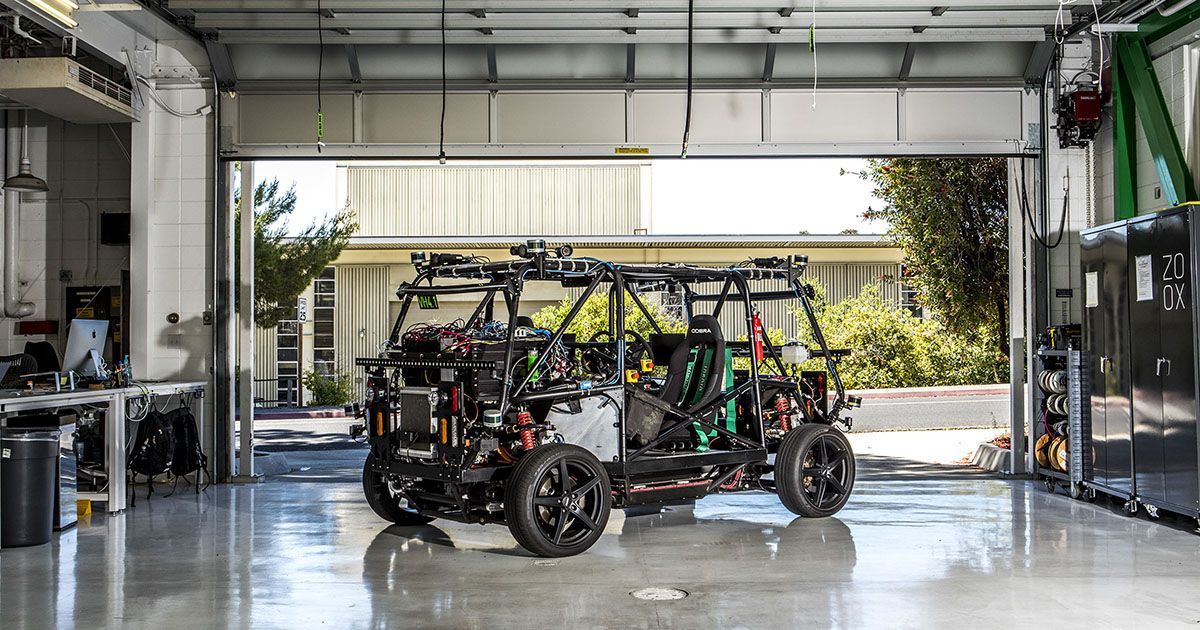
Remote-access software and modems on election equipment ‘is the worst decision for security short of leaving ballot boxes on a Moscow street corner.’




Life extension would allow everyone to enjoy a higher degree of freedom.
Freedom is a rather big deal in this age. We want freedom of speech, political freedom, press freedom, religious freedom, and freedom of choice over anything that may concern us directly. Different kinds of freedom are available in different amounts in different areas of the world, and while many people tend to see the glass half empty and complain that freedom is not equally distributed everywhere, it’s undeniable that we enjoy far greater liberty than previous generations. It’s not always easy to act upon your choices, and sometimes you’re free to choose in theory but not in practice, but overall, we enjoy options that who came before us couldn’t even dream of.
Take health, for example. Two hundred years back, if you didn’t want to get the flu, or any other infectious disease, you didn’t have the option not to do so. The mechanism through which infectious diseases manifest and spread wasn’t even remotely understood, so you didn’t have any idea what you should or shouldn’t do to minimize your risk of falling ill; basic hygiene wasn’t exactly a standard, and drugs and vaccines were nowhere in sight. If you actively wanted to do something to prevent getting the flu—which, at the time, might have killed you—you simply didn’t have this option.
Today, however, if you want to avoid infectious diseases, you have plenty of options to do so. Hygiene is common in most of the world, and there are vaccines available. You may well choose to not care, live in filth, and never get even a flu shot, but you do have the option. It’s a choice that, two hundred years back, could simply not be made. Depending on where you live and your access to medical care, acting upon your choice can be difficult, but this is a different matter. The option of preventing disease exists, and in principle, you may avail yourself of it, unlike in the past, when the option wasn’t there to begin with.

We are immensely proud to continue a long tradition of aeronautical expertise that helps maintain security and defend nations as well as bringing significant economic, technological and skills benefits. The UK Government has launched its Combat Air Strategy at the 2018 Farnborough International Air Show with the aim of delivering the next generation of combat air capability by 2035.

Transhumanists aim to do just that: to transcend the limits of the human body through the use of technology. Swiss photographer Matthieu Gafsou’s new book, H+ (Kehrer Verlag), documents Transhumanism through portraiture, still lifes and documentary photographs of Tranhumanist people, facilities, tools and technology. In photographing surgical procedures, laboratories, conferences and the like, Gafsou employed a hard flash to add a “clinical aspect” to his pictures. “This was important to me because I think [Transhumanism] is quite cold and [it] is about, not necessarily killing death but working on living longer,” he tells PDN. “But we are forgetting the body, we are forgetting the flesh, we are forgetting desire.”
In “H+,” Gafsou uses the visual language of science and technology to explore Transhumanism, the belief that the human body needs to be enhanced, perhaps even overcome.
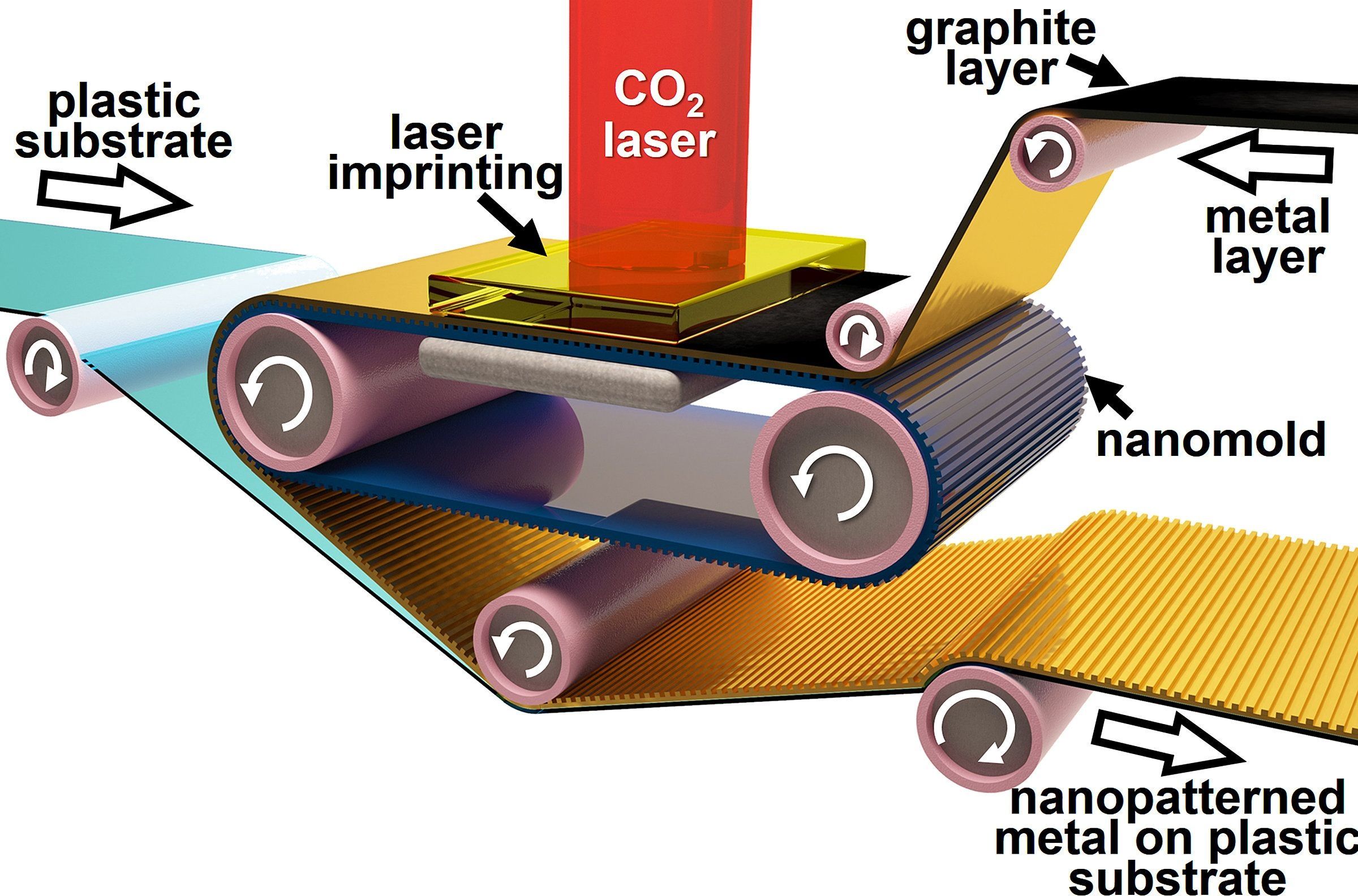
A new manufacturing technique uses a process similar to newspaper printing to form smoother and more flexible metals for making ultrafast electronic devices.
The low-cost process, developed by Purdue University researchers, combines tools already used in industry for manufacturing metals on a large scale, but uses the speed and precision of roll-to-roll newspaper printing to remove a couple of fabrication barriers in making electronics faster than they are today.
Cellphones, laptops, tablets, and many other electronics rely on their internal metallic circuits to process information at high speed. Current metal fabrication techniques tend to make these circuits by getting a thin rain of liquid metal drops to pass through a stencil mask in the shape of a circuit, kind of like spraying graffiti on walls.

Nicholas Papernot discusses “Making Machine Learning Robust Against Adversarial Inputs” (cacm.acm.org/magazines/2018/7/229030), a Contributed Article in the July 2018 CACM.


Akka Technologies is developing pods with detachable wings that would integrate aviation and public transit. The AKKA Group is an engineering and technology consulting company with 16000 employees.
The detachable wings would make for vastly more efficient boarding and improve the utilization of the engines and wings.