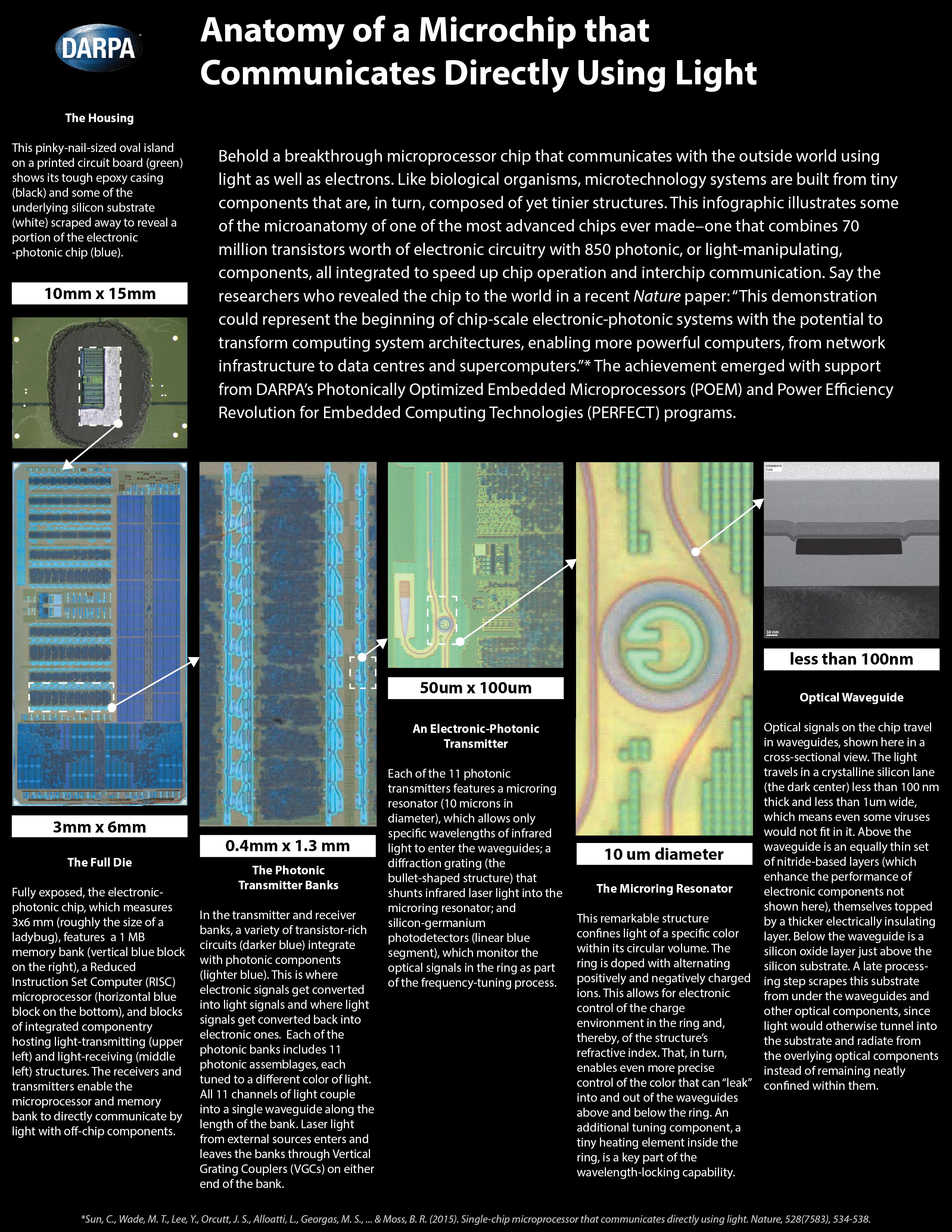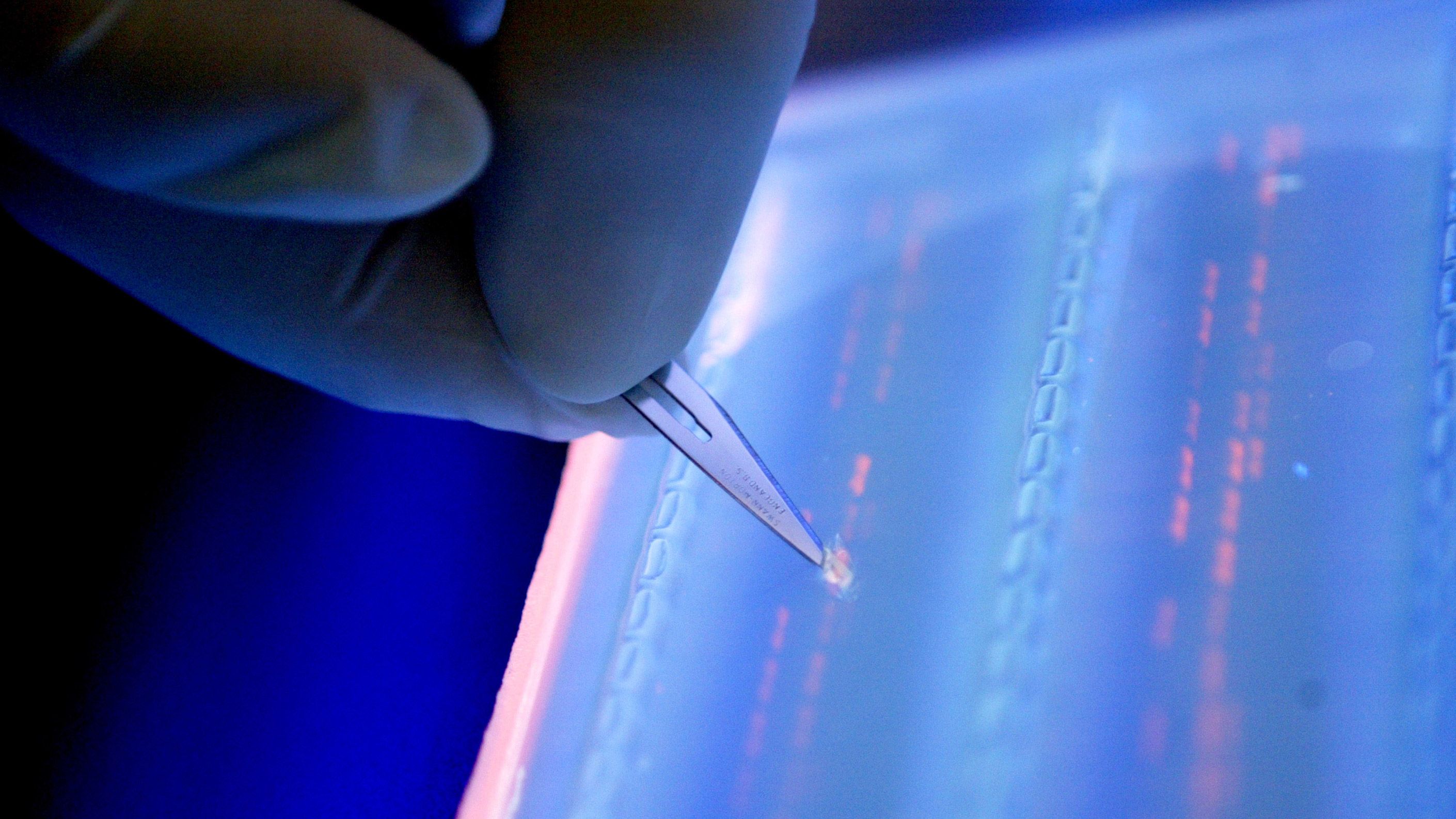
Even though it’s looking increasingly likely that humanity will find a way to wipe itself off the face of the Earth, there’s a chance that our creative output may live on. Servers, hard drives, flash drives, and disks will degrade (as will our libraries of paper books, of course), but a group of researchers at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology have found a way to encode data onto DNA—the very same stuff that all living beings’ genetic information is stored on—that could survive for millennia.
One gram of DNA can potentially hold up to 455 exabytes of data, according to the New Scientist. For reference: There are one billion gigabytes in an exabyte, and 1,000 exabytes in a zettabyte. The cloud computing company EMC estimated that there were 1.8 zettabytes of data in the world in 2011, which means we would need only about 4 grams (about a teaspoon) of DNA to hold everything from Plato through the complete works of Shakespeare to Beyonce’s latest album (not to mention every brunch photo ever posted on Instagram).
There are four types of molecules that make up DNA, which form pairs. To encode information on DNA, scientists program the pairs into 1s and os—the same binary language that encodes digital data. This is not a new concept—scientists at Harvard University encoded a book onto DNA in 2012—but up to now, it had been difficult to retrieve the information stored on the DNA.