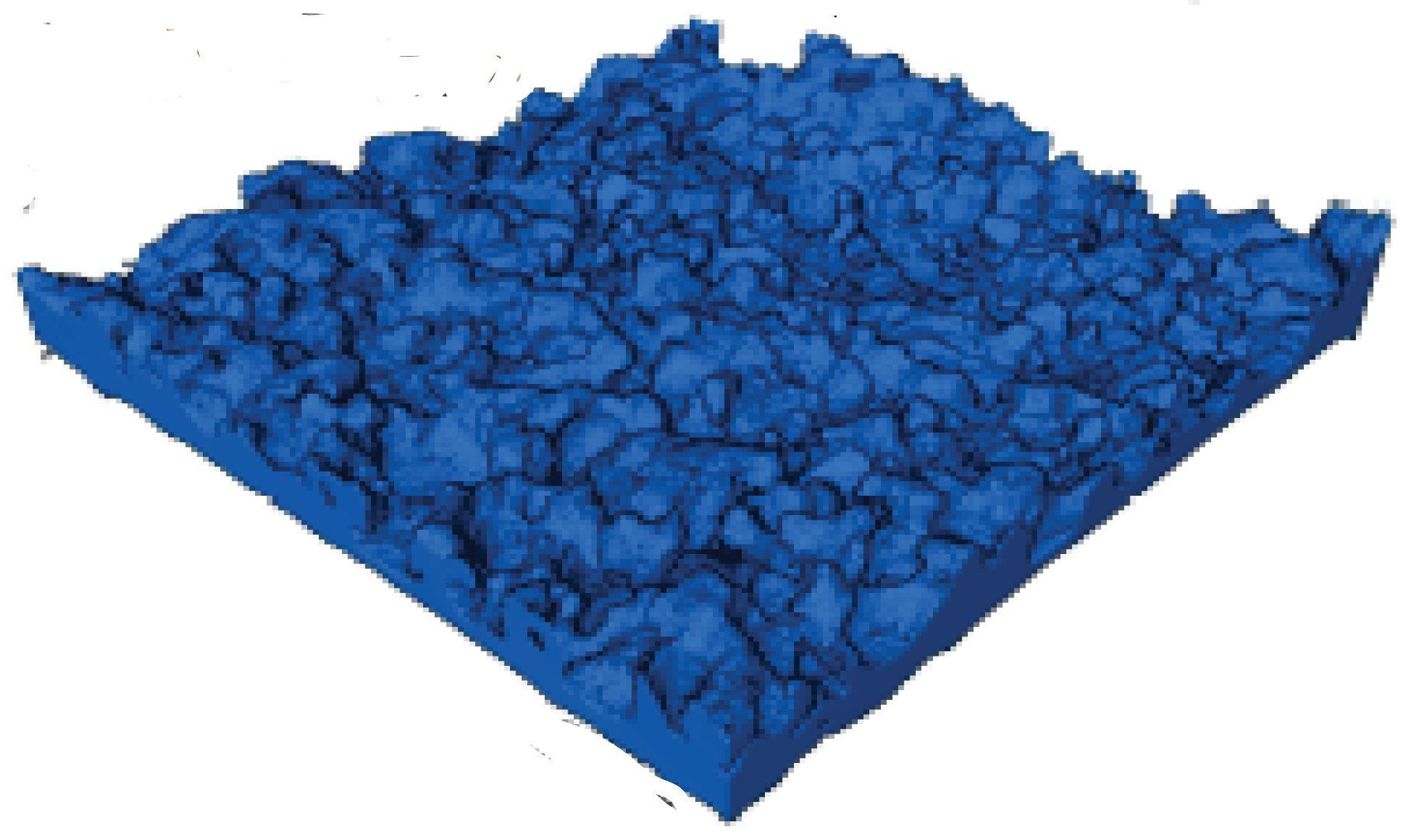
Careful sample preparation, electron tomography and quantitative analysis of 3D models provides unique insights into the inner structure of reverse osmosis membranes widely used for salt water desalination wastewater recycling and home use, according to a team of chemical engineers.
These reverse osmosis membranes are layers of material with an active aromatic polyamide layer that allows water molecules through, but screens out 99 to 99.9 percent of the salt.
“As water stresses continue to grow, better membrane filtration materials are needed to enhance water recovery, prevent fouling, and extend filtration module lifetimes while maintaining reasonable costs to ensure accessibility throughout the world,” said Enrique Gomez, professor of chemical engineering, Penn State. “Knowing what the material looks like on the inside, and understanding how this microstructure affects water transport properties, is crucial to designing next-generation membranes with longer operational lifetimes that can function under a diverse set of conditions.”